Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
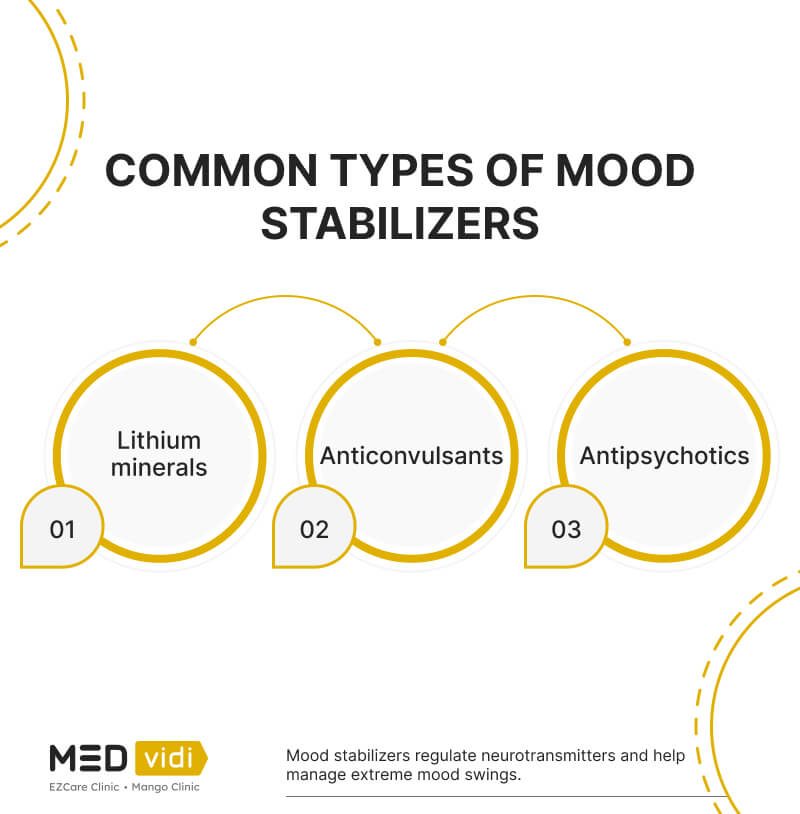 |  |
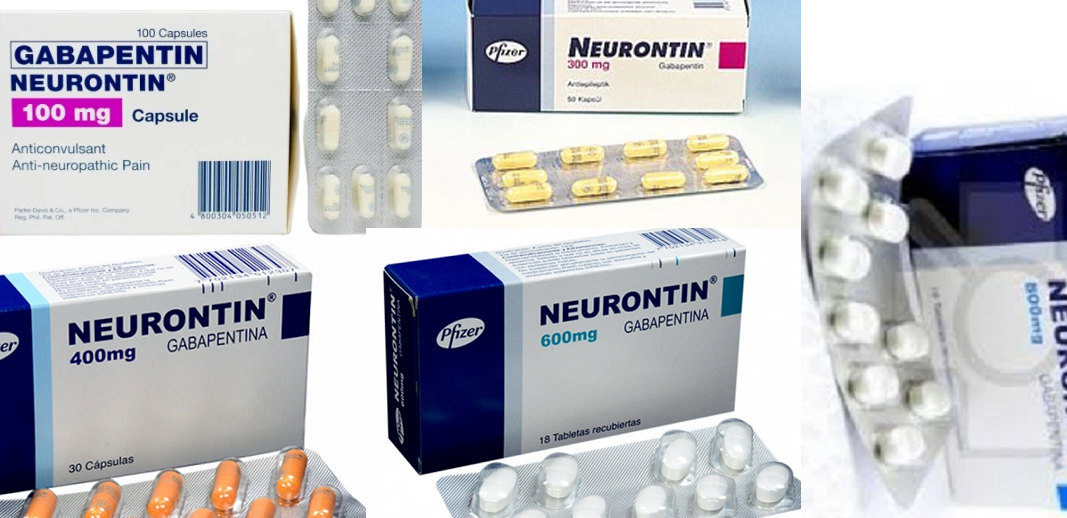
medications, mood stabilizer use and dosage, evidence regarding poor response to standard mood stabilizers be-fore gabapentin use, evidence regarding whether during gabapentin treatment mania or hypomania occurred, ad-verse events, maximum and maintenance gabapentin dose and duration of treatment, indications for treatment Adjunctive therapy of gabapentin to stable doses of mood stabilizers or atypical antipsychotics, initiated at 300 mg at bedtime and increased by 300 mg every four nights until symptom relief or adverse effects were noted. Final GBP dose was clinically determined. Maximum dose 3600 mg per day in divided doses (range 600 mg to 3300 mg). Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use disorder. There is sufficient evidence to consider gabapentin as a third-line treatment for social anxiety disorder and severe panic disorder. Some research suggests that gabapentin might have mood-stabilizing properties, potentially helping with conditions like bipolar disorder. It’s like the medication is acting as an emotional shock absorber, smoothing out the highs and lows. Currently, the most useful mood stabilizer combinations are the mixtures of anticonvulsants and lithium, particularly valproate plus lithium. Carbamazepine, lamotrigine, and gabapentin have also been added to lithium with apparent safety. For 1 year, 13 patients received adjunctive gabapentin with standard mood stabilizers and 12 patients received adjunctive placebo. On the basis of the CGI-BP, gabapentin-treated patients showed significant improvement from baseline to month 12. Patients frequently express an interest in using gabapentin rather than standard mood-stabilizing agents (like lithium carbonate, divalproex sodium, or carbamazepine) due to its limited side effect profile. Thus, clinical interest regarding its use in mood disorders has grown. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA approved to treat seizure disorder and nerve pain from shingles. But it’s also used off-label to treat many other conditions, including anxiety, nerve pain from diabetes, and hot flashes. Gabapentin may be effective for anxiety, but it’s usually not a first-choice medication for this use. American Psychological Association: Gabapentin has been “largely discredited as a mood stabilizer for bipolar disorder.” Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance: Gabapentin “was used frequently for treatment of bipolar disorder, but controlled studies found it was no more effective than a placebo.” Gabapentin and topiramate are also anticonvulsants that may act as mood stabilizers, but they are usually given in addition to other medications. Lithium (lithium carbonate or lithium citrate) Lithium (Carbolith, Duralith, Lithane) is found in nature in some mineral waters and is also present in small amounts in the human body. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. When I finally met the doctor who diagnosed my bipolar disorder, he prescribed gabapentin as a mood stabilizer, as well as a sleeping aid (Ambien), and Zoloft (the only antidepressant that ever worked for me). I have been on this regimen for almost 3 years now and I fully believe it has saved my life!" Benefits of Gabapentin and mood stabilizer for chronic pain. Reduced pain intensity: Gabapentin can help alleviate chronic pain, making it more manageable for individuals. Improved functionality: By reducing pain, Gabapentin and mood stabilizers can improve an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks without discomfort. The relatively low frequency of bipolar disorder diagnoses in the sample of off-label gabapentin visits suggests that use of gabapentin as a mood stabilizer has declined, which corresponds with more recent psychopharmacology literature concluding that gabapentin’s mood-stabilizing effects are minimal to negligible (13, 32). We found few We conclude that there is moderate evidence of the efficacy of gabapentinoids in anxiety states, but minimal evidence in bipolar disorder and insomnia and they should be used for these disorders The results suggest that gabapentin may be of benefit to bipolar patients who only partially respond to other mood stabilizers. A favorable side-effect profile and rapid action make this drug an attractive choice as an adjunctive therapy. A psychiatrist answers common questions about mood stabilizers for bipolar depression. Other medications, like topiramate (Topamax) or gabapentin (Neurontin), may be prescribed in some cases For 1 year, 13 patients received adjunctive gabapentin with standard mood stabilizers and 12 patients received adjunctive placebo. On the basis of the CGI-BP, gabapentin-treated patients showed significant improvement from baseline to month 12. Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision. If used as a mood stabilizer or anti-depressant, the dose is usually between 900 and 2,000 mg a day. But, it may also be increased for better results. Some people see improvement in their
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |