Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 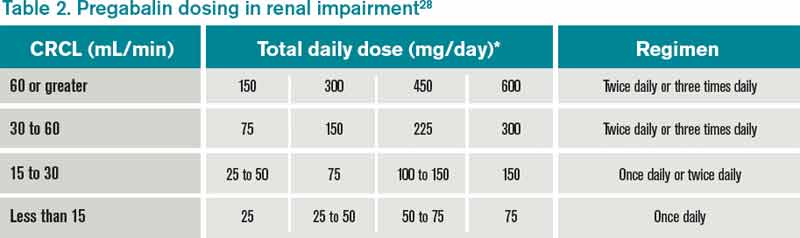 |
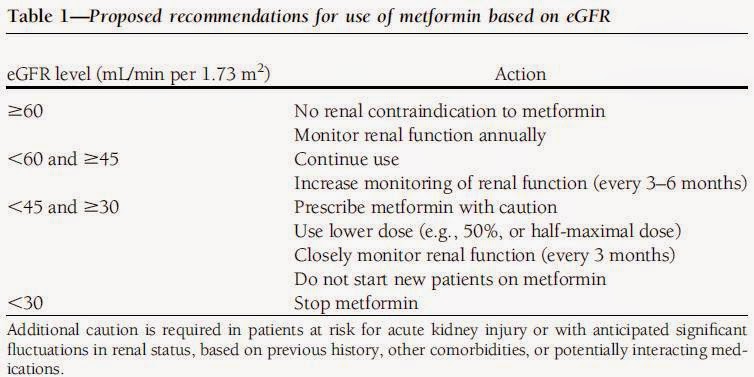
The recommended maximal daily dose of gabapentin is 1,500 mg in people with grade 3 chronic kidney disease (CKD), 700 mg in those with grade 4 CKD, 300 mg in those with grade 5 CKD, and 100 to 300 Pharmacology. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used first-line agents for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and other common neuropathies. Pharmacologically, both agents inhibit alpha-2-delta (α2δ) subunit of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels, a key receptor involved in regulating the excitability of neurons. 3 Peripheral nerve injury results in the upregulation of α2δ-1 receptors Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. Gabapentin Dosage Guidelines in Adults, Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older with Renal Impairment 1-5. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease J Pain Res. 2017 Jan 27:10:275-278. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S130942. eCollection 2017. Authors Concordance of kidney function estimates with measured GFR for recommended drug dosages was 88% for MDRD Study equation compared with 85% for the CG equation (P < 0.001) and 82% for the CG IBW equation (P < 0.001), with lower concordance when dosing recommendations for drugs included narrow GFR ranges. Dose Adjustment: 400-1400 mg/day BID; How Often to Take: Twice a Day; Notes: Your doctor will decide the best dose for you. Severe Kidney Problems (CrCl <30 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 200 - 700 mg/day QD. How Often to Take: Once a Day; Notes: Careful monitoring is needed. End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) on Dialysis: Dose Recommendations: 100 Dose as in GFR=15– 30 mL/min. No dosage adjustments are needed unless there is concomitant renal dysfunction. Loading dose of 300–400 mg in patients who have never received gabapentin. Maintenance dose of 200–300 mg after each HD : session and increase according to tolerability. Dosages of drugs cleared renally should be adjusted according to creatinine clearance or glomerular filtration rate and should be calculated using online or electronic calculators. Recommended Dose reductions for meperidine are the same as those recommended for morphine. 36. Because patients with CKD have a high incidence of diabetic neuropathy, they often are prescribed medications for neuropathic pain. Gabapentin, a drug commonly used for neuropathic pain, requires dose adjustment in patients with renal impairment . Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication in critically ill patients with various etiologies and risk factors. Admissions for AKI have increased in the past decade, 1 compounded by COVID-19 critical illness, 2 and have surpassed the incidence of hospitalizations from end-stage renal disease (ESRD). 3 The varying etiologies of AKI create complex interactions when evaluating changes in Patienten. Gabapentin 100 mg Hartkapseln können bei Patienten mit Niereninsuffizienz gemäß den folgenden Dosierungsempfehlungen gegeben werden. Tabelle 2: GABAPENTIN-DOSIERUNG BEI ERWACHSENEN MIT EINGESCHRÄNKTER NIERENFUNKTION Kreatinin-Clearance (ml/min) Tagesgesamtdosisa (mg/Tag) ≥80 900 - 3.600 50 - 79 600 - 1.800 Many analgesics that are typically used in the non-CKD population should not be used among patients with advanced CKD (ie, estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] <30 mL/min/1.73 m 2; including those on dialysis). This topic reviews the epidemiology, assessment of pain, and management of pain among patients with advanced CKD. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. Table 1 shows maximum recommended dose of gabapentin in renal impairment: Table 2 shows the maximum recommended dose of pregabalin in renal impairment: In this scenario you are carrying out an audit of gabapentinoid prescribing in your work area, to ensure that the doses prescribed in renal impairment are safe and appropriate. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |