Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
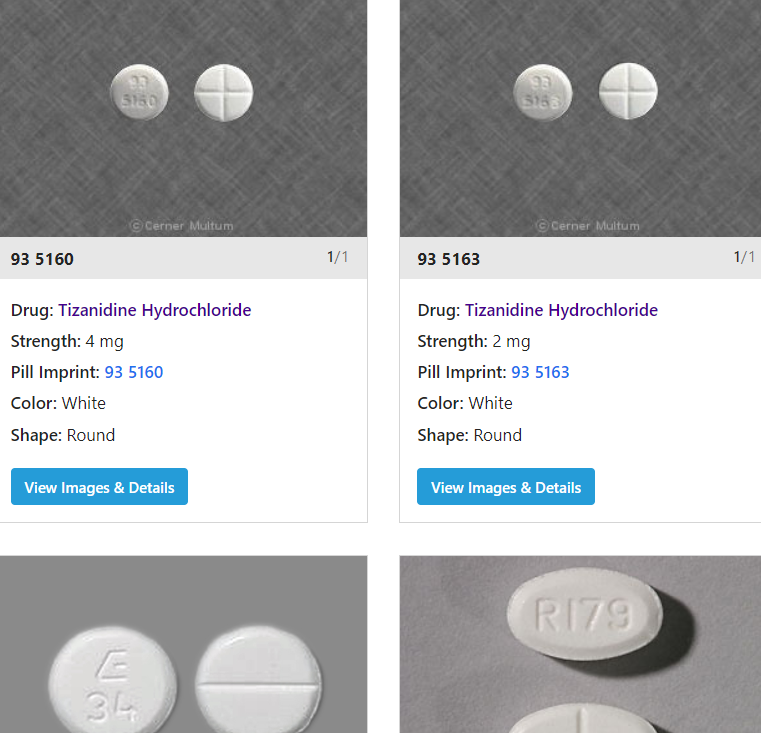
Taking muscle relaxers with gabapentin can increase sedation. Consult a healthcare provider for safe use and explore alternatives for pain relief. There are many prescription and over-the-counter medications available that can provide relief for muscle spasms and muscle spasticity. Muscle relaxers, or muscle relaxants, are medications used Is gabapentin a muscle relaxer? Gabapentin was initially investigated for its muscle relaxing and anti-spasmodic properties, but it’s primarily used as an anticonvulsant and nerve pain reliever . Although it has some relaxing effects, it is not classified as a primary muscle relaxant. Combining muscle relaxers and gabapentin can increase the risk of overdose, especially when taken in high doses or with other central nervous system depressants. It's crucial to follow your healthcare provider's instructions and never exceed the recommended dosage. Gabapentin works by inhibiting certain neurotransmitters, which can help alleviate pain signals sent to the brain. Muscle relaxers, on the other hand, typically work by acting on the central nervous system to reduce muscle tension and spasms. Gabapentin and Muscle Relaxation: What Does Research Say? Research into gabapentin’s effects on muscle relaxation is somewhat limited but indicative. Studies have indicated that patients with neuropathic pain often experience muscle spasms and tightness due to their condition. Gabapentin slows this neuronal firing down to rates that make having a seizure impossible. That’s different than cyclobenzaprine, the most frequently studied skeletal muscle relaxer for pain, Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Muscle relaxers, also known as skeletal muscle relaxants, are medications used to treat muscle spasms or muscle pain. They work by reducing muscle tension and improving range of motion. These medications are typically prescribed for short-term use, as they can be habit-forming and have the potential for abuse. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and relieve pain for certain conditions in the nervous system. It is not used for routine pain caused by minor injuries or arthritis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. How Skeletal Muscle Contracts. A single α-motor neuron can innervate up to 200 muscle fibers, forming a complex called motor unit (Figure 1).¹⁰ With movement, an action potential originates from the UMN in the motor cortex.⁹ This action potential depolarizes the motor neuron terminal, resulting in the opening of voltage-gated calcium (Ca²⁺) channels and the subsequent release of the Gabapentin is used as a nerve relaxer besides what it was intended for seizures. I have a lot more things wrong just from this one pill. It's up to you if you'd want to try it, but I wouldn't recommend it to anyone for muscle pain when there was nothing wrong with my nerves until now. Gabapentin is not a muscle relaxer. The mechanism by which Gabapentin exerts its analgesic action is unknown, but in animal models of analgesia, Gabapentin prevents allodynia (pain-related behavior in response to a normally innocuous stimulus) and hyperalgesia (exaggerated response to painful stimuli). Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that is primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain. It was initially developed as a muscle relaxer and anti-spasmodic medication, but its anticonvulsive properties were discovered later. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Muscle relaxer side effects: Find out more about what you can expect when taking muscle relaxers, including the most common side effects. Alcohol and muscle relaxers don’t mix. Learn why this can be a dangerous combination that should be avoided. Common muscle relaxer dosing: Wondering if you’re on a low dose? Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used to treat nerve pain and anxiety. Muscle relaxers, on the other hand, are prescribed to relieve muscle spasms and stiffness. Both medications work differently and can be prescribed together in certain situations. I have been taking Gabapentin 3 times a day for neuropathy for a couple years now. The pain was really bad that I had to take pain pills on a daily basis. Now with the gabapentin and Dermatran that is a topical cream that I rub into my feet daily or 2-3 times a day. I actually don't need it some days at all. Skeletal Muscle Relaxants Table 1. Skeletal Muscle Relaxants (Antispasmodic Agents) Drug Recommended dosage Most common adverse effects Comments Monthly cost*
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |