Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 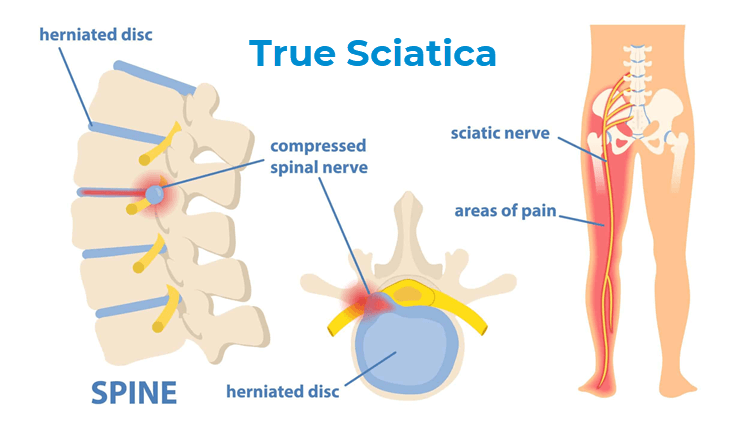 |
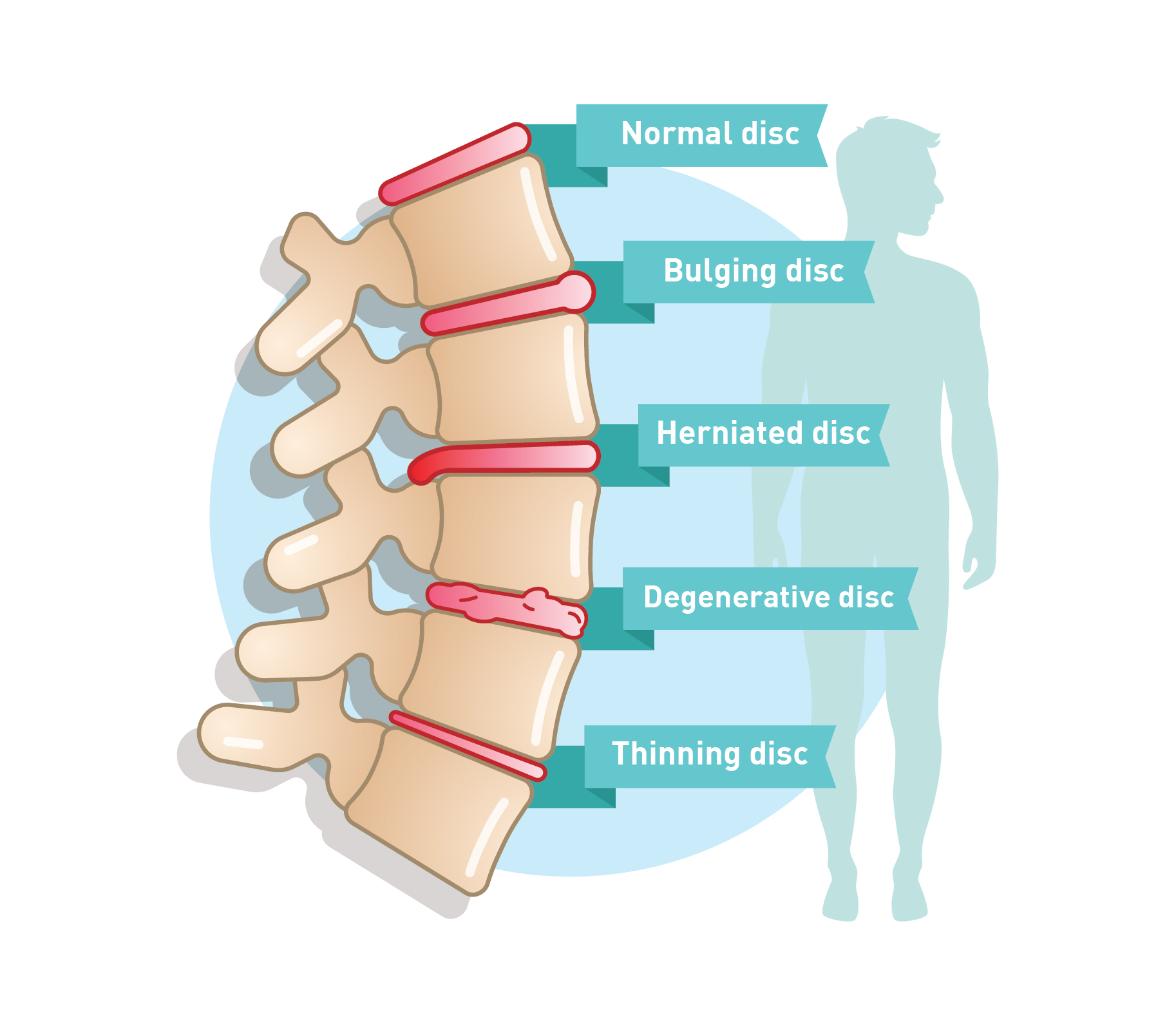
