Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
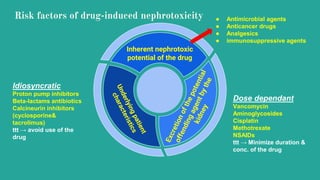
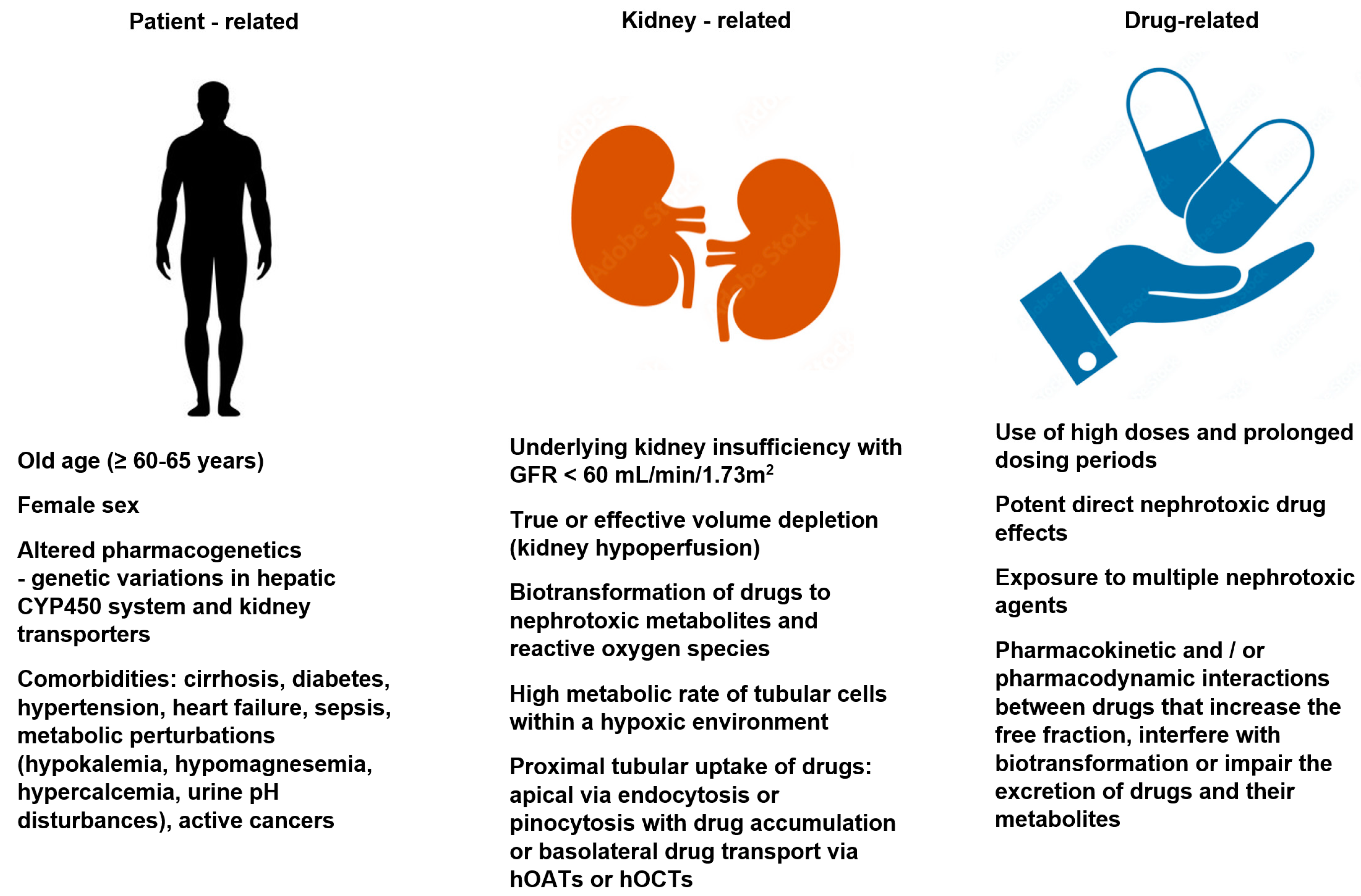
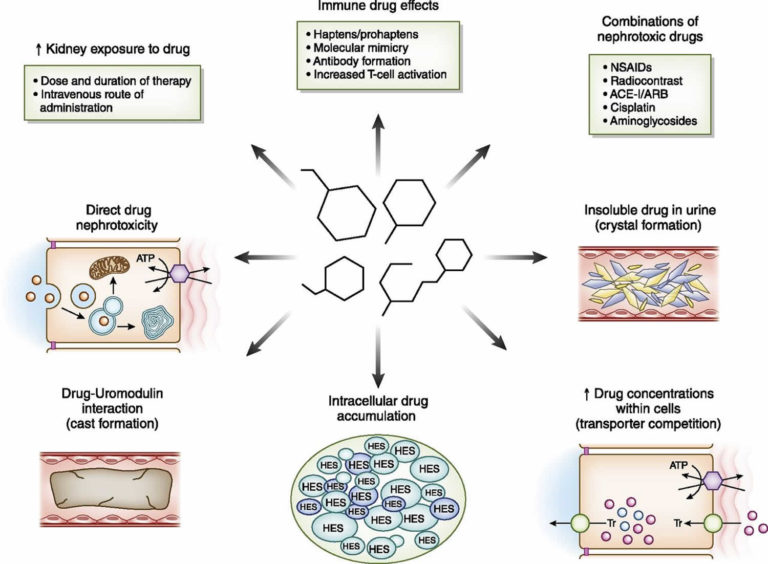
Programme has taken the decision to avoid the use of the term nephrotoxic. In addition, many medications are cleared via. the kidneys, so have the potential to accumulate during an episode of AKI. The result of this may be a further deterioration in kidney function, Potentially nephrotoxic drugs are more likely to cause harm at higher doses, with longer durations of therapy, and/or in combination with other nephrotoxic agents. Impaired drug elimination becomes increasingly prominent as kidney function declines and is most challenging for patients on renal replacement therapy (RRT, or dialysis). Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. The kidneys play a large role in the way we handle and excrete drugs. This makes assessment of renal function key when prescribing drugs, to ensure patient safety. Drugs can also be associated with causing kidney injury and the presentation of this can vary. This article details considerations when prescribing drugs in renal impairment and highlights a number of ways in which drugs can cause Gabapentin is also sometimes used to relieve the pain of diabetic neuropathy (numbness or tingling due to nerve damage in people who have diabetes) The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of this drug were dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. Importantly, clinicians must understand the mechanisms of drug-induced nephrotoxicity and prioritize the safe prescribing of nephrotoxic drugs, monitor for potential nephrotoxicity, and be aware of both patient- and drug-specific risk factors, as well as the drug’s inherent nephrotoxic potential (NxP), to mitigate these events . Medications that are harmful to the kidneys are called nephrotoxic medications. Some of these medications only slightly worsen kidney function, while others could cause more serious injury. Your risk for kidney damage depends on your individual health conditions and the medication (s) you’re taking. Search is powered by a third party. Following concerns about abuse, gabapentin has been reclassified as a Class C controlled substance and is now a Schedule 3 drug, but is exempt from safe custody requirements. Healthcare professionals should evaluate patients carefully for a history of drug abuse before prescribing gabapentin, and observe patients for signs of abuse and dependence. Loop diuretics (furosemide & bumetanide) preferred as thiazides less effective if GFR < 25ml/min. However thiazides can potentiate the effects of loop diuretics. Stop if AKI due to rhabdomyolysis. Stop if patient develops unexplained / persistent muscle pain. May accumulate leading to increased risk of bleeding. list of all drugs licensed in the UK. The range of drugs covered will continue to grow with subsequent editions. The Handbook is not a guide to diagnosis nor to a drug’s side-effect profile, except where adverse drug events are more pronounced in the presence of renal impairment. For more in-depth information, However, carambola, with its unspecified toxin, is nephrotoxic while gabapentin does not seem to affect renal function and its duration of effect depends solely on creatinine clearance. In addition, the adverse effects of gabapentin on the central nervous system vary from person to person. Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. Nephrotoxic medications can elicit damage to the kidney via various mechanisms, including alteration in its structure and function. When evaluating the primary etiologies in renal injury, the incidence of drug-induced toxicity has accounted for 20% of all-cause incidents. Drugs eliminated via the kidneys can accumulate during acute kidney injury (AKI) or chronic kidney disease (CKD) and this can lead to further renal impairment or adverse effects. A review of these drugs is therefore required; any drug which can cause or exacerbate renal impairment should be avoided in AKI, and the appropriateness reviewed in CKD. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Gabapentin 340 Galantamine 341 Ganciclovir 342 Gemcitabine 343 Gemfibrozil 344 Vinorelbine 776. The Renal Drug Handbook . The Renal Drug Handbook. We found that patients with chronic kidney disease had elevated serum gabapentin concentrations, in some cases leading to gabapentin toxicity; those with advanced age and multiple comorbidities were more prone to the toxicity, and the toxicity tended to be underrecognized. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin. An elderly lady with AKI taking prescribed gabapentin experienced serious mental status changes resulting in the need for transfer to intensive care 7. Consciousness was restored in this patient by stopping gabapentin treatment and starting continuous venovenous haemofiltration. Drug dosing errors are common in patients with renal impairment and can cause adverse effects and poor outcomes. the least nephrotoxic agents should be used, and alternative medications should
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |