Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
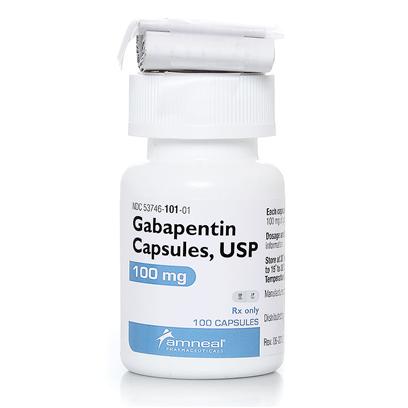
It is especially good for nerve pain, such as burning, shooting or stabbing pain. Gabapentin belongs to the anticonvulsant group of medications, which are also used to treat epilepsy. You are on this medicine to . treat your pain. How does gabapentin work? Gabapentin works by changing the way that nerves send messages to your brain. Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. Substance P plays a role in how you perceive pain. Gabapentin dosage for sciatica nerve pain. Gabapentin dosages for sciatica nerve pain typically start at 300 mg to 900 mg by mouth 3 times a day. This dosage is slowly increased by your prescriber depending on your response to the medication. Common side effects of gabapentin Gabapentin can help relieve nerve pain in some people with postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain after shingles) and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain in the feet in people with diabetes). This makes you actually feel pain. By altering the way nerves work, gabapentin may reduce your pain. Isn’t gabapentin for treating Epilepsy? Yes, gabapentin is used for treating epilepsy by ‘calming down nerves’. Research has shown that gabapentin by a ‘similar process’ is also effective in helping to relieve certain types of pain Gabapentin alleviates pain by modulating nerve signals, providing relief for various chronic pain conditions. Gabapentin, originally developed to treat epilepsy, has gained recognition for its effectiveness in managing various types of pain. But the process is complex and personal. What works for one person's chronic low back pain may not bring relief for another person's osteoarthritis. There are a number of reasons for this. The cause of the chronic pain, a person's biology and history all play a role in pain management. And finding pain therapies that bring you relief can take time. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Titrate dose as needed for pain relief; Maintenance dose: 900 to 1800 mg/day orally in 3 divided doses Maximum dose: 1800 mg per day Extended-release: Gralise (gabapentin) 24-hour extended-release tablets: Initial dose: Day 1: 300 mg orally with the evening meal Day 2: 600 mg orally with the evening meal If these treatments do not provide adequate pain relief, Dr. Insinga says a combination of gabapentin and naproxen or ibuprofen (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and Tylenol can be very effective in No one has time to be in pain. And for those who live with pain every day, relief can’t come soon enough, regardless of when the pain started or how long it has lasted. Chronic pain is pain that lasts and lingers — sometimes defined as pain that persists for more than six months. This is in contrast to acute pain — such as pain from a Gabapentin can provide significant pain relief following spinal disk surgery . Subjects who used a combination of gabapentin and epidural steroid injections reported better pain relief than those who relied on injections and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) ( 24 ). Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Common side effects include dizziness or drowsiness and it may cause a withdrawal syndrome on discontinuation so should not be stopped abruptly. Gabapentin, commonly prescribed for nerve pain, has been explored as an option for arthritis pain relief. Compared to other pain medicines: NSAIDs (e.g., Ibuprofen): Widely used for arthritis pain. They reduce inflammation but can have side effects like stomach issues. Pain relief takes many forms. This Special Health Report, Pain Relief Without Drugs or Surgery, looks beyond the standard approaches of drugs and surgery and explores alternate pain-relief strategies, from acupuncture and mind-body therapies to spinal manipulation, physical and occupational therapies, herbal remedies, mindfulness meditation, and music therapy among others. While potentially useful for treating severe knee OA, there is no strong evidence that gabapentin can provide relief from autoimmune forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Although providers often prescribe gabapentin, high-quality studies show that gabapentin does not work well to treat all types of back pain. Evidence suggests that gabapentin works best for nerve pain caused by diabetes and shingles. Back pain can have a huge effect on your day-to-day life. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat some types of nerve pain but is classified as an anticonvulsant medicine, not as an opioid or painkiller. Gabapentin was first approved in 1993 and is used to treat: postherpetic neuralgia, a nerve pain caused by the shingles virus (herpes zoster), Many people stay on gabapentin for long-term management of their nerve pain and take it daily. Talk to your healthcare provider if you don't have pain relief within a couple of weeks after starting treatment. Some evidence suggests that high-concentration (8%) capsaicin patches (available by prescription) can give at least moderate pain relief to a minority of people with postherpetic neuralgia (a
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |