Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
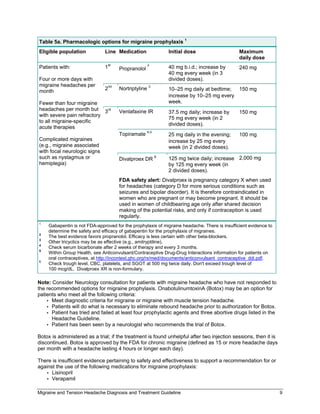
Presence of certain migraine conditions: hemiplegic migraine; basilar migraine (now called migraine with brainstem aura); frequent, prolonged, or uncomfortable aura symptoms; or migrainous infarction A preventive migraine drug is considered successful if it reduces migraine attack frequency or days by at least 50% within 3 months. Carbamazepine (Tegretol) is an antiepileptic that has been studied for use in migraine prevention and is considered possibly effective. Gabapentin (Neurontin) has been compared with placebo in Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. We found moderate certainty evidence that beta-blockers, valproate, and amitriptyline increase the proportion of patients who experience a 50% or more reduction in monthly migraine days, and low certainty evidence that gabapentin may not be different from placebo. The studies showed that neither gabapentin nor gabapentin enacarbil was more effective than placebo at reducing the frequency of migraine headaches. Gabapentin commonly caused side effects, especially dizziness and somnolence (sleepiness). No studies of pregabalin were identified, and research on this drug is desirable. Four trials with a total of 351 patients compared gabapentin in a dosage of 900 to 2,400 mg per day with placebo. The meta-analysis found no significant reduction in the frequency of migraine Discover whether gabapentin is a reliable treatment for migraines, including benefits, potential risks, and alternatives to consider. A 2016 study found that gabapentin showed some benefits for migraine headaches. However, it concluded that there wasn't enough evidence to recommend it as a primary therapy. Another study review in 2023 found that gabapentin was no more effective than a placebo in reducing monthly migraine days. GBP has some efficacy in migraine headache, but not sufficient evidence to suggest primary therapy. When primary headache treatments fail, a GBP trial may be considered in the individual patient. The 2021 American Headache Society consensus guideline recommends that preventive pharmacologic therapy should be considered for patients with 4 or more migraine headache days per month or those with 2 or more migraine headache days per month that are associated with substantial disability despite use of acute medication. 2 Preventive treatment There is some research to suggest that gabapentin can be helpful for migraine and headaches, though. One study from 2004 compared gabapentin with placebo as a preventive treatment option for people with migraine and found it to be an effective preventive agent. Despite the conflicting data arising from clinical studies, considerable evidence suggests that gabapentin has benefits in the treatment of headaches, including migraine headaches. Headaches. Gabapentin is quite effective in the treatment of cluster and chronic daily headaches. Abortive treatments are more effective if they are given early in the course of the headache; a large single dose tends to work better than repetitive small doses. For some patients, oral agents are less effective because of poor absorption secondary to migraine-induced gastric stasis and vomiting. Some nonpharmacologic treatments are effective for most headaches. Aerobic exercise and progressive strength training decrease headache frequency for numerous headache disorders. Gabapentin’s role in migraine prevention isn’t well known. It’s believed that it may influence electrical activity in the brain through neurotransmitters and block calcium channels. It may also Recurrent migraines can be functionally disabling and can impair quality of life. The disabling nature of migraine headaches leads to frequent visits to outpatient clinics and emergency department facilities, causing significant health and financial burdens. Headaches fall in the top five causes of emergency department visits and the top twenty reasons for outpatient visits.[1] The overall Migraine attacks can not only cause severe throbbing head pain or pulsing sensations, but also nausea, vomiting, and extreme sensitivity to light and sound.There are as-needed treatments to stop symptoms of a migraine attack (acute treatment) and long-term treatments to decrease the frequency and severity of migraine attacks (preventive treatment). For nausea, the anti-emetic ondansetron (Zofran) is very effective, but one of the side effects is headache. You're better off using promethazine or prochlorperazine (Compazine), both of which treat nausea but also help ease headache pain, says Dr. Loder. To describe and assess the evidence from controlled trials on the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin/gabapentin enacarbil or pregabalin for preventing migraine attacks in adult patients with episodic migraine.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |