Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_JessicaOlah_WhatToKnowAboutGaba_4000x2700-c7a290db74574d1eb6fab03c9008b9a0.png) |  |
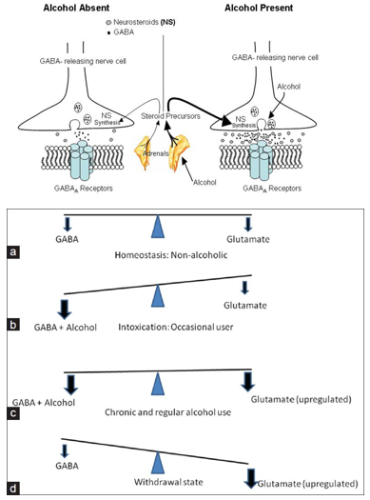
Recommended doses range from 20 mg to 40 mg daily, preferably dissolved under the tongue. However, it's crucial to emphasize that GABA supplementation should not be viewed as a substitute for professional medical advice in addressing prostate problems. GABA's therapeutic potential has been harnessed in the treatment of various medical conditions. How Long Does Gabapentin Take to Work for Nerve Pain? After taking a dose, IR gabapentin starts to work in the body within two to three hours. However, the full effects of gabapentin can take one to two weeks to become noticeable, and some people may need to wait longer to experience significant pain reduction. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a synthetic medication designed to mimic GABA’s effects. GABA is available as a supplement, whereas gabapentin requires a prescription and is used for specific medical conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that regulates its excitability. How does GABA and gabapentin work? GABA acts as a neurotransmitter and interacts with GABA receptors in the central nervous system, while gabapentin interacts with the α2δ subunit of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel. Research regarding gabapentin's effects on GABA and glutamate synthetic and metabolizing enzymes reveals a complex pattern of activity and provides an incomplete explanation for its anticonvulsant effects. It’s best to avoid taking gabapentin within 2 hours of taking these medications so gabapentin can achieve its full effect. Foods you eat: Taking gabapentin with high-protein foods may increase the amount of gabapentin your body absorbs. This may also affect how quickly gabapentin starts to work. You can take gabapentin IR with or without food. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Gabapentin was formed by the addition of a cyclohexyl group to GABA, which allowed this form of GABA to cross the blood–brain barrier. Despite its structural similarity to GABA, gabapentin does interact with GABA receptors in the CNS. Its mechanism of action is unknown, but may involve enhanced neuronal GABA synthesis. However, in other studies [7,12,13], gabapentin increases GABA levels in both rodents and humans, either by increasing GABA synthesis via the activation of GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase or by decreasing GABA metabolism via the inhibition of GABA transaminase. How Does Gabapentin Work? It’s not clear exactly how this unique medication works, but it appears to inhibit the release of certain excitatory neurotransmitters. Gabapentin is a unique medication and its mechanism of action as both a pain medication, sedative, and as an add-on drug for seizures, is not completely understood. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Gabapentin (Neurontin) Carisoprodol (Soma) Diazepam (Valium) Alprazolam (Xanax) Lorazepam (Ativan) There are also herbs and amino acids available without a prescription that can be used as GABA surrogates: Valerian root. Ashwagandha. Taurine. Brahmi. Bacopa. Glutamine: GABA’s Precursor In the present study, we examined whether gabapentin is an agonist at native GABA (B) receptors using a rat model of postoperative pain in vivo and periaqueductal gray (PAG) slices in vitro; PAG contains GABA (B) receptors, and their activation results in antinociception. Take-home message: - gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a major neurotransmitter that regulates much of our brain function. It was previously thought that ingested GABA could not cross the blood-brain barrier, but new research suggests that it may be able to. - Drugs that mimic the action of GABA are numerous, work in a variety of ways, and can have effects ranging from treating epilepsy to Conversely, gabapentin was first synthesized to be a GABA analog. However, gabapentin does not possess the same chemical composition or capacity as GABA. Gabapentin was designed to more readily cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB), in contrast to GABA, and its initial application was in the treatment of epilepsy [3]. Gabapentin (Neurontin®) is a second-generation antiepileptic drug widely used for treatment of neuropathic pain. It is also used to treat anxiety, insomnia, bipolar disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Although first introduced as an adjunct therapy for epilepsy, gabapentin became a blockbuster drug for the management of chronic pain from many nerve conditions [8]. Side effects are usually Gabapentin crosses several lipid membrane barriers via system L amino acid transporters. In vitro, gabapentin modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_JessicaOlah_WhatToKnowAboutGaba_4000x2700-c7a290db74574d1eb6fab03c9008b9a0.png) |  |