Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
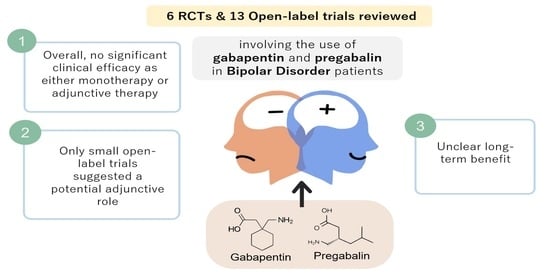 |  |
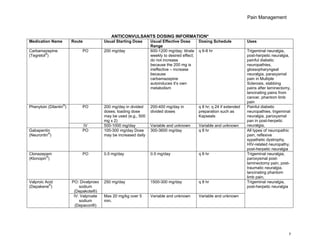
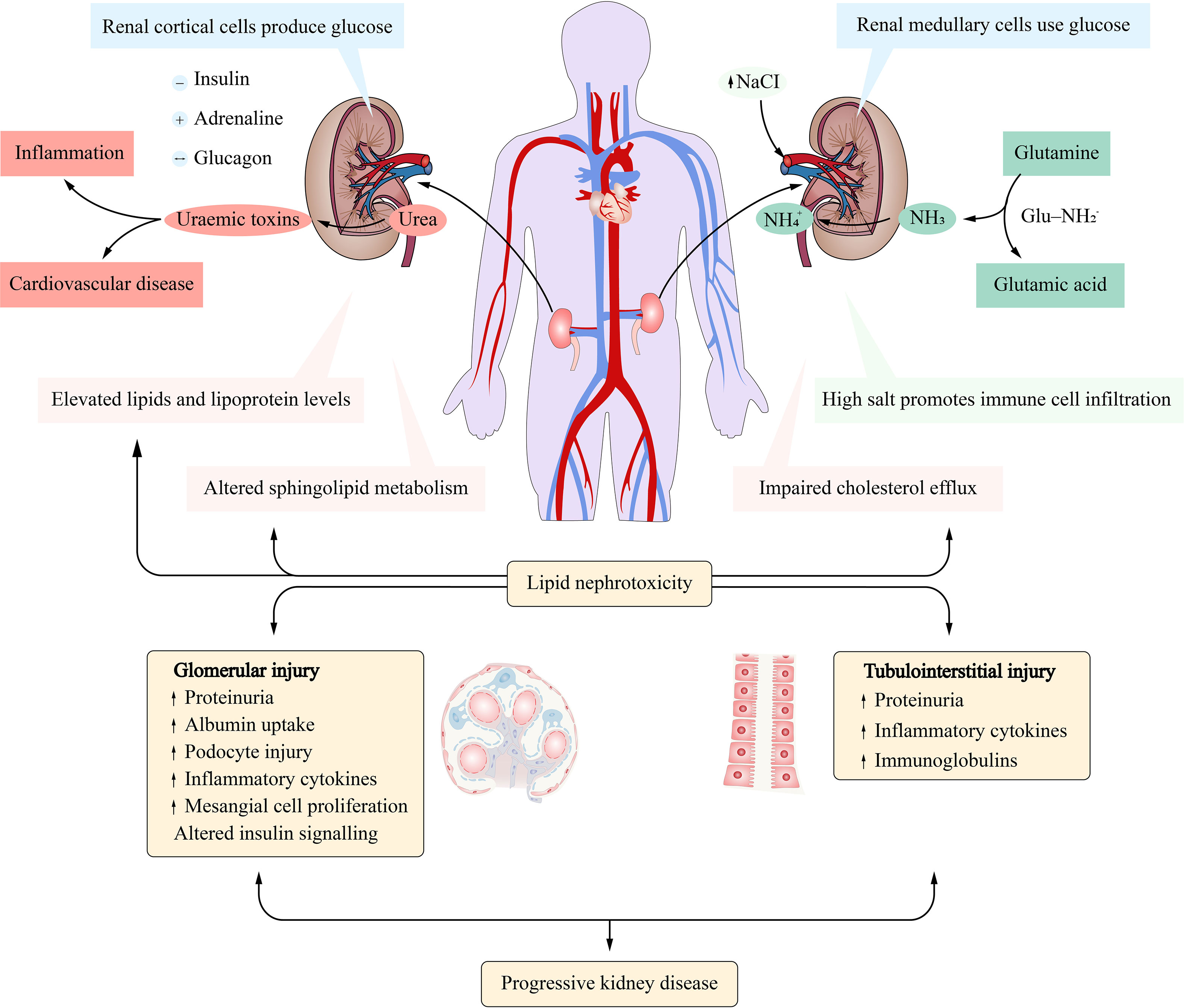
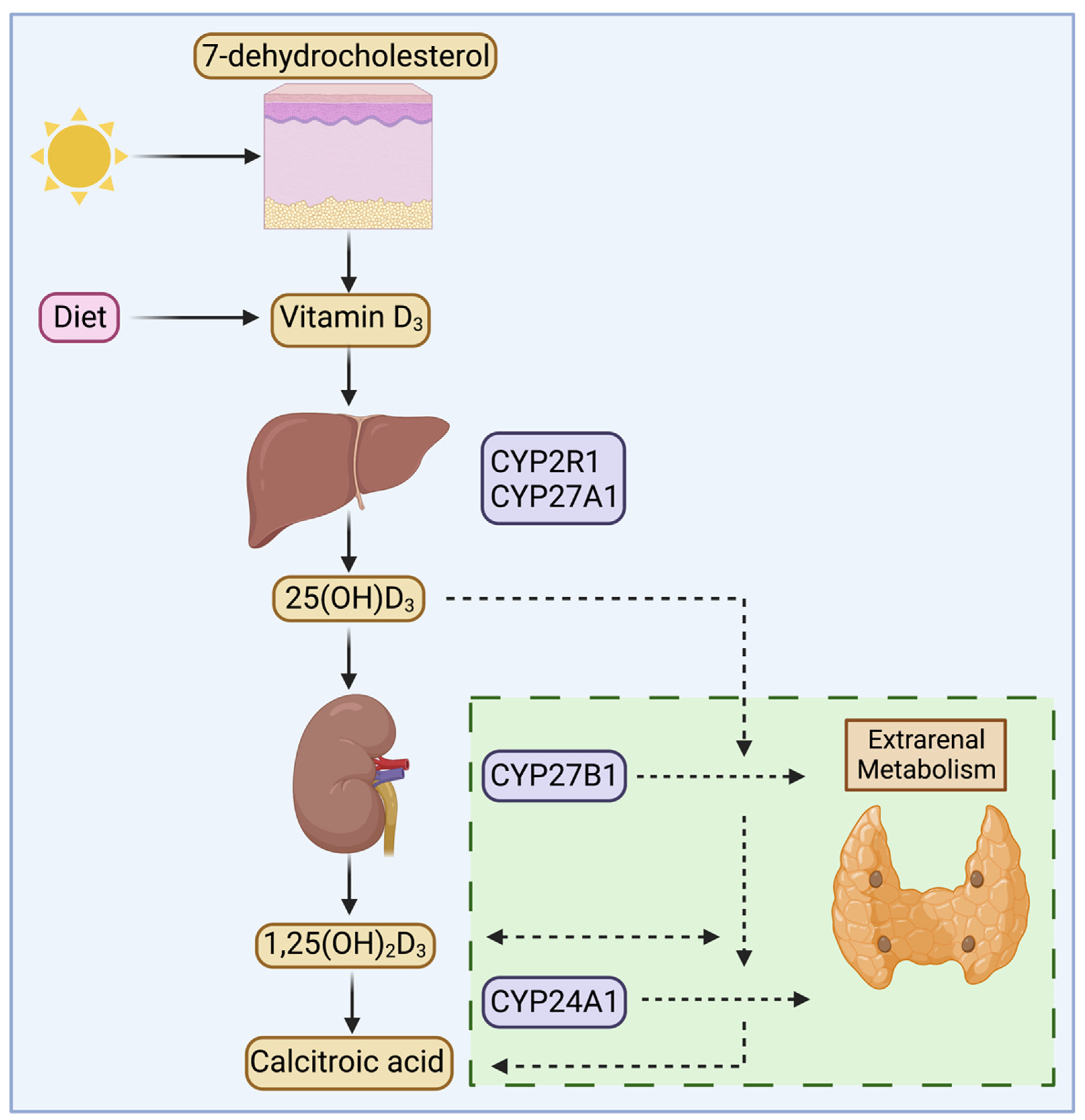
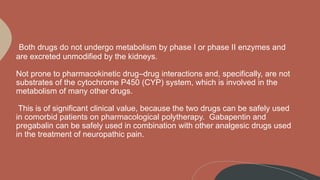
Metabolism and Renal Excretion. Gabapentin is not metabolized in humans and is excreted primarily as unchanged drug in the urine. Renal clearance is linearly related to creatinine clearance in both pediatric and adult populations. Therefore, dosage reductions based on declining renal function are recommended (Table 268-1). CKD alters renal drug elimination by affecting glomerular blood flow, filtration rate, tubular secretion and reabsorption, and renal bioactivation and metabolism. 18 Additionally, pharmacokinetic handling of medications (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination) may be affected. 19 Reducing the dose is recommended for medications Unlike other drugs, gabapentin is not metabolized in the liver and is solely excreted by the kidneys. Therefore, it is crucial to adjust the dosage in patients with renal insufficiency to avoid severe adverse effects. Gabapentin is eliminated in urine unmetabolized at a rate proportional to creatinine clearance. 24 In patients with renal impairment, with unaltered gastrointestinal absorption, gabapentin half-life can be prolonged up to 132 hours (without dialysis), 30 placing patients with chronic kidney disease at an increased risk for toxicity. