Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
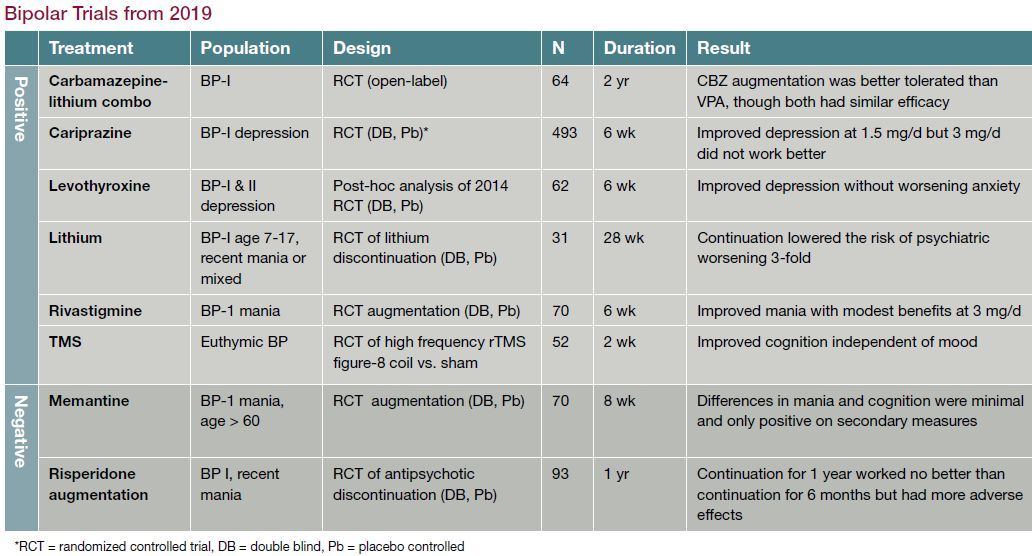
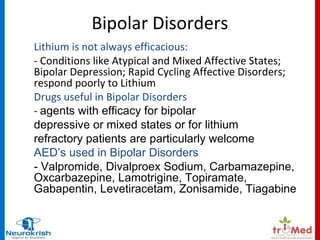
"I have bipolar disorder, chronic depression, and anxiety, and gabapentin has helped tremendously without the use of other narcotic medicines. Yeah, it makes you feel a little loopy for the first few weeks, but after that, it does a wonderful job calming the nerves. Lithium and gabapentin. Gabapentin is currently being studied as a treatment for bipolar disorder, and there have been favorable reports regarding its potential as a mood stabilizer (82, 83). The advantages of gabapentin include the lack of interactions with other drugs in the cytochrome P450 system and the lack of protein binding . Since there The gabapentinoids, gabapentin, and pregabalin, target the α2δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. Initially licensed for pain and seizures, they have become widely prescribed drugs. Many of these uses are off-label for psychiatric Despite of the lack of evidence, reviews of gabapentin prescribing patterns in the United States show that this medication is still being used with alarming frequency for bipolar disorder. There are now five medications with specific, FDA approval for acute bipolar depression. Neurontin - also known as Gabapentin - is a drug that is sometimes prescribed to those who experience anxiety especially in situations where the anxiety is co-occurring with bipolar disorder. Gabapentin use in elderly patients. Gabapentin can be used in elderly patients, but caution should be exercised due to age-related changes in renal function. A lower starting dose may be necessary to prevent overdose and accumulation of the drug in the body. Monitoring of kidney function is recommended. Gabapentin use in pediatric patients Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. These results should be confirmed in randomized clinical trials. Gabapentin was significantly more effective than lamotrigine and carbamazepine in reducing depressive symptoms on the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory-2 (MMPI-2) depression The most common diagnoses in this study were depressive disorders, followed by anxiety disorders and bipolar disorders, which supports case reports suggesting an increase in gabapentin use for these disorders despite limited high-quality evidence. Gabapentin isn’t usually used to treat anxiety alone. More often, it’s given to ease anxiety symptoms for someone who also has depression or bipolar disorder. (Anxiety is commonly Abstract. Despite its prevalence and disease burden, several chasms still exist with regard to the pharmacotherapy of bipolar disorder (BD). Polypharmacy is commonly encountered as a significant proportion of patients remain symptomatic, and the management of the depressive phase of the illness is a particular challenge. Gabapentin appears to have acute anti-manic and anti-depressant properties as an adjunctive agent for refractory bipolar illness. Prospective double-blind studies are needed to further delineate its acute efficacy when used as monotherapy and its prophylactic efficacy as monotherapy or in conjuction Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal. Gabapentin has less likely benefit adjunctively for bipolar disorder. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. mum dose used was 1699 ± 1237 mg/day (range, 100– 6000). As shown in Figure 1, the overall response rate in the total sample based on moderate to marked response on the CGI-I (score≥2) was 30% (15/50). Response in the other parts of the bipolar spectrum (bipolar disorder, type II, and bipolar disorder, NOS; 11/27, 41%) was over A psychiatrist answers common questions about mood stabilizers for bipolar depression. Other medications, like topiramate (Topamax) or gabapentin (Neurontin), may be prescribed in some cases RESULTS. Bipolar Disorder. The randomized controlled trials 19 –21 investigating gabapentin for treating bipolar disorder indicate it is likely to be ineffective. Data interpretation is difficult: dosing varies by trial, gabapentin is used as both monotherapy and adjunctive therapy, patients have heterogeneous diagnoses, and primary outcomes differ between studies. practice, particularly for bipolar mania and particularly in combination with lithium and divalproex.3 Now the newer atypical antipsychotics are emerging, and not just for acute ma-nia, but also for depression associated with bipolar I, bipolar II, and treat-ment-resistant depression.3 Thus, the new FDA approvals for bipolar mania Researchers found that gabapentin does not help people with bipolar disorder. Learn more about the history of why some doctors prescribe gabapentin for bipolar as an adjunct therapy, even though there’s no evidence that it works for bipolar treatment or maintenance.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |