Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
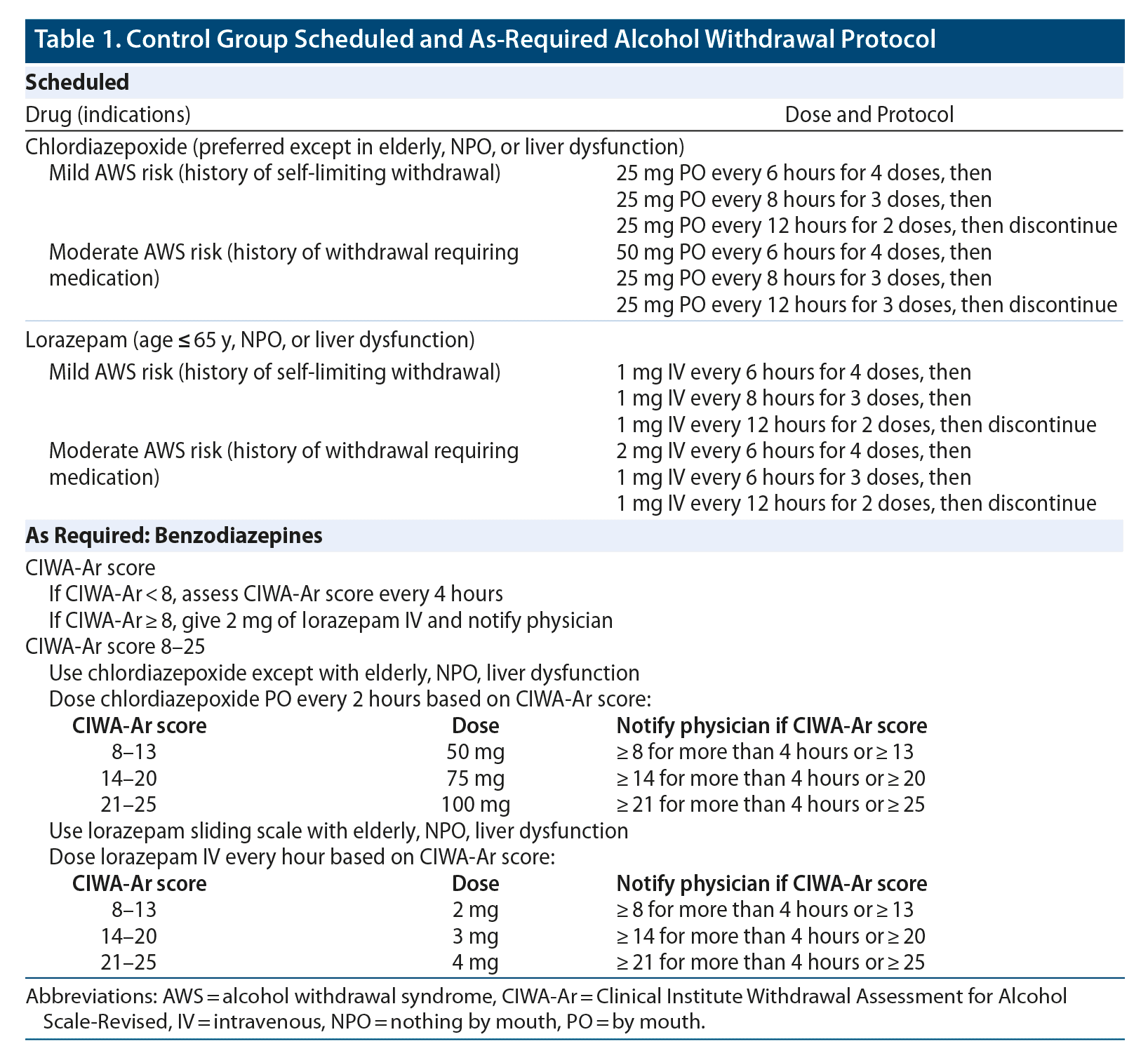
Benzodiazepine (BZD) use disorders are a common clinical problem among methadone maintenance treatment patients and have adverse effects on clinical outcomes. To evaluate gabapentin for the outpatient treatment of BZD abuse or dependence in Coprescribing of benzodiazepines or gabapentinoids (e.g., gabapentin, pregabalin) with opioids is increasingly used in the multimodal treatment of acute and chronic pain, despite limited Gabapentin works by showing a high affinity for binding sites throughout the brain corresponding to the presence of the voltage-gated calcium channels, especially α-2-δ-1, which seems to inhibit the release of excitatory neurotransmitters in the presynaptic area that participate in epileptogenesis.” criteria). Subjects requiring hospitalization or taking benzodiazepines or nonbenzodiazepine anticonvulsants were excluded. Twenty-six participants were randomized: 17 received gabapentin and 9 received chlordiazepoxide. Gabapentin doses were 1200 mg orally for 3 days, followed by 900 mg, 600 mg, and 300 mg for 1 day each. No, Gabapentin is not a Benzodiazepine drug. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used to treat various types of nerve pain and to reduce seizure frequency in people with epilepsy. It has been used to treat anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and to help with alcohol withdrawal. Overall, Neurontin Gabapentin is a valuable treatment option for benzodiazepine withdrawal. Its ability to reduce withdrawal symptoms, stabilize mood, prevent seizures, improve sleep quality, and minimize discomfort make it an effective and supportive medication for individuals navigating the challenges of benzodiazepine withdrawal. Gabapentin has growing evidence to support its use in the treatment of alcohol use disorder, however there is limited evidence regarding its role in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal. The purpose of this study was to determine if adjunctive gabapentin reduces the need for benzodiazepine (BZD) administration during alcohol withdrawal. Is Gabapentin a Benzodiazepine? Benzodiazepines fall under the class of depressants since they can produce hypnosis and sedation, relieve muscle spasms, treat anxiety, and minimize seizures. On the surface, we can see how gabapentin can be associated with benzodiazepines. After all, they both deal with altering the nervous system. Benzodiazepine withdrawal can be a long and difficult process, but there are steps that physicians can take to help their patients survive the process. Tapering the drug slowly and switching to a long half-life benzodiazepine may be helpful, as may adjunctive medications and coping skills. Encouraging acceptance and finding a support system can also be key to surviving benzodiazepine withdrawal. Gabapentin is the older version of lyrica basically. Lyrica was made because the bioactivity was/is so poor on Gabapentin (the body's ability to use it). So 300mg of lyrica is around 900mg of Gabapentin (+-) I have a friend who had a 3 months wd from it and it didn't look like fun. So be careful. Tapering Patients Off of Benzodiazepines Commentary by CHINYERE I. OGBONNA, MD, MPH, sant (e.g., gabapentin [Neurontin]) should be considered for high-dosage withdrawal. Benzodiazepine Withdrawal is a group of symptoms experienced by patients who have taken benzodiazepines for a period of time and have developed a dependence and try to stop or reduce their dose. These results suggest the potential use of gabapentin as an adjunct to the use of benzodiazepines for treating benzodiazepine withdrawal. The limitations of this study included a small sample size and variability in medication management strategies across the sample. al is necessary. Gabapentin, an anxiolytic drug that is also used off-label to treat alcohol withdrawal, is a potential candidate for modulating benzodiazepine withdrawal. Using electronic records from a large inpatient psychiatric facility, a retrospective study of 172 patients presenting with benzodiazepine withdrawal was conducted to determine if the coincidental use of gabapentin for other The combination of gabapentin and benzodiazepine can be safe in the treatment of benzodiazepine withdrawal, according to data presented at American Psychiatric Association annual We highlight that the gabapentin with benzodiazepine group had a higher baseline CIWA score compared to the benzodiazepine-only group, indicating more severe withdrawal symptoms. Despite this, patients in the gabapentin group received a significantly lower cumulative dose of benzodiazepines. Among Medicare disabled beneficiaries, concurrent utilization of gabapentin, opioids, and benzodiazepines is associated with multiple adverse outcomes. Given this, it is imperative that the benefits and risks of co-prescribing these medications be comprehensively examined. When prescribed at a low dosage for a short time (fewer than 30 days), benzodiazepines can effectively treat generalized and social anxiety, panic disorder, and sleep disorders. Long-term use for USA: Gabapentin and benzodiazepine combination is safe for the treatment of benzodiazepine withdrawal, according to findings from a recent study. The results were presented at the American Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting (virtual meeting) held from May 1-3, 2021. Gabapentin 300 mg HS the day before stopping the final 10-20% of benzodiazepine dose. Titrate to gabapentin 300 mg TID - QID Continue gabapentin for 3 months or longer depending on benzodiazepine dose and duration Prior to beginning taper: 1. Initiate an SSRI 2. Over 3 weeks, increase dose to moderate or high (sertraline 100-200
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |