Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | /arthritic-feetsies-56570427-resized-56a315a93df78cf7727bba2b.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 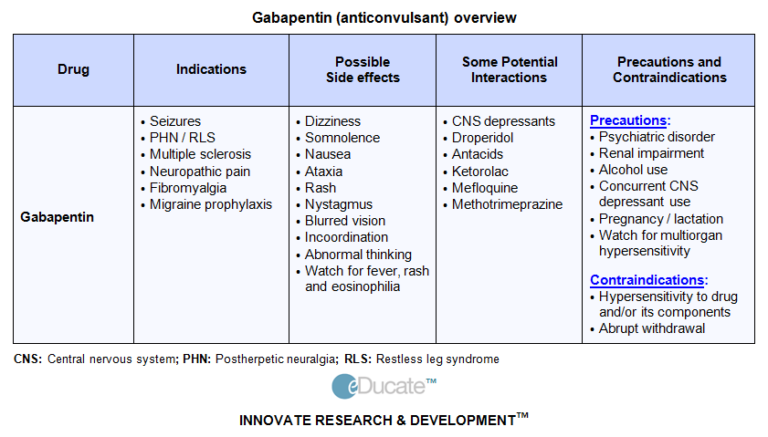 |
The Arthritis Today Drug Guide is meant for education – not self-medicating. Arthritis Today, the Arthritis Foundation and the Drug Guide Medical Review Panel do not endorse any products mentioned in this guide. While we endeavor to keep the information up to date, we make no representations or warranties about the completeness of the The finding of a roughly 30% reduction in pain is very consistent with studies of many treatments for chronic pain. While we are fairly good at acute pain management, many chronic pain conditions such as OA, low back pain, and others are harder to treat effectively. We used the Osteoarthritis Policy Model, a validated Monte Carlo simulation of knee OA, to examine the value of gabapentin in treating knee OA by comparing three strategies: 1) usual care, gabapentin sparing (UC-GS); 2) targeted gabapentin (TG), which provides gabapentin plus usual care for those who screen positive for nociplastic pain on the modified PainDETECT questionnaire (mPD-Q) and Gabapentin shows promise in managing arthritis pain, particularly in knee osteoarthritis, by reducing pain severity and improving functional status over time. Its mechanisms involve both central and peripheral actions, including modulation of pain-related growth factors and nerve sensitivity. Gabapentin and duloxetine were found to provide comparable analgesia and improvement in functional status in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA) after 3 months of treatment, according to a study published in Clinical Rheumatology. Objective: Gabapentin can treat neuropathic pain syndromes and has increasingly been prescribed to treat nociplastic pain. Some patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA) suffer from both nociceptive and nociplastic pain. We examined the cost-effectiveness of adding gabapentin to knee OA care. We used the Osteoarthritis Policy Model, a validated Monte Carlo simulation of knee OA, to examine the value of gabapentin in treating knee OA by comparing three strategies: 1) usual care, gabapentin sparing (UC-GS); 2) targeted gabapentin (TG), which provides gabapentin plus usual care for those who screen positive for nociplastic pain on the modified PainDETECT questionnaire (mPD-Q) and Researchers compared the efficacy of gabapentin in treating knee OA using the Osteoarthritis Policy Model, a validated Monte Carlo simulation of the disease. Evidence-based guidelines recommend the anticonvulsant gabapentin as a first-line analgesic for the treatment of neuropathic pain (pathologic pain that results from abnormal processing of stimuli • Gabapentin and duloxetine are both effective in reducing pain in knee osteoarthritis. • Medical treatment is used for releiving pain in knee osteoarthritis. Efficacy of duloxetine and gabapentin in pain reduction in patients with knee osteoarthritis Neurontin (gabapentin), generally prescribed for the treatment of nerve pain, is sometimes used to relieve severe pain caused by knee osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthritis, also known, as wear-and-tear arthritis, can often become so severe that joint replacement surgery is needed. Gabapentin can treat neuropathic pain syndromes and has increasingly been prescribed for nociplastic pain, which some knee osteoarthritis patients can feel along with nociceptive pain. Some studies have also tried to determine whether gabapentin can have anti-inflammatory effects, but nothing conclusive has been found so far. Is gabapentin good for osteoarthritis because I have been taking 300 mg for years for nerve pain from shingles and my arthritis started hurting really bad so I Gabapentin is not a painkiller, but it works by changing the way your brain perceives pain signals. Gabapentin is bad for arthritis because it does not address the underlying cause of the pain, which is inflammation. In a study involving knee osteoarthritis (OA) patients, gabapentin significantly reduced pain severity and improved functional status over a 12-week period, comparable to duloxetine. Another study on rats with induced arthritis showed that gabapentin increased the paw withdrawal mechanical threshold (PWMT), indicating reduced pain sensitivity . Gabapentin’s Role in Osteoarthritis Treatment. Some studies suggest that gabapentin, in its oral form, may help alleviate OA symptoms. By targeting specific nerve pathways, gabapentin could potentially reduce pain and inflammation in the joints. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Objective: Gabapentin can treat neuropathic pain syndromes and has increasingly been prescribed to treat nociplastic pain. Some patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA) suffer from both nociceptive and nociplastic pain. We examined the cost-effectiveness of adding gabapentin to knee OA care. Interest has grown in gabapentinoids for arthritis, since gabapentin inhibits pain sensitization. 18, 19 Arthritic pain can be improved by NSAIDs and pregabalin in OA. 20, 21 Ohtori et al 20 found that pregabalin combined with meloxicam was more effective for knee OA pain compared to either drug alone and Arendt-Nielsen et al 21 showed that Gabapentin has been studied for its effectiveness in reducing pain associated with knee osteoarthritis (OA). In a clinical trial involving 150 patients with moderate to severe knee OA, gabapentin was compared to duloxetine and acetaminophen.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | /arthritic-feetsies-56570427-resized-56a315a93df78cf7727bba2b.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |