Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | 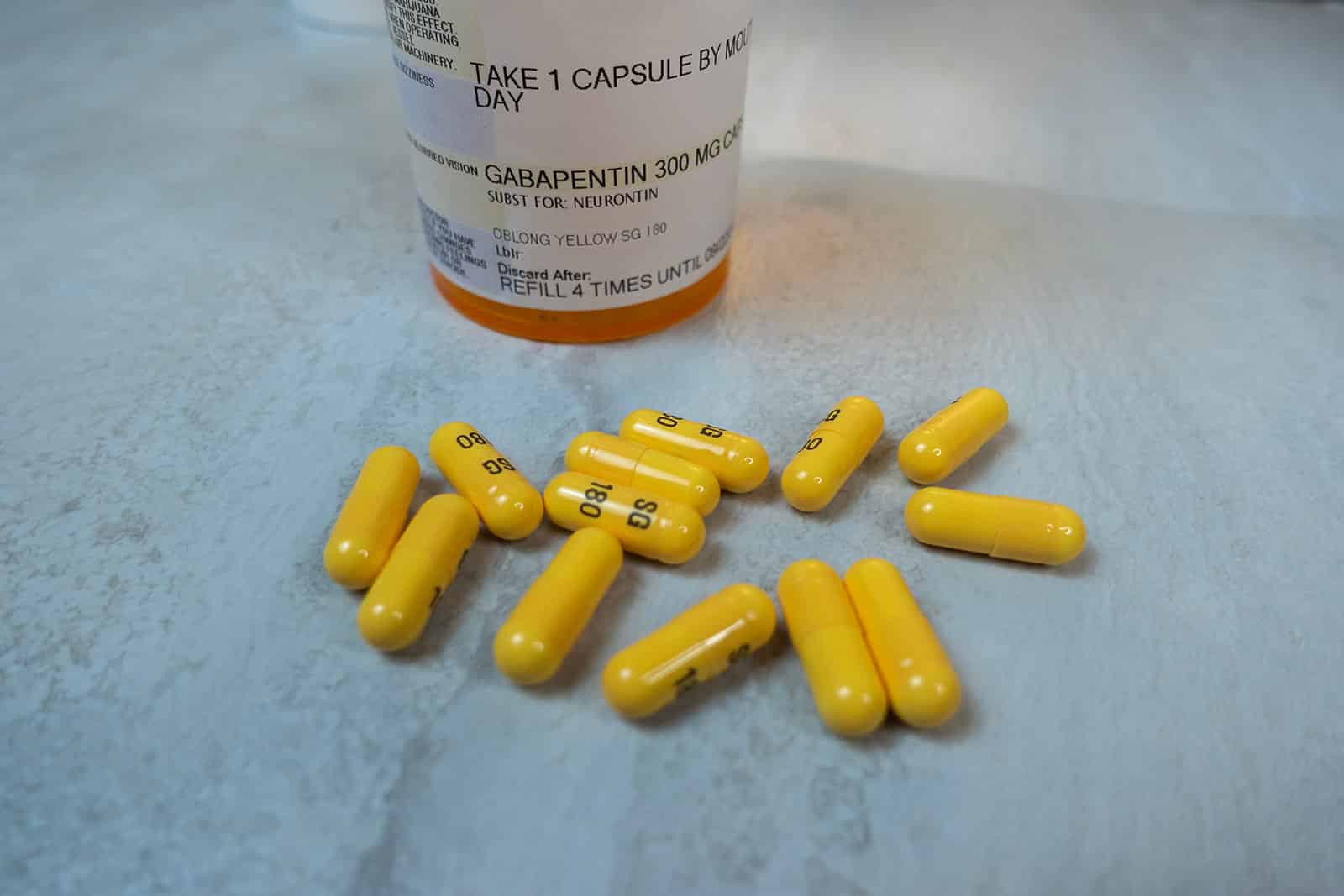 |
 |  |
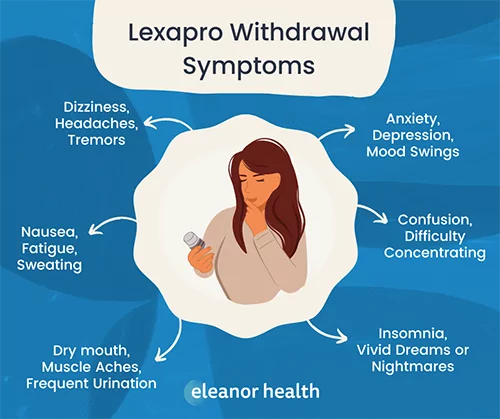
Dependence and Withdrawal: Prolonged use of gabapentin may result in physical dependence, and sudden discontinuation can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms are diverse and can include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, vomiting, headache, muscle spasms, muscle pain, mood changes, and sweating. Gabapentin withdrawal lasts between 5 to 10 days, with symptoms such as anxiety, headaches, and nausea peaking during the first few days. According to Krebs and Tzeng (2019), in their study “Gabapentin Withdrawal: A Case Series,” withdrawal symptoms begin within 24 to 72 hours after the last dose and intensify over the next 1 to 5 days Withdrawal symptoms from gabapentin may begin as early as 12 hours after the last dose and can continue to manifest for up to 7 days. The most intense symptoms are usually observed within 24 to 48 hours post-cessation, often peaking around the third day. Mood Swings: Fluctuations in mood, ranging from irritability to periods of sadness. Fatigue: Persistent tiredness, even after a full night’s sleep. Mild Anxiety: Continued feelings of nervousness or unease, though less severe than during peak withdrawal. In addition to potential addiction, gabapentin is associated with an increased risk of suicidal ideation, mood swings and sudden significant changes in behavior. The Drug and Enforcement Administration (DEA) reported that prescriptions of gabapentin doubled from 2011 to 2017 and it was in the top 10 of the most prescribed medications in 2021 Many people experience mood swings, feelings of sadness, and even depression during gabapentin withdrawal. In some cases, individuals may develop suicidal thoughts or behaviors, especially if they were already struggling with mental health issues. Gabapentin Withdrawal Timeline. Understanding the timeline of Gabapentin withdrawal can help you anticipate and manage the challenges that come with it. Withdrawal from Gabapentin is typically divided into three phases: early withdrawal, acute withdrawal, and protracted withdrawal. Each phase has its own set of symptoms and duration, and Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. It can also cause suicidal thoughts or behaviors in children and adults. If you or your child experience changes in behavior or mood while taking gabapentin, contact your prescriber immediately. Mood changes: Gabapentin withdrawal may precipitate changes in mood or affect, including symptoms of depression, irritability, or emotional lability. Individuals may experience mood swings or difficulty regulating their emotions during withdrawal, which can impact interpersonal relationships and daily functioning. Gabapentin Withdrawal Symptoms. Before diving into the gabapentin withdrawal timeline, it helps to understand what symptoms might arise. People often fear the return of their original pain or seizures, and they also worry about new or unexpected gabapentin withdrawal side effects. Common gabapentin withdrawal symptoms reported include: Post-Acute Withdrawal Syndrome (PAWS) can last from a few months to two years, largely influenced by the duration and intensity of substance use prior to cessation. During this time, common symptoms such as anxiety, depression, insomnia, mood swings, and cravings manifest as the brain attempts to regain a chemical equilibrium following addiction. Even if you’ve taken gabapentin for a short period, like two weeks, you might still experience withdrawal symptoms when you try to quit. These symptoms may include bloating, mood changes, and difficulty sleeping. But don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! Withdrawal symptoms usually begin 12-48 hours after the last dose and can last up to 7-10 days, though this varies. When Do Withdrawal Symptoms Start? Symptoms typically begin within the first 24-48 hours after stopping gabapentin. Acute Withdrawal: Lasts around 5-7 days. Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms can range from mild to severe, depending on factors such as dosage and individual health conditions. Some common withdrawal symptoms include: Anxiety and panic attacks; Insomnia and restlessness; Irritability and mood swings; Nausea and vomiting; Sweating and chills; Muscle pain and tremors; Increased sensitivity Common symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, muscle pain, flu-like symptoms, and stomach pain. Some people experience mood swings, panic attacks, and light sensitivity due to changes in brain chemistry. To address these issues, healthcare providers might consider adjusting the gabapentin dosage or exploring complementary therapies. Non-pharmacological interventions can also help manage mood swings and agitation, such as: Relaxation techniques (e.g., focused breathing, mindfulness practices) 2. Cognitive-behavioral therapy 3. The withdrawal symptoms of gabapentin can be quite diverse, affecting both physical and mental health. Common symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain, and sweating. These arise as the body and brain adjust to the absence of the drug, which moderates neurotransmitter activity. Gabapentin withdrawal refers to the symptoms that can occur when a person who has been using gabapentin regularly, especially at high doses, suddenly reduces or stops taking the medication. Individuals who have been using gabapentin regularly may experience withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation, which can begin within 12 hours to 7 days and Beyond the common side effects that people experience when they are on Neurontin including, dizziness, fatigue, weight gain, peripheral edema, mood swings, hyperactivity, and even hepatotoxicity, there are specific gabapentin withdrawal symptoms that occur when you suddenly stop taking it. A comprehensive guide to safely stopping gabapentin, managing withdrawal symptoms, and addressing withdrawal-induced depression. Seek professional help throughout the process.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | 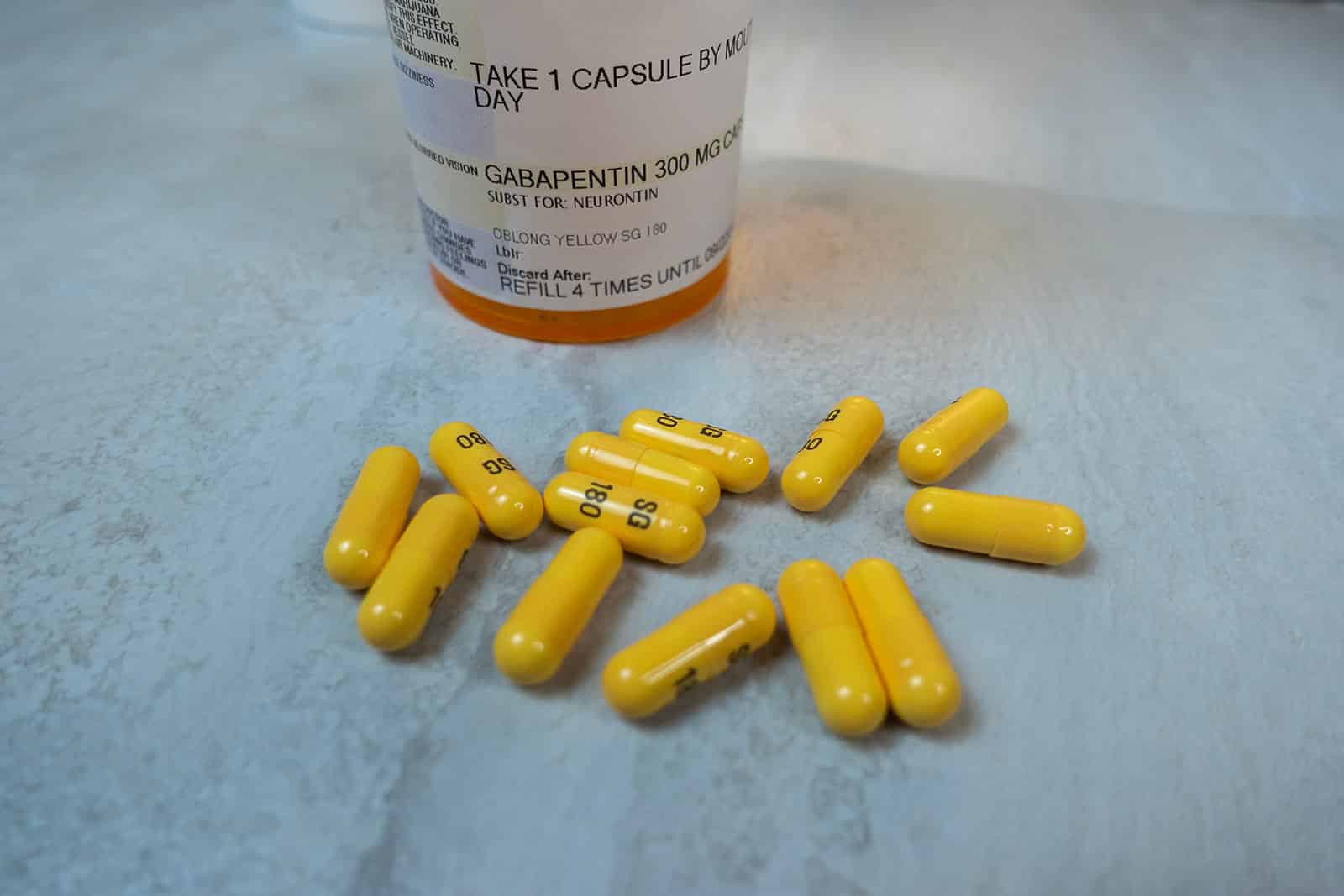 |
 |  |