Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
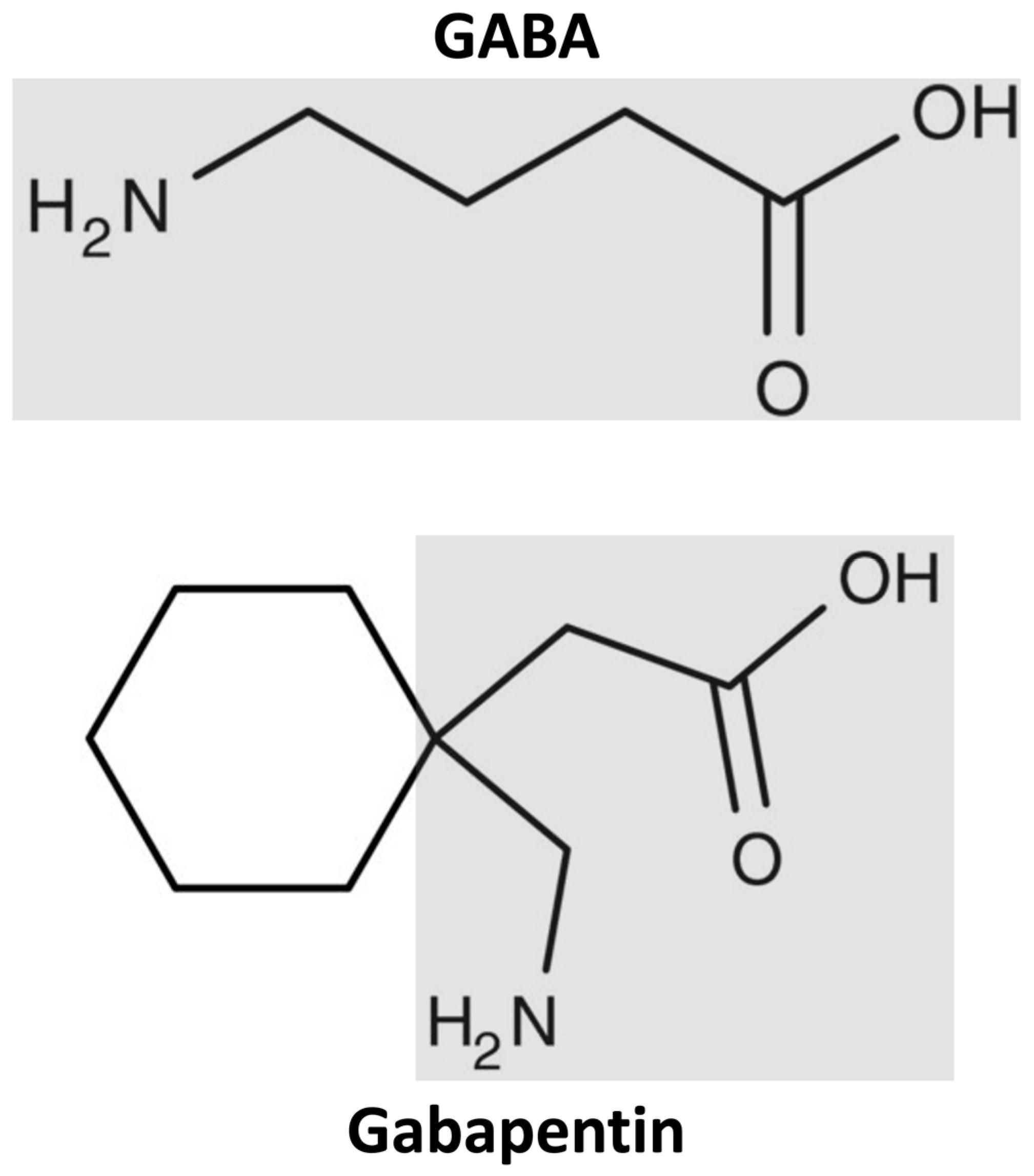
Gabapentin has established efficacy in the reduction of burn-induced hyperalgesia and allodynia in animal and human experimental burn models. This article reports a case series of six patients who, following admission to hospital with burn injury, described burning dysesthesia at either the injury or graft donor site. The latest guidelines for acute burn pain from the American Burn Association in 2020 suggest the adjunctive use of gabapentinoids for refractory burn pain and neuropathic pain, based on only two RCTs and three non-RCTs . Gabapentin is a prescription antiepileptic medication commonly used to treat postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain, and other neuropathic pain conditions. Learn more about how long it takes to treat nerve pain and what to expect when you're prescribed it. This pain is called post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN), and it can be severe and chronic; Nerve pain as a result of diabetic neuropathy, which happens when nerves in the feet damaged by diabetes cause chronic burning pain. How does gabapentin work in nerve pain? The exact way that gabapentin works to relieve pain is not known. Gabapentin has established efficacy in the reduction of burn-induced hyperalgesia and allodynia in animal and human experimental burn models. This article reports a case series of six patients who, following admission to hospital with burn injury, described burning dysesthesia at either the injury or graft donor site. Pain relief takes many forms. This Special Health Report, Pain Relief Without Drugs or Surgery, looks beyond the standard approaches of drugs and surgery and explores alternate pain-relief strategies, from acupuncture and mind-body therapies to spinal manipulation, physical and occupational therapies, herbal remedies, mindfulness meditation, and music therapy among others. Gabapentin has analgesic efficacy for neuropathic pain and is increasingly used in burn care. This study investigated the effect of a neuropathic pain control protocol, as well as early gabapentin initiation (<72 hours from injury) on total inpatient opioid use, chronic pain, and itch. Gabapentin is an agent that has been studied in both the acute and chronic management of burn pain. The use of gabapentin as an adjunct to standard analgesia has shown reduction in the severity neuropathic pain in limited studies of burn patients and burn injury models (Gray 2008, Dirks 2002). It calms the nerves by blocking pain-causing neurotransmitters, making gabapentin an effective treatment for sciatica and neurogenic pain. Prescribing gabapentin for chronic, non-specific low back Neurontin (gabapentin), generally prescribed for the treatment of nerve pain, is sometimes used to relieve severe pain caused by knee osteoarthritis (OA).Osteoarthritis, also known, as wear-and-tear arthritis, can often become so severe that joint replacement surgery is needed. Gabapentin for other types of nerve pain. Gabapentin can also treat nerve pain from PHN, which is the most common complication of shingles. It’s also used off-label to treat diabetes-related nerve pain. If you have nerve pain from other causes — like back injury, nerve injury, or after surgery — it still may help. Consider pregabalin for neuropathic pain not responsive to gabapentin. (Ketamine infusion) If a patient has altered mental status attributed to the ketamine infusion, turn the infusion off for two hours and then resume at a lower rate. (Dexmedetomidine infusion) Recommended in intubated patients. Gabapentin has established efficacy in the reduction of burn-induced hyperalgesia and allodynia in animal and human experimental burn models. This article reports a case series of six This element of the burn patients' pain experience is frequently difficult to manage and contributes significantly to their suffering. The onset may be either immediate or delayed. Gabapentin has established efficacy in the reduction of burn-induced hyperalgesia and allodynia in animal and human experimental burn models. Capsaicin cream can cause temporary redness, burning, or pain. Serious problems appear to be uncommon, even with highly concentrated doses. CBD. Gabapentin isn't a narcotic, but it is a It is especially good for nerve pain, such as burning, shooting or stabbing pain. Gabapentin belongs to the anticonvulsant group of medications, which are also used to treat epilepsy. You are on this medicine to . treat your pain. How does gabapentin work? Gabapentin works by changing the way that nerves send messages to your brain. Agents for the treatment of neuropathic pain (eg, gabapentin or pregabalin) should be considered as an adjunct to an opioid in patients who are having neuropathic pain or who are refractory to standard therapy (Level C). In people experiencing nerve pain after having had shingles, gabapentin is thought to change the way pain signals are sent through the body and brain. It's not entirely clear how gabapentin works to treat restless legs syndrome. Side effects of gabapentin. Common side effects of gabapentin include: drowsiness or dizziness; headache or blurred The use of gabapentin, pregabalin, or both is effective for reducing pruritus and neuropathic pain in burn survivors, according to the findings from a small retrospective review Heat pain thresholds, pain during the burn, and mechanical pain in the area of secondary hyperalgesia were not significantly changed by gabapentin (P <.2). Ratings of drowsiness and unsteadiness during walking were significantly higher for gabapentin than for placebo (P <.05).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |