Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
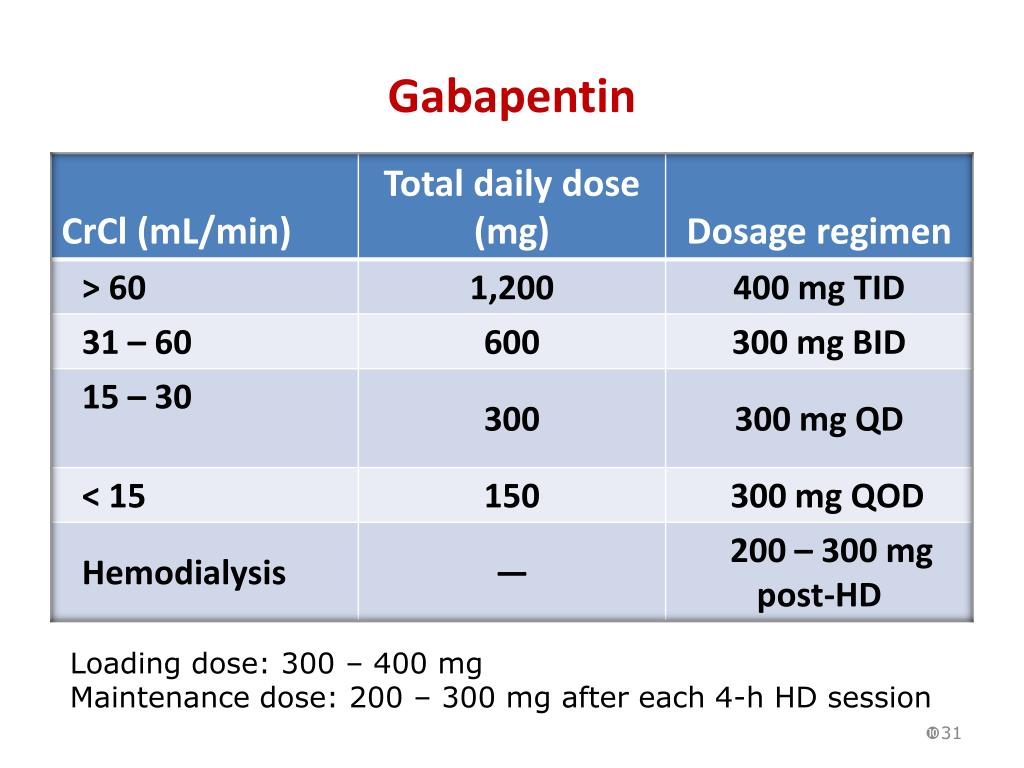 |  |
Gabapentin may cause breathing problems in people who use opioid pain medicines and those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Older adults who take gabapentin also are at higher risk of breathing problems. The maximum dosage of gabapentin is 3,600 mg per day. However, doses greater than 1,800 mg per day haven’t been shown to be more effective than lower doses. The capsules, tablets, and solution can be taken with or without food. Bioavailability of gabapentin is approximately 60%, 47%, 34%, 33%, and 27% following 900 mg/day, 1,200 mg/day, 2,400 mg/day, 3,600 mg/day, and 4,800 mg/day given in 3 divided doses, respectively. Food has only a slight effect on the rate and extent of absorption of gabapentin (14% increase in AUC and C max ). At daily dosages of 4800 mg however, between 230 and 312 mg more gabapentin is predicted to be absorbed following q6h administration as compared to q8h. When doses of 4800 mg/day are given q6h, our data would predict an increase in gabapentin bioavailability of 13–22%, relative to a q8h administration schedule. The recommended daily dose of gabapentin depends on various factors, including what it is used to treat. Initial treatment with gabapentin is usually started with 300 mg a day and may increase to up to 4800 mg a day, depending on the individual. A third study compared gabapentin 900 mg/day, in three divided doses (N=111), and placebo (N=109). An additional gabapentin 1,200 mg/day dosage group (N=52) provided dose-response data. A statistically significant difference in responder rate was seen in the gabapentin 900 mg/day group (22%) compared to that in the placebo group (10%). Absorption: Increasing gabapentin's dosage leads to reduced bioavailability; for example, daily doses of 900 mg, 1200 mg, 2400 mg, 3600 mg, and 4800 mg yield bioavailability of approximately 60%, 47%, 34%, 33%, and 27%, respectively. The impact of food is minor, resulting in a 14% increase in area under the curve (AUC) and Cmax. Safety and efficacy have not been established. Appropriate studies performed to date have not demonstrated geriatric-specific problems that would limit the usefulness of gabapentin in the elderly. Bioavailability of gabapentin is approximately 60%, 47%, 34%, 33%, and 27% following 900 mg, 1200 mg, 2400 mg, 3600 mg, and 4800 mg/day given in 3 divided doses, respectively. Food has only a slight effect on the rate and extent of absorption of gabapentin (14% increase in AUC and C max ). To make sure this medicine is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have ever had: kidney disease (or if you are on dialysis). Some people have thoughts about suicide while taking seizure medicine. Children taking gabapentin may have behavior changes. Stay alert to changes in your mood or symptoms. A third study compared gabapentin 900 mg/day divided TID (N = 111) and placebo (N = 109). An additional gabapentin 1200 mg/day dosage group (N = 52) provided dose-response data. A statistically significant difference in responder rate was seen in the gabapentin 900 mg/day group (22%) compared to that in the placebo group (10%). The only medicine I take is gabapentin for peripheral neuropathy that was caused by the chemotherapy drugs I received during the cancer treatment. the target dose of gabapentin was 900 mg four Gabapentin can be taken by most adults and children aged 6 and over. Gabapentin is not suitable for some people. To make sure it's safe for you, tell your doctor if you: NHS medicines information on who can take gabapentin and who may not be able to take it. Gabapentin dosage for neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is most frequently prescribed off-label to treat nerve pain (neuralgia) due to nerve damage (neuropathy), compression, or irritation. Standard gabapentin dosage for adults: 300 to 1200 mg taken three times per day by mouth. Maximum gabapentin dosage for adults: 3600 mg daily in three divided doses. Gabapentin bioavailability is not dose proportional; i.e., as dose is increased, bioavailability decreases. Bioavailability of gabapentin is approximately 60%, 47%, 34%, 33%, and 27% following 900, 1200, 2400, 3600, and 4800 mg/day given in 3 divided doses, respectively. If your doctor prescribes 600 mg or 800 mg tablets and you need to break one in half for dosing, be sure to take the other half at your next scheduled dose or within 28 days of breaking it. Don't store a broken tablet for extended periods. While you state your doctor has prescribed you 4,600mg a day (which is higher than the maximum recommended dose, but they may be trying alternative dosing for your specific situation), you are taking more than two to three times this dose day. This is dangerous and should not be done. Possible side effects from overdose include: Doses up to 2400 mg/day have been well tolerated in long-term studies; doses of 3600 mg/day have be used in a small number of patients for a relatively short duration and have been well tolerated. The maximum time between doses should not exceed 12 hours. Absorption: Increasing gabapentin's dosage leads to reduced bioavailability; for example, daily doses of 900 mg, 1200 mg, 2400 mg, 3600 mg, and 4800 mg yield bioavailability of approximately 60%, 47%, 34%, 33%, and 27%, respectively. The impact of food is minor, resulting in a 14% increase in area under the curve (AUC) and Cmax. GBP monotherapy is well tolerated in daily doses of up to 4,800 mg and is effective in a subgroup of patients with medically refractory partial epilepsy.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |