Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
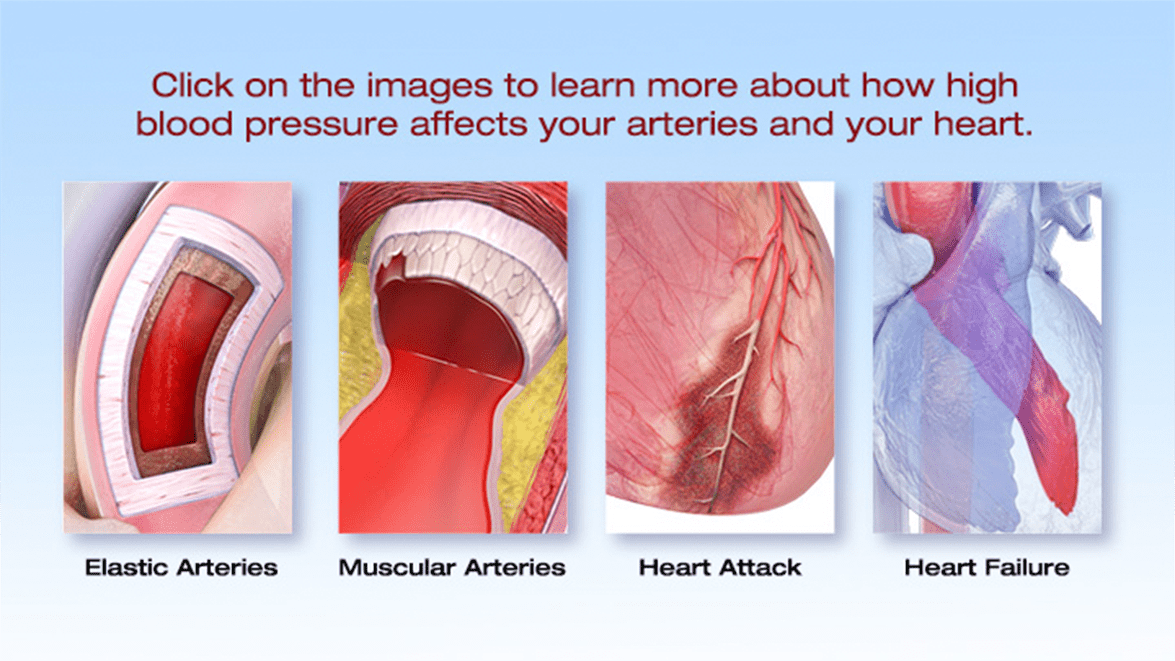
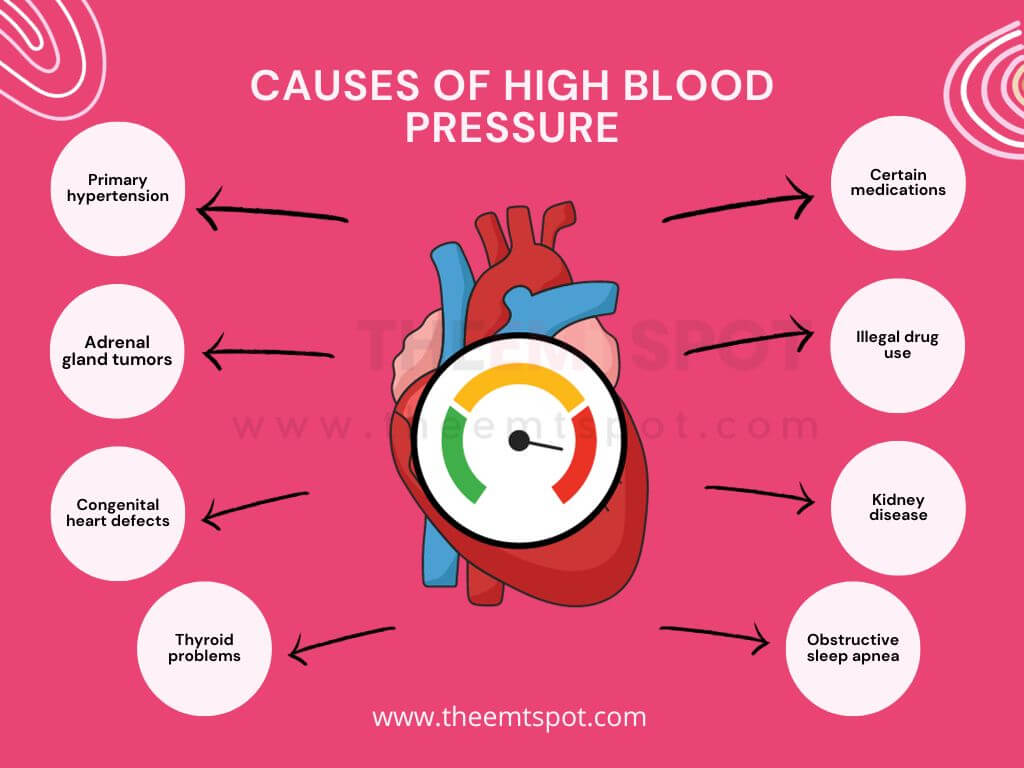
Below, we’ll look at seven medications that commonly cause swollen ankles and legs. But keep in mind medications aren’t the only cause. Sometimes, swelling is caused by something more serious, like a blood clot or a medical condition getting worse. 1. Amlodipine Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant (antiseizure) medication approved by the FDA to treat several conditions. Doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin "off-label" to treat other conditions as well. A 2022 report stated that gabapentin was among the 10 most commonly prescribed medications in the U.S. What is gabapentin and what is it used for? Caffeine can cause a short-term spike in blood pressure in people who don't use it all the time. Caffeine helps to keep blood vessels open. This allows blood to easily pass through blood vessels. I started taking Gabapenti 2 months ago for insomnia. It works great for that. I take 300mg at 5pm and 300mg at 10pm. My problem now is my blood pressure. I have heart desease and have always been able to keep a good normal blood pressure through exercise and eating healthy. Now it doesn't matter what I do. My B/P is high if I do anything. We have explained how gabapentin can cause high blood pressure. However, not every individual taking gabapentin would experience high blood pressure or the same side effects. Other factors can increase one’s risk of high blood pressure besides gabapentin. High blood pressure is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Tylenol, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. Gabapentin is fairly safe when you use it correctly. It does come with some possible side effects, though. People who misuse this drug are also at risk of additional side effects. Gabapentin is More rarely, gabapentin can cause fluid buildup (edema), weight gain, and vision problems. It can also cause diarrhea. More serious (but rare) side effects include suicidal thoughts or behavior, and mood changes in children. This may cause your blood pressure to rise even higher, putting greater stress on your heart and kidneys. NSAIDs can also raise your risk for heart attack or stroke, especially in higher doses. Can gabapentin cause high blood pressure? Yes, abruptly stopping gabapentin can lead to rebound hypertension , a withdrawal symptom. Additionally, while not a direct cause, the cardiovascular risks associated with long-term use can indirectly affect blood pressure. For patients who have other medical issues — osteoarthritis or high blood pressure, for example — “the excess weight can potentially worsen” those conditions, says, John Batsis, M.D., an associate professor of medicine in the Department of Medicine and Nutrition at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Reported increased blood creatinine phosphokinase levels and muscle damage caused by inflammation. Antiepileptic drugs increase risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication; monitor for emergence or worsening depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior. Given the potential for both hypertensive and hypotensive effects, it is crucial for healthcare providers to closely monitor blood pressure in patients receiving gabapentin, particularly during the initiation of therapy or dose titration. Yes, it can cause High Blood Pressure (hypertension) Cardiovascular side effects including hypertension have been reported to occur in more than one percent of patients taking gabapentin. Read more at: Gabapentin is associated with a risk of dependence and withdrawal. Abrupt discontinuation of the drug may result in symptoms similar to those of benzodiazepine or alcohol withdrawal and may include: Hypertension (high blood pressure). Sweating. Confusion. Incoherent speech. Impaired ability to pay attention. Nausea. Pain. Insomnia. Restlessness Hypertension is one of the most common chronic diseases and public health problems worldwide. 13, 14 Our previous study indicated that oral gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure in chronic kidney disease-induced hypertension. 15 Another study showed that the intravenous administration of gabapentin decreased blood pressure in Not everyone who takes gabapentin will experience changes in blood pressure. However, certain factors may increase your risk, including: * Age: Older adults may be more susceptible to blood pressure changes. * Existing blood pressure issues: If you already have high or low blood pressure, gabapentin may exacerbate these issues. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. Does Gabapentin Raise Blood Pressure? Understanding the Cardiovascular Effects. The Initial Paradox: Gabapentin and Lower Blood Pressure; The Emerging Concern: Gabapentin and Elevated Blood Pressure. Mechanisms Behind the Possible Increase; Other Cardiovascular Side Effects of Gabapentin. The FDA Warning and Respiratory Depression The Risks of Taking Gabapentin for High Blood Pressure. Research indicates that gabapentin can cause blood pressure to rise in some cases, which may be due to its effects on the body’s blood vessels. When blood vessels constrict, blood pressure can increase, leading to potential complications.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |