Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 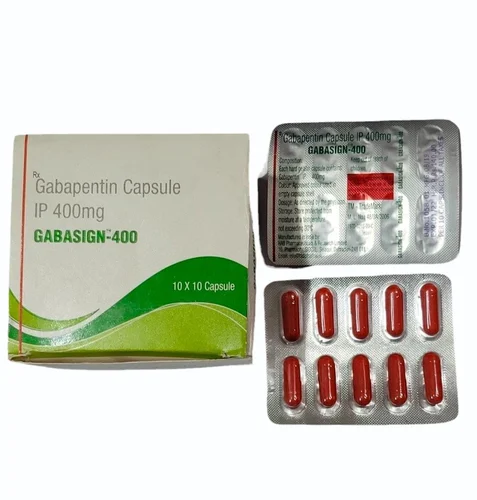 |
Gabapentin - Brand name: Neurontin. Read about how gabapentin treats epilepsy and nerve pain and how to take it. Gabapentin is a drug used to treat nerve pain. This type of pain is often not relieved by normal painkillers. It can be used in combination with other painkillers to improve your pain relief. How does gabapentin work? Gabapentin works by changing the way in which nerves send messages to your brain. painkillers like paracetamol, both in how they work and how long they take to work. Everyone is different, and their pain responds differently to drug treatment – some people find that the drugs start to help straight away, and for others it takes a bit more time. It is Pain killers which are NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) works on the patho-physiological processes that elicit pain, fever and other signs of swelling in the body. Corticosteroids pain reliever are usually given for the management of musculoskeletal injuries due to its effect on shutting down inflammation causing processes. “I do believe most people are generally informed about the risks of opioids, and the vast majority are very cautious about using an opioid pain medication,” he says. However, opioids can be useful in treating a limited number of chronic pain conditions including cancer-associated pain. Gabapentin is prescribed for long-term pain control. It isn't used to treat short-term pain. Researchers aren't sure exactly how it works, but it may change how your body feels and reacts to gabapentin (Neurontin) lamotrigine (Lamictal) pregabalin (Lyrica) SIDE EFFECTS. Dry mouth, sexual dysfunction, dizziness, constipation, blurred vision, and upset stomach. Nausea, dizziness, sweating. Tend to have fewer side effects than tricyclic antidepressants. Drowsiness, dizziness, and nausea. Avoid alcohol when taking these drugs. Gabapentin, often prescribed for nerve pain, seizures, and other conditions, can interact with a range of other medications, sometimes leading to adverse effects. It’s essential to be aware of these potential interactions to ensure safe and effective treatment. The most powerful pain reliever is a class of medications known as “opioids,” which have a significant risk of addiction and dependency. These drugs are routinely recommended by doctors for severe pain treatment, as well as a variety of other illnesses. Take the lowest dose of pain medication that still gives you an effect you’re happy with. Always try non-medication strategies and non-NSAID pain relievers first. Continue using them even if you also have to take opioids. If you take multiple pain medications, make the safest one your go-to painkiller. More than half of the people in the study noted an improvement in pain relief when gabapentin was added. However, side effects from gabapentin were common. More than a third of the people in the study stopped taking gabapentin due to side effects. People who had side effects also didn’t experience as much improvement in their sciatica symptoms. Gabapentin, a widely-used medication, has gained attention for its potential as a painkiller. But just how strong is it? In this article, we will explore the efficacy of Gabapentin as a pain reliever, examining its mechanisms of action and its effectiveness compared to other commonly-used pain medications. There are a number of drugs that should not be taken with gabapentin, including certain antibiotics, antifungal medications, and drugs used to treat seizures. In some cases, taking these drugs with gabapentin can increase the risk of side effects or make the gabapentin less effective. Gabapentin can be safely taken with certain pain medications, but always consult your doctor for personalized advice. Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures. It’s often prescribed for conditions like neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and postherpetic neuralgia. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat some types of nerve pain but is classified as an anticonvulsant medicine, not as an opioid or painkiller. Gabapentin was first approved in 1993 and is used to treat: postherpetic neuralgia, a nerve pain caused by the shingles virus (herpes zoster), Anti-seizure medications used to treat chronic nerve pain include gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica). These medications treat the burning pain of shingles, known as postherpetic neuralgia. And they treat pain related to nerve damage in the legs and feet due to diabetes, known as diabetic neuropathy. How they work. In short, the most common over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil), are generally considered safe to take with gabapentin. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug that’s often used for pain due to herpes zoster infection. This condition is known as postherpetic neuralgia. What Are Nonaddictive Pain Medication Is gabapentin considered a painkiller? Gabapentin is commonly used to treat some types of nerve pain but is classified as an anticonvulsant medicine, not as an opioid or painkiller. Gabapentin is used to treat postherpetic neuralgia, a type nerve pain that can occur due to an outbreak of shingles, and restless legs syndrome (RLS), an Gabapentin works on nerve endings. It is not intended to be a painkiller. It works on quieting the nerve endings that end up relieving pain. That again is when the dosage strength is reached for an individual. It is surely different for everyone. Please see your Dr. about this issue. I hope you feel better soon.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |