Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rotatorcufffinal-01-5c05dbf4c9e77c0001105ecf.png) |
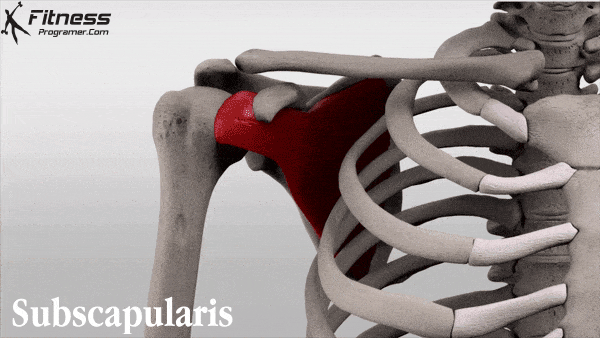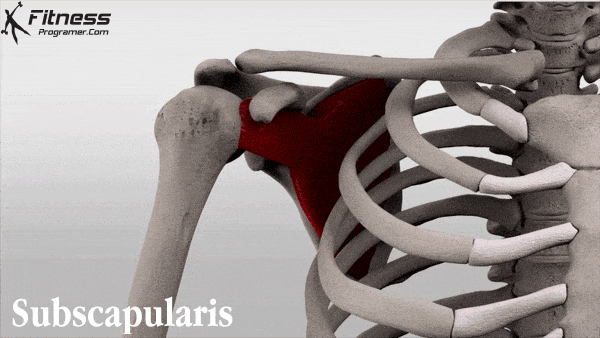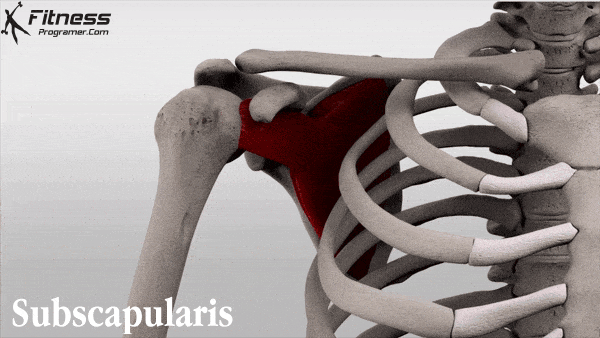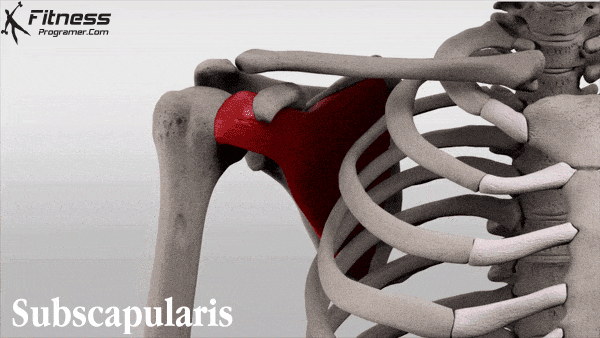
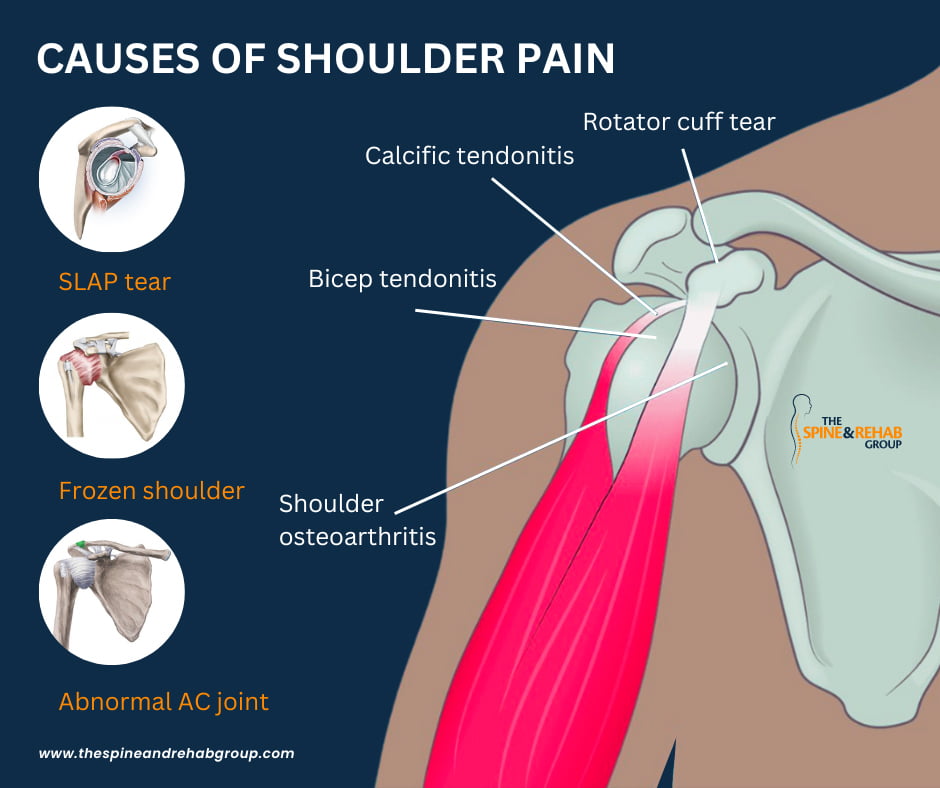
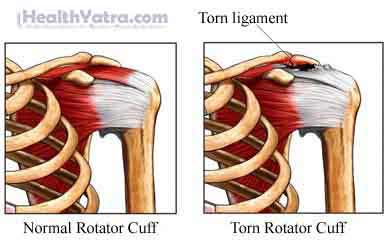
Bang et al found that gabapentin significantly reduced postoperative pain following shoulder rotator cuff repair, with patients in the gabapentin group showing notably lower Visual Analog Scale scores at 2, 6, and 12 hours postoperation compared to the placebo group. 6 Conversely, Mardani et al reported that a single 600 mg dose of gabapentin Rotator Cuff Injury. In the second study, patients undergoing rotator cuff repair were randomly assigned to oxycodone (n=23) or the multimodal nonopioid pain regimen (n=17). gabapentin, and A full-thickness rotator cuff tear is 1 of the most common conditions for shoulder joint surgery, and the incidence increases with age. 12, 13 After arthroscopic rotator cuff repair, severe pain can occur during the early postoperative period. 3 Various methods have been proposed to reduce the postoperative pain after shoulder arthroscopic Administering gabapentin perioperatively at 600 mg daily and divided over a minimum duration of four days postoperatively may significantly reduce postoperative pain intensity and opioid consumption in open shoulder rotator cuff repair surgery patients. Conclusion: Administering gabapentin perioperatively at 600 mg daily and divided over a minimum duration of 4 days postoperatively may significantly reduce postoperative pain intensity and opioid consumption in open shoulder rotator cuff repair surgery patients. Level of evidence: Level I; Randomized Controlled Trial; Treatment Study Rotator cuff injuries and tears are extremely common. According to the Hospital for Special Surgery, around two to four million Americans injure their rotator cuff every year. Athletes, especially baseball pitchers, are notorious for rotator cuff injuries. Despite this, it’s actually the elderly who most often end up with rotator cuff injuries. Major Finding: Arthroscopic rotator cuff surgery significantly improved pain and function in older adults, and a 300-mg dose of gabapentin significantly reduced pain scores immediately after surgery.Data Source: Two studies of outcomes after arthroscopic rotator cuff surgery. Disclosures: Dr. Purpose: The aim of the study was to determine the effect of low-dose gabapentin on postoperative pain management in patients undergoing arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Methods: This randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study included 46 patients. A full-thickness rotator cuff tear is 1 of the most common conditions for shoulder joint surgery, and the incidence increases with age. 12,13 After arthroscopic rotator cuff repair, severe pain can occur during the early postoperative period. 3 Various methods have been proposed to reduce the postoperative pain after shoulder arthroscopic In one prospective, randomized, double-blind study, a single 300-mg dose of gabapentin before arthroscopic rotator cuff surgery significantly reduced pain during the first 24 hours after surgery, compared with a placebo, with no increase in side effects. Are patients being informed about gabapentin risks? Does Gabapentin Have Anti-Inflammatory Activity? Q. I had rotator cuff surgery on my shoulder almost a decade ago. Last year I started having pain in that shoulder again. The doctor said I have a lot of inflammation there and prescribed gabapentin. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used for managing neuropathic pain. Its effectiveness and dosing strategies for postoperative pain, particularly in open shoulder rotator cuff repair, are still debated. This study assesses gabapentin’s impact on postoperative pain intensity in open rotator cuff repair. Your pain is lasting more than 4-6 weeks, despite trying the above recommended treatments. Your pain is caused from a sudden injury or fall, and you are worried that something may be broken or dislocated. If your shoulder is red or significantly bruised. Your pain is severe and not controlled by the above treatments. A single dose of 300 mg of gabapentin reduced the VAS score during the first 24 hours postoperatively in patients undergoing shoulder arthroscopic rotator cuff repair, without significant side effects when compared with placebo. However, the fentanyl consumption did not differ between the gabapentin and placebo groups. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used for managing neuropathic pain. Its effectiveness and dosing strategies for postoperative pain, particularly in open shoulder rotator cuff repair, are still debated. This study assesses gabapentin’s impact on postoperative pain intensity in open rotator cuff repair. This study aimed to explore the relationship between pain outcomes and functional recovery six months after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair (ARCR), with a focus on the role of different Purpose: The aim of the study was to determine the effect of low-dose gabapentin on postoperative pain management in patients undergoing arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Methods: This randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study included 46 patients. The patients were divided into 2 Rotator cuff tear — The rotator cuff tendon(s) may be torn as a result of injury, chronic tendinopathy, or a combination of both. Typically, the injury is caused by a fall, direct blow, or a rapid use of force (pulling on a starter cable, for instance). Gabapentinoids are increasingly used in preoperative premedication despite controversial results. The aim of our study was to evaluate the effects of preemptive use of gabapentin or pregabalin on postoperative shoulder pain and rehabilitation quality after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Shoulder pain may be brought on by rotator cuff swelling, injury, or bone changes. When you raise your arm above your head or move it in front of or behind your back, you might experience pain. When rotator cuff tendons get caught under the shoulder\’s bony area, shoulder pain is most frequently the result. The tendons swell up or sustain damage.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rotatorcufffinal-01-5c05dbf4c9e77c0001105ecf.png) |