Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
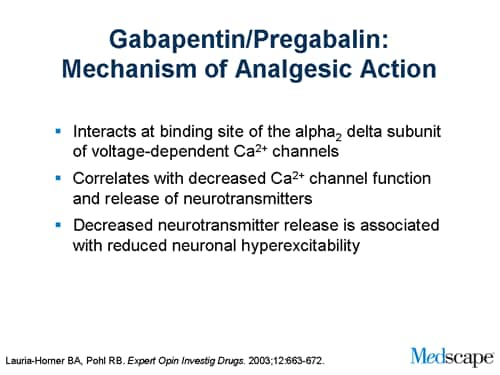
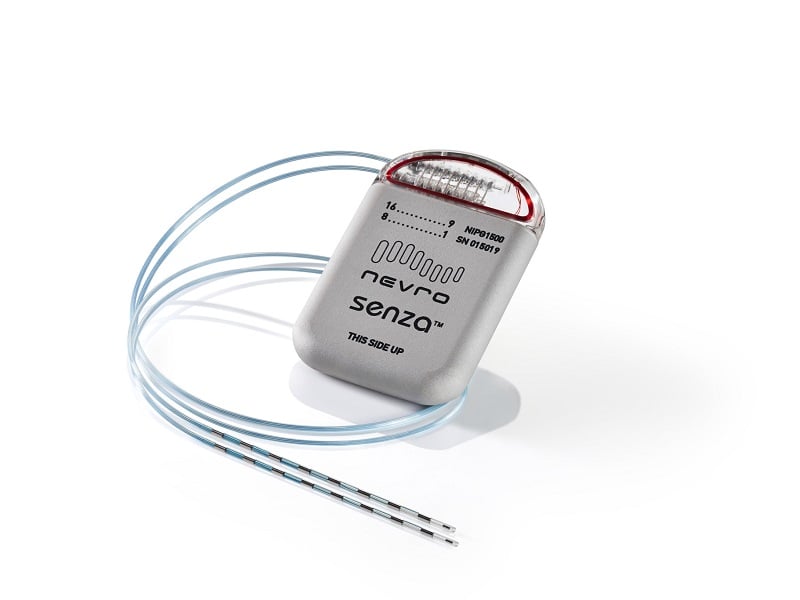
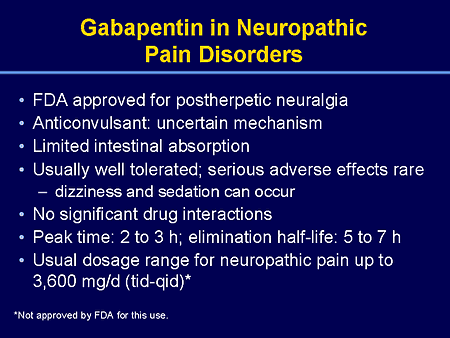
Oral gabapentin dosed at 1,200 mg or more daily demonstrated a 50% reduction in pain intensity, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of eight for postherpetic neuralgia and an NNT of six for FDA Approved Labeling Text dated 03/01/2011 Page 3 . Elimination: Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. In patients with painful DPN refractory to conventional treatment, neuromodulation with low- or high-frequency SCS is an FDA-approved option. 20, 21 Intrathecal drug delivery may also improve pain management. 158, 159 Although its FDA approval is not specific to painful DPN, intrathecal drug delivery using either ziconotide or morphine is Pregabalin has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in treating PDN, and is recommended by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) as a first-line treatment [18,23], and while gabapentin is not approved for this indication, it is also recommended by the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) and ADA for this use [18 Pregabalin and duloxetine are the only medications approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treating this disorder. Based on current practice guidelines, these medications, with Gralise is an extended-release gabapentin formulation that also is FDA approved for PHN with a titration schedule that begins with 300 mg on day 1; 600 mg on day 2; 900 mg on days 3 to 6; 1,200 mg on days 7 to 10; 1,500 mg on days 11 to 14; and 1,800 mg on day 15 and thereafter.² Pregabalin (Lyrica) is FDA-approved to treat diabetic neuropathy. It’s an oral medication that’s usually taken 2 to 3 times per day. Among all the medications used for diabetic neuropathy, pregabalin has the most research behind it. However, pregabalin’s cost — both brand-name and generic — runs higher than the other medications in FDA approved for the treatment of pain due to generalized diabetic peripheral neuropathy. The FDA has also approved the once-daily treatment Lyrica CR (pregabalin extended-release tablets) for the pain of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Pregabalin is excellent in treating pain described as dysesthetic, such as burning or pins and needles. Four pharmacologic options are currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat painful DPN. These include three oral medications (duloxetine, pregabalin, and tapentadol extended release) and one topical agent (capsaicin 8% topical system). As a 2022 review notes, the Food Drug and Administration (FDA) has approved different classifications of medications for diabetic neuropathy. In addition, some doctors and other regulatory boards Gabapentin is indicated for: Neuropathic pain caused by postherpetic neuralgia Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalization; Neuropathic pain caused by diabetic peripheral neuropathy and spinal cord injury Restless leg syndrome (gabapentin enacarbil) Gabapentin is frequently used off-label for: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Pregabalin and Duloxetine nearly 25 years ago and Tapentadol nearly 6 years ago for the management of pain in patients with PDPN. Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. – Painful Diabetic Neuropathy about 10-20% of diabetic patients have pain Requirements for FDA Approval Gabapentin (neurontin) First Line . Pregabalin (lyrica) Sometimes other terms are used, including cryptogenic neuropathy or chronic polyneuropathy of undetermined cause. For some people, neuropathy is due to diabetes, alcohol abuse, medications, or other conditions. But in nearly half of all cases, sensory polyneuropathy is idiopathic. No cause, no cure Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more The FDA-approved drugs for painful diabetic neuropathy include pregabalin, duloxetine, tapentadol, and capsaicin (for foot pain only). These are discussed below in detail. 7.1. Duloxetine. Duloxetine inhibits the reuptake of neurotransmitters, i.e., norepinephrine and serotonin, and shows less affinity towards dopamine transporters. The authors concluded that gabapentin is associated with reduction in acute pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (the later indication is not approved by the FDA), and that there is limited evidence to support the use of gabapentin for other types of neuropathic pain and pain disorders. 1 This Editorial This medication may not be approved by the FDA for the treatment of this condition. An Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) allows the FDA to authorize unapproved medical products or unapproved uses of approved medical products to be used in a declared public health emergency when there are no adequate, approved, and available alternatives. Pregabalin and duloxetine are the only medications approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treating this disorder. Based on current practice guidelines, these medica-tions, with
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |