Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
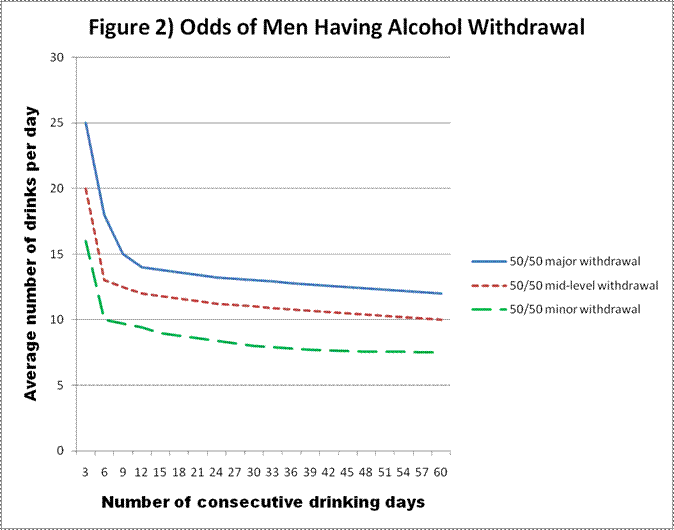
In fact, seizures are among the more extreme reactions people can have to alcohol withdrawal, and can be prevented by taking gabapentin. For alcohol use disorder (AUD), gabapentin is considered “off-label.” An off-label medication is a drug indicated for one purpose, but prescribed for another because a doctor deems it safe and useful. Gabapentin can help with alcohol withdrawal by counteracting the physiological effects of the syndrome. Evidence indicates that symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome stem from reduced treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demon-strated effi cacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line al-ternative to standard therapies, and only after screening How Does Gabapentin Affect Alcohol? It is important to note that gabapentin does not tackle the underlying reasons for alcohol addiction. However, it can help with some alcohol withdrawal symptoms, making detoxification easier to handle. Gabapentin may have benefits in terms of decreased daytime sedation and decreased alcohol craving. 12 However, alcohol withdrawal seizures in patients treated with gabapentin have been reported in several studies. 13,14 Therefore, gabapentin monotherapy should not be used in severe AWS or in those with a history of AWS seizures or who are at Study objective: Gabapentin has been proved to be beneficial in promoting abstinence, decreasing alcohol cravings, and improving mood and sleep quality when given at higher doses; however, data are limited regarding the efficacy and safety of using high-dose gabapentin as part of the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). The aim of How Much Gabapentin is Taken for Alcohol Withdrawal? Typically, Gabapentin is prescribed for alcohol withdrawal in doses ranging from 300 to 800 mg, three times daily, with adjustments made based on symptom severity and patient response. Gabapentin is already widely prescribed to treat pain conditions and epilepsy. “Gabapentin adds to the list of existing medications that have shown promise in treating alcohol dependence,” said Kenneth R. Warren, Ph.D., acting director of the NIAAA. Study Objective. Gabapentin has been proved to be beneficial in promoting abstinence, decreasing alcohol cravings, and improving mood and sleep quality when given at higher doses; however, data are limited regarding the efficacy and safety of using high-dose gabapentin as part of the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Gabapentin has been found to help with alcohol withdrawal symptoms, including easing alcohol cravings, as well as reducing alcohol consumption and maintaining abstinence after withdrawal. 4,5,6 Using gabapentin for withdrawal constitutes one example of off-label use of the drug. 4. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Another compared valproate (300 mg given 3 to 4 times daily) versus carbamazepine (200 mg 3 times daily) and reported longer hospital length of stay and greater requirement for ICU admission with carbamazepine.55 Limited data suggest a potential benefit for gabapentin (particularly for tapering), although this is primarily based on Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Benzodiazepines are considered the drugs of choice for treating alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin has been studied as a potential treatment for acute alcohol withdrawal, based on its modulatory action on brain excitatory (i.e., glutamergic) and inhibitory (i.e., GABAergic) pathways. Remember, your health and safety are paramount. Avoid mixing gabapentin with alcohol to minimize the risks and maximize the benefits of this medication. Gabapentin Withdrawal. Abruptly stopping neurontin after long-term use can lead to withdrawal symptoms, which can range from mild to severe. While gabapentin is not yet an FDA-approved treatment for alcoholism, a number of studies support the its use withdrawal and cravings: In a 12-day study detoxifying with either gabapentin or lorazepam (a benzodiazepine prescribed with the brand name Ativan), the former was less likely to drink – and had less craving, anxiety, and sedation. Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: Help stop the impulse Gabapentin is available in various forms, including oral capsules, tablets, and oral solutions. It is commonly prescribed for conditions such as epilepsy, postherpetic neuralgia, and restless leg syndrome. Indications. Gabapentin is commonly prescribed for the treatment of various conditions. A study published this week concluded that gabapentin can relieve alcohol withdrawal symptoms but is most effective for people with a history of more severe symptoms after a few days of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |