Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
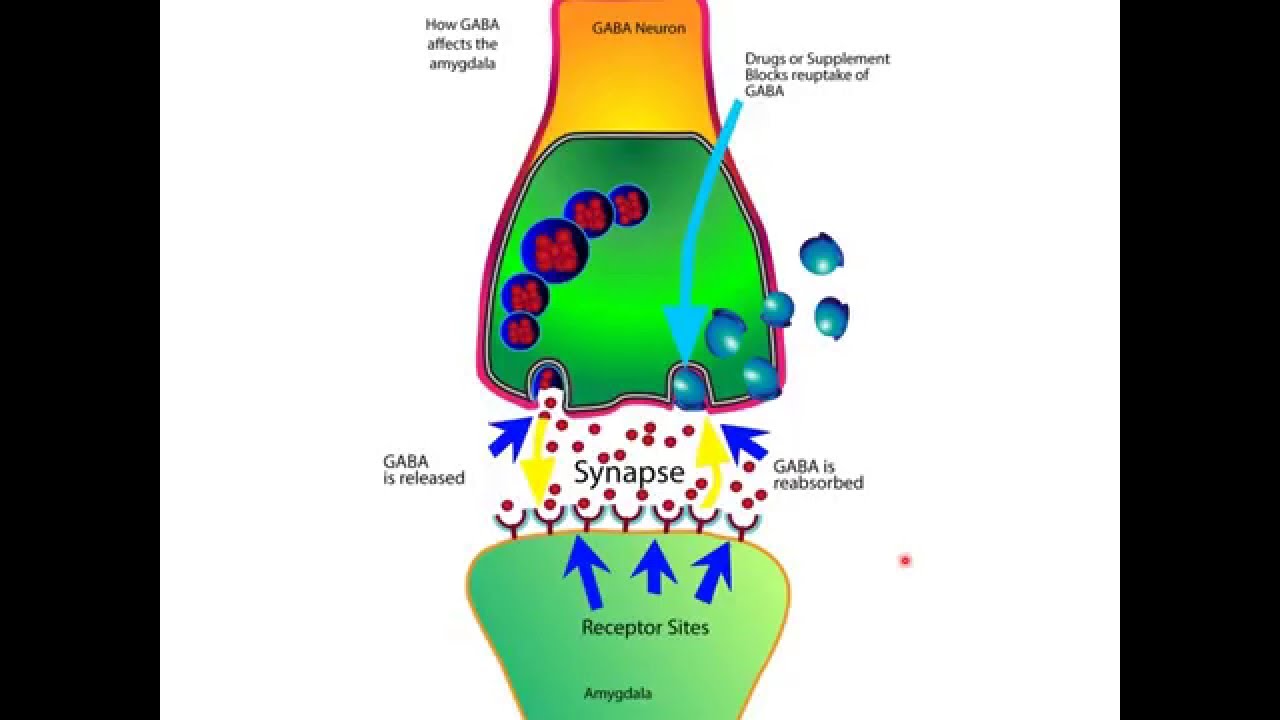
Gabapentin works by showing a high affinity for binding sites throughout the brain corresponding to the presence of the voltage-gated calcium channels, especially α-2-δ-1, which seems to inhibit the release of excitatory neurotransmitters in the presynaptic area that participate in epileptogenesis. Gabapentin works its magic by calming overactive nerves in the brain. It’s like a gentle hand soothing a frazzled mind, bringing relief to those who’ve long suffered. But here’s the rub: our brains are intricate machines, and tinkering with one part can have unexpected effects on others. The study shows that gabapentin halts the formation of new synapses, possibly explaining its therapeutic value in mitigating epileptic seizures and chronic pain. This insight, however, may lead physicians to reconsider the circumstances in which the drug should be prescribed to pregnant women. Gabapentin, originally developed to treat epilepsy, has gained recognition for its effectiveness in managing various types of pain. This medication works by altering the way the brain and nervous system respond to pain signals. gabapentin’s effects on GABA and glutamate synthetic and metabolizing enzymes reveals a complex pattern of activity and provides an incomplete explanation for its anticonvulsant Gabapentin prevents pain responses in several animal models of hyperalgesia and prevents neuronal death in vitro and in vivo with models of the neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Gabapentin is also active in models that detect anxiolytic activity. Gabapentin is a medication used in the treatment of various conditions such as epilepsy, post-herpetic neuralgia, neuropathic pain, and spasticity. It works by affecting calcium channels, leading to a decrease in excitatory neurotransmitters. AI generated definition based on: Brain Research, 2016 Gabapentin is usually taken with a meal or snack to protect against possible gastrointestinal disturbances (such as nausea) when taken on an empty stomach. How does gabapentin work in the brain? Gabapentin is believed to work by altering the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, although the exact mechanism is not fully understood. How Does Gabapentin Work? Gabapentin is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analog that plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance between nerve cell excitation and inhibition in the brain. It is commonly prescribed to treat seizures and nerve pain. The dosage strength of Gabapentin in different forms is: Gabapentin Tablets - It is available as 300 and 600-milligram tablets (Gralise) and 600 and 800-milligram tablets (Neurontin or generic gabapentin). Gabapentin Oral Solution - The oral solution of Gabapentin includes 250 mg (milligram) of Gabapentin per five milliliters (50 mg per mL). Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Gabapentin works by “slowing the brain down.” If you take gabapentin with other medications or substances that slow down the brain, dangerous effects can occur. This includes slowed breathing, confusion, and extreme sleepiness. And the risk is higher for people with existing breathing problems. GABA is the natural (endogenous) biochemical substance in the brain, spinal cord, and all nerves that control electrical conduction. Without proper GABA function, we experience pain. New research also shows that low levels of GABA make it harder to keep negative emotions such as fear, worry, anxiety and depression in check. To understand how gabapentin might influence dopamine levels, we first need to explore its primary mechanisms of action. Contrary to its name, gabapentin does not directly interact with GABA receptors or influence GABA levels in the brain. Instead, its primary mode of action involves modulating voltage-gated calcium channels. Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. In people with partial seizures, gabapentin works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Experts believe gabapentin may cause brain cells to produce more of a chemical called GABA, which reduces abnormal electrical activity of brain cells. Gabapentin can be an effective treatment for brain damage symptoms such as neuropathy, seizures, and autonomic dysfunction. However, it is not without side effects or risks. Therefore, consult with your doctor carefully before trying it, and alert your doctor immediately if any side effects appear. In this episode of I CARE FOR YOUR BRAIN with Dr. Sullivan, board certified neuropsychologist, Dr. Karen D. Sullivan provides some of the latest research on What is gabapentin, and how does it work for dogs? Gabapentin is a medication commonly used to treat seizures and pain in dogs. It’s classified as an anticonvulsant, meaning it helps to reduce the frequency and severity of seizures. Gabapentin works by calming the nerves in the brain and reducing the electrical activity that can trigger seizures. Gabapentin initiation was significantly associated with cognitive/functional status decline: worsening CDRGLOB at index+1 visit (odds ratio [95% confidence interval]: 1.55 [1.07, 2.25]); CDR-SB at index+1 visit (1.94 [1.22, 3.09]); and mean of FAQ at index+2 visit (1.78 [1.12, 2.83]).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |