Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
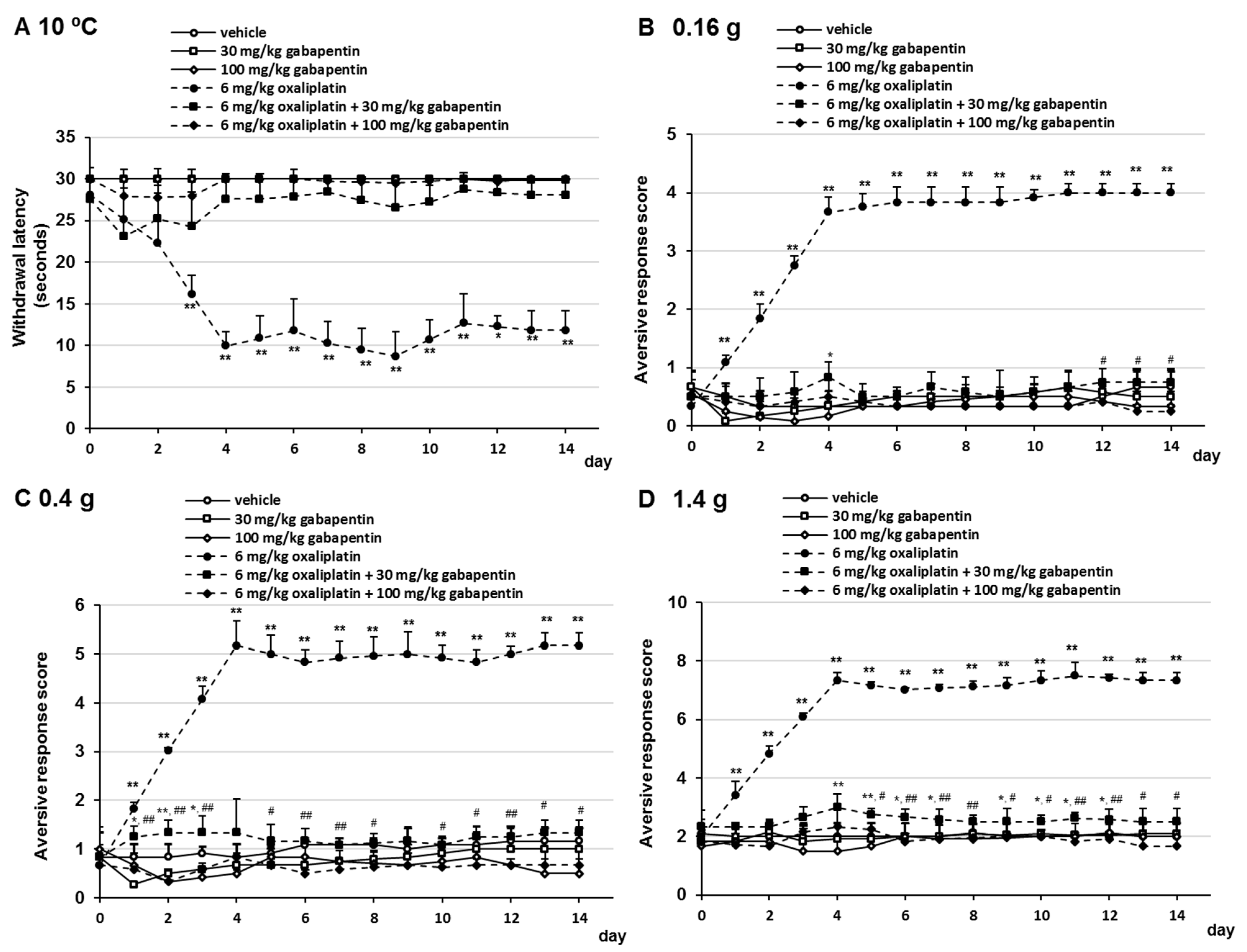
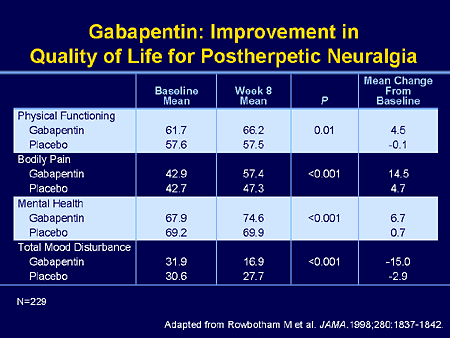
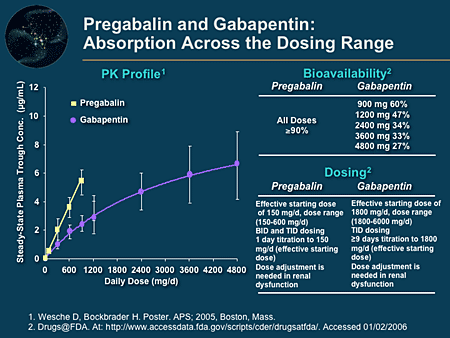
The established therapeutic dosing for gabapentin in neuropathic pain trials is 1800-3600 mg/day in 3 divided doses in patients with normal renal function. 3 This means the minimum effective dose is 600 mg 3 times a day. Renal adjustments are recommended in patients with CrCl below 60 mL/min. Gabapentin was effective in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and other neuropathic pain syndromes. It relieved symptoms of allodynia, burning pain, shooting pain, and hyperesthesia. Doctors prescribe gabapentin for pain because it is effective for certain nerve pain types, such as diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia. It is also sometimes used off-label for other types of pain, such as migraines and chronic pain. Gabapentin was shown to be better than placebo across all studies for IMMPACT outcomes. The review concentrated on gabapentin doses of 1,200 mg/d or greater and reported that doses at or above this threshold were reasonably effective for treatment of various neuropathic pain types. The authors conclude that gabapentin provides safe, effective pain relief in patients with diabetic neuropathy. The effects of gabapentin are similar to those found with tricyclic antidepressants Gabapentin and pregabalin both have been shown to be effective in post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic peripheral neuropathy [52,56,57]. Pregabalin also has been shown to be superior to placebo in the treatment of spinal cord injury [ 58 , 59 ]. Gabapentin is approved to treat seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain from shingles. It is thought to work by changing how nerves send messages to your brain. It is also used off-label to treat other neuropathic pain conditions. The purpose of this report is to review the clinical evidence on the efficacy, safety and guidelines for use of gabapentin in adults with neuropathic pain, and to examine evidence on the misuse or abuse of gabapentin and other drugs for neuropathic pain. If your lab tests show no condition that's causing the neuropathy, your health care professional might recommend watchful waiting to see if your neuropathy stays the same or gets better. Medicines. Medicines can be used to treat conditions associated with peripheral neuropathy. There also are medicines used to improve peripheral neuropathy Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. “Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. While gabapentin has its place in neuropathy treatment, many patients find better relief through alternative approaches. The Foot Institute offers a range of treatment that can be more effective and have fewer side effects than gabapentin alone. Gabapentin (1-[aminomethyl]-cyclohexaneacetic acid; Neurontin, Parke-Davis, Division of Warner-Lambert Co, Morris Plains, NJ) is an anticonvulsant approved in the United States in 1994 for use in adult patients with partial epilepsy that has been reported anecdotally and in open-label case series to be effective in the treatment of pain For this study, a key measure was whether a medication reduced discomfort by 50%. The most effective treatment was nortriptyline. Of the study subjects taking this medication, 25% reported their discomfort improved by at least 50%. The least effective treatment was pregabalin: only 15% of study subjects reported that much improvement. The same review compared gabapentin to an inactive medicine (placebo) in almost 6,000 adults with chronic pain from PHN or diabetic neuropathy. Study participants were given either gabapentin or a placebo for 4 to at least 12 weeks. Keywords: pregabalin, gabapentin, neuropathic pain, pain, meta-analysis, systematic review. 1. Introduction. The prevalence of neuropathic pain in the general population is estimated to range from 3.2% to 10.3%, with an even higher prevalence in cases of diabetic neuropathy, ranging from 23% to 46.5% . Twenty-four systematic reviews or meta-analyses and one RCT met the inclusion criteria and provided data on efficacy and safety of gabapentin in patients with neuropathic pain. This Rapid Response Report, however, focused on four reports which provided either direct or indirect comparisons between gabapentin and active agents. Critical appraisal of included RCTs indicated that gabapentinoids are effective in reducing neuropathic pain in adults. The Neuropathic Pain Special Interest Group (NeuPSIG) has recommended antiepileptic drugs to manage neuropathic pain [1]. Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Evidence for other types of neuropathic pain is very limited. This summary uses a Cochrane review, updated in 2014, to address the efficacy of gabapentin compared with placebo to palliate neuropathic pain. 3 The Cochrane review includes 37 trials enrolling
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |