Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
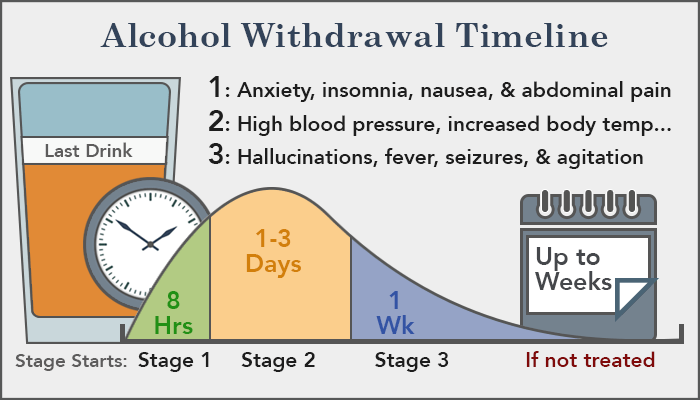
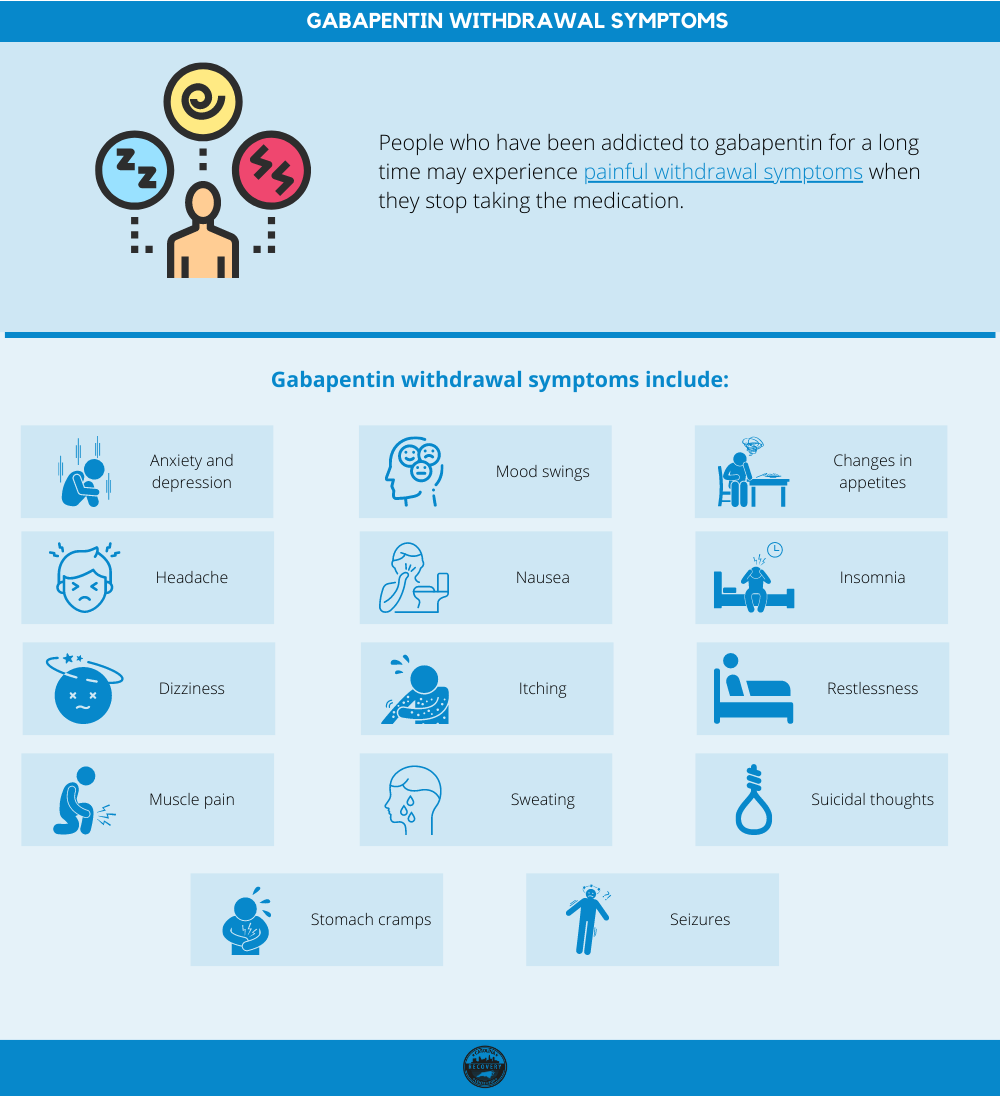
But, you shouldn’t stop taking gabapentin suddenly. Withdrawal symptoms can start as soon as 12 hours after stopping it. Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms occur more commonly in people taking this medication at a high dose or in those who take it for a long time. They include: Case reports have shown that gabapentin withdrawal often lasts for 5 to 10 days, but some people have taken as long as 18 weeks to completely taper off gabapentin while managing withdrawal symptoms. Symptoms may start within 12 hours to 7 days after stopping gabapentin and may be severe. If this happens, you'll have withdrawal symptoms after you stop taking the medicine. When you stop taking gabapentin, you'll need to reduce your dose gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor. Talk to your doctor if you're concerned about becoming physically dependent on gabapentin. * Existing blood pressure issues: If you already have high or low blood pressure, gabapentin may exacerbate these issues. * Other medications: Taking gabapentin with certain other medications may increase your risk of blood pressure changes. The most common symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal are agitation, excessive sweating, stomach upset, tremor, fast heartbeat, high blood pressure, and insomnia. Withdrawal from gabapentin is more likely to occur in individuals who have a history of substance use disorder and who take daily doses of gabapentin greater than or equal to 3000 mg. Prescribing information and the American Addiction Centers recommend tapering gabapentin over a minimum of one week. Using a slow taper by reducing the daily dose at a rate of 300 mg every 4 days may be particularly useful for elderly patients or other patients vulnerable to withdrawal symptoms. Withdrawal symptoms can begin within 12 hours to 7 days after quitting the medication and last up to 10 days. Symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal may include nausea, dizziness, headaches, insomnia, and anxiety. The safest way to stop using gabapentin is to taper off the medication under the supervision of a doctor. Are You Covered For Treatment? Understand the withdrawal symptoms of gabapentin and their impact. Learn effective strategies on how to stop gabapentin withdrawal. Assess whether is gabapentin withdrawal dangerous and the necessary precautions. Explore the duration of symptoms and how long does gabapentin withdrawal last. Some people may experience tremors, rapid heart rate, high blood pressure, and insomnia when they stop taking gabapentin suddenly. Never stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor first. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. Is Gabapentin Bad for Blood Pressure? Understanding the Cardiovascular Effects. Why This Paradox? 1. Can gabapentin cause high blood pressure? 2. Is gabapentin hard on the heart? 3. Who should avoid gabapentin? 4. What is the biggest side effect of gabapentin? 5. What is the most common side effect of gabapentin? 6. Common symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal include: Anxiety; Agitation; Restlessness; Fatigue; Insomnia; Irritability; Headache; Dizziness; Light sensitivity; Irregular heartbeat; Sweating; Upset stomach; Nausea; Aches and pains; Tremors; High blood pressure; Seizures are also possible during gabapentin withdrawal. Gabapentin is associated with a risk of dependence and withdrawal. Abrupt discontinuation of the drug may result in symptoms similar to those of benzodiazepine or alcohol withdrawal and may include: Hypertension (high blood pressure). Sweating. Confusion. Incoherent speech. Impaired ability to pay attention. Nausea. Pain. Insomnia. Restlessness For some people, gabapentin (Neurontin) withdrawal symptoms can be more severe and may require intervention or treatment changes. This could include: Extreme changes in mental state, such as severe anxiety or depression; Severe chest pain and increased blood pressure; Severe or persistent pain Individuals who have been using gabapentin regularly may experience withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation, which can begin within 12 hours to 7 days and may last up to 10 days. Symptoms of withdrawal can include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, sweating, irritability, and flu-like symptoms. If you want to stop taking gabapentin but have concerns about withdrawal symptoms and other side effects, talk with your doctor and create a plan that works for you. Gabapentin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. What are the brand names of gabapentin? Gabapentin is available as both a brand name product and a generic product (chemically the same, usually lower cost than the brand name product). Brand names of gabapentin include Horizant®, Gralise® and Neurontin®. Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause serious problems, like withdrawal symptoms or the return of seizures. Your doctor will help you stop taking the drug safely. Drug interactions Older adults who take gabapentin also are at higher risk of breathing problems. Because gabapentin can enhance the psychological effect of opioids, it has the potential to be abused and has contributed to drug overdose deaths. Drugs such as gabapentin have been linked in rare cases to an increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Oxycodone may lower your blood pressure when you stand up. Get up slowly to avoid feeling dizzy or lightheaded. Drinking alcohol while taking oxycodone can be dangerous and even deadly. Oxycodone can make you drowsy and slow your reflexes. Avoid driving or activities requiring alertness until you know how oxycodone affects you.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |