Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gabapentin-withdrawal-symptoms-timeline-and-treatment-4176217-FINAL-updated-61b1abea5c98489fa075d8fdce211c50.jpg) |
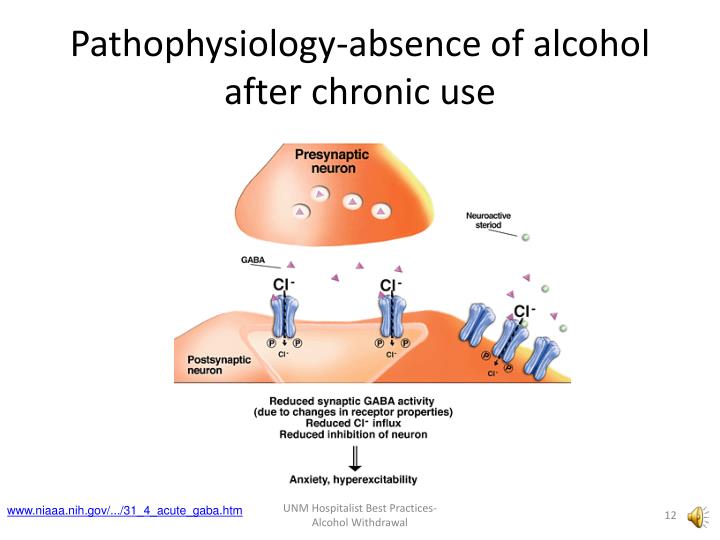 |  |
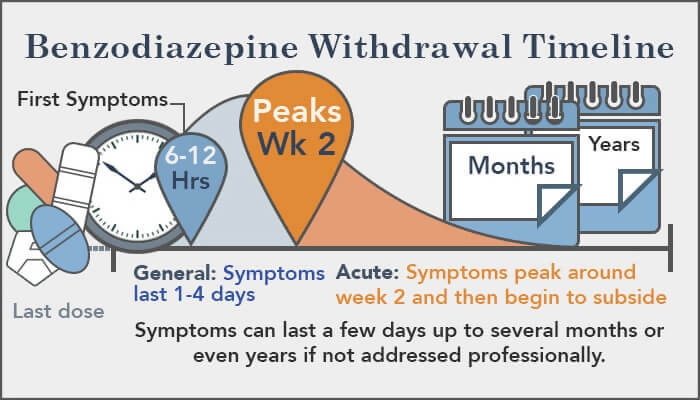
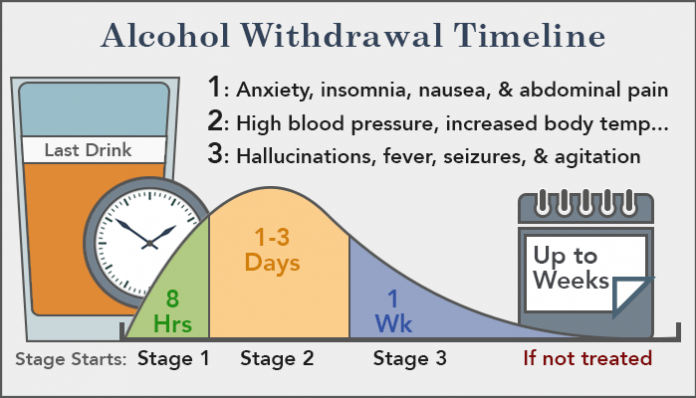
Gabapentin, a medication initially developed to treat seizures, has become widely prescribed for various conditions, including nerve pain, restless legs syndrome, and anxiety. While generally considered safe, stopping gabapentin abruptly, especially after prolonged use, can lead to a range of withdrawal symptoms. Alcohol withdrawal seizures most commonly occur 12–24 hrs after the individual’s last drink, though the risk for seizures can last for up to 48 hrs following abstinence. 24 Seizures occur in 5–10% of individuals with active AWS and are typically generalized tonic-clonic. 21, 25 Approximately two-thirds of individuals who have an initial Case reports have shown that gabapentin withdrawal often lasts for 5 to 10 days, but some people have taken as long as 18 weeks to completely taper off gabapentin while managing withdrawal symptoms. Symptoms may start within 12 hours to 7 days after stopping gabapentin and may be severe. Gabapentin 400 mg four times a day was compared to placebo in 61 alcohol-withdrawing patients and throughout the 7-day trial was found to have no advantage over placebo in reducing amount of clomethiazole required to decrease symptoms of alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin was also noted to be safe, well-tolerated, and have a low side effect profile. Gabapentin is a medication originally developed as an anticonvulsant to prevent seizures, but it is now widely used in addiction treatment to manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings. It is especially effective for individuals recovering from alcohol or opioid use disorders by alleviating anxiety, insomnia, and physical discomfort during Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric properties. These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. Symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal may include nausea, dizziness, headaches, insomnia, and anxiety. The safest way to stop using gabapentin is to taper off the medication under the supervision of a doctor. What Is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is a prescription medication commonly used for nerve pain, seizures, alcohol use disorder, alcohol withdrawal and insomnia. It was once thought to be a safe, non-addictive drug that became widely used for chronic pain and neurological conditions. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Neurological Symptoms: Seizures, particularly in individuals who were prescribed gabapentin for seizure control. Recognizing these symptoms early can help in managing them effectively and seeking appropriate treatment when necessary. While most withdrawal reactions are relatively mild in severity, abrupt withdrawal of gabapentin has been associated with rebound seizures in those who are treating epilepsy. Below, we discuss why gabapentin should be tapered and recommendations to do so. Potential Withdrawal Reactions From Gabapentin Discontinuing gabapentin can lead to withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures, has become increasingly popular over the years. Gabapentin Withdrawal Warnings . While gabapentin withdrawal may not be well understood, the recorded cases are alarming. Many of the gabapentin withdrawal case studies involve people with a history of psychiatric disorders or substance abuse problems. If you share either of these risk factors, there is cause for concern. Gabapentin withdrawal happens when a person stops taking the medication abruptly, which may lead to symptoms such as confusion, disorientation, and seizures. The duration of these symptoms can vary, so it's crucial to take preventive steps. Although gabapentin withdrawal has been previously reported and usually consists of anxiety, diaphoresis, and palpitations, this is the first reported patient with generalized seizures and status epilepticus secondary to gabapentin withdrawal. Rarely, Seizures: In some cases, especially after very high doses, seizures may occur upon abrupt withdrawal. These symptoms can be highly uncomfortable and are a major reason why people may struggle to stop taking gabapentin. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant medication commonly prescribed for seizures and nerve pain, can lead to physical dependence. Those who develop a dependency may face challenging withdrawal symptoms when discontinuing the drug. Gabapentin Withdrawal and Pregnancy. Gabapentin withdrawal during pregnancy requires careful management to protect both the mother and the developing baby. Abruptly stopping gabapentin can lead to severe withdrawal symptoms, including anxiety, seizures, and other complications, which can be dangerous during pregnancy. Some of the common gabapentin withdrawal symptoms may include. People who take gabapentin for seizures may experience rebound symptoms or an uptick in seizure activity, including ongoing, uncontrollable seizures. Drug Category: Anticonvulsant. Commercial & Street Names: None. DEA Schedule: Uncontrolled. Administration: Oral. Can gabapentin withdrawal cause seizures? Yes, especially in those taking it for epilepsy, abrupt discontinuation can lead to seizures. Is gabapentin addictive?
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gabapentin-withdrawal-symptoms-timeline-and-treatment-4176217-FINAL-updated-61b1abea5c98489fa075d8fdce211c50.jpg) |
 |  |