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Unlike many drugs metabolized by the liver, gabapentin’s primary pathway out of the body is through the kidneys. In healthy individuals, the kidneys efficiently filter gabapentin from the blood, ensuring the medication is removed as waste in urine. Although both gabapentinoids are absorbed in the small intestine, pregabalin is also absorbed in the proximal colon. Absorption of gabapentin is solely dependent on LAT that are easily saturable, resulting in dose-dependent pharmacokinetics. Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. Pretty simple: Neurontin (gabapentin) is not metabolized. It is eliminated by the kidneys. Because the elimination of Neurontin (gabapentin) is entirely renal, patients with renal insufficiency usually need lower dosages and less frequent dosing. The liver is the organ that is responsible for breaking down (metabolizing) most of the substances in a person’s system. However, gabapentin is one of the few drugs that is not metabolized by the liver; instead, it is primarily metabolized by the kidneys. Gabapentin enacarbil is a long acting form of gabapentin that is used for restless leg syndrome and for painful postherpetic neuropathy. Gabapentin enacarbil and gabapentin are associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme elevations during treatment and with rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Gabapentin CL/F and CLR were linearly correlated with creatinine clearance. Total urinary recovery of unchanged drug was comparable in all subjects, indicating that the extent of drug absorption was unaffected by renal function. There was no evidence of gabapentin metabolism even in subjects with severe renal impairment. In summary, impaired As a result, metabolism-related factors do not necessitate dosage alterations of gabapentin and concomitant AEDs after prolonged therapy. The drug is excreted unchanged in urine; plasma clearance is linearly related to creatinine clearance; and dosage is readily adjusted based on renal function. Drug manufacturer Pfizer classifies abnormal liver function tests as an infrequent side effect for gabapentin 5. There is insufficient data to estimate incidence for these or establish whether gabapentin is the sole cause of elevated liver function tests, notes Pfizer. Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver. Gabapentin is a new antiepileptic drug (AED) with an attractive pharmacokinetic profile. It is absorbed by an active and saturable transport system, and has a high volume of distribution. Gabapentin is not bound to plasma proteins, does not induce hepatic enzymes and is not metabolized. At steady st Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant that is used as adjunctive therapy in management of epilepsy and for neuropathic pain syndromes. Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Hi, Gabapentin is exclusively excreted by the Kidneys and undergoes no appreciable metabolism by the Liver. As to whether it is toxic to your Kidneys is probably a question that you should be asking your prescribing doctor. The kidneys, liver, and gastrointestinal tract all play roles in how gabapentin is metabolized and eliminated from the body. Gabapentin is primarily excreted unchanged by the kidneys. Therefore, renal function significantly influences drug levels in the body.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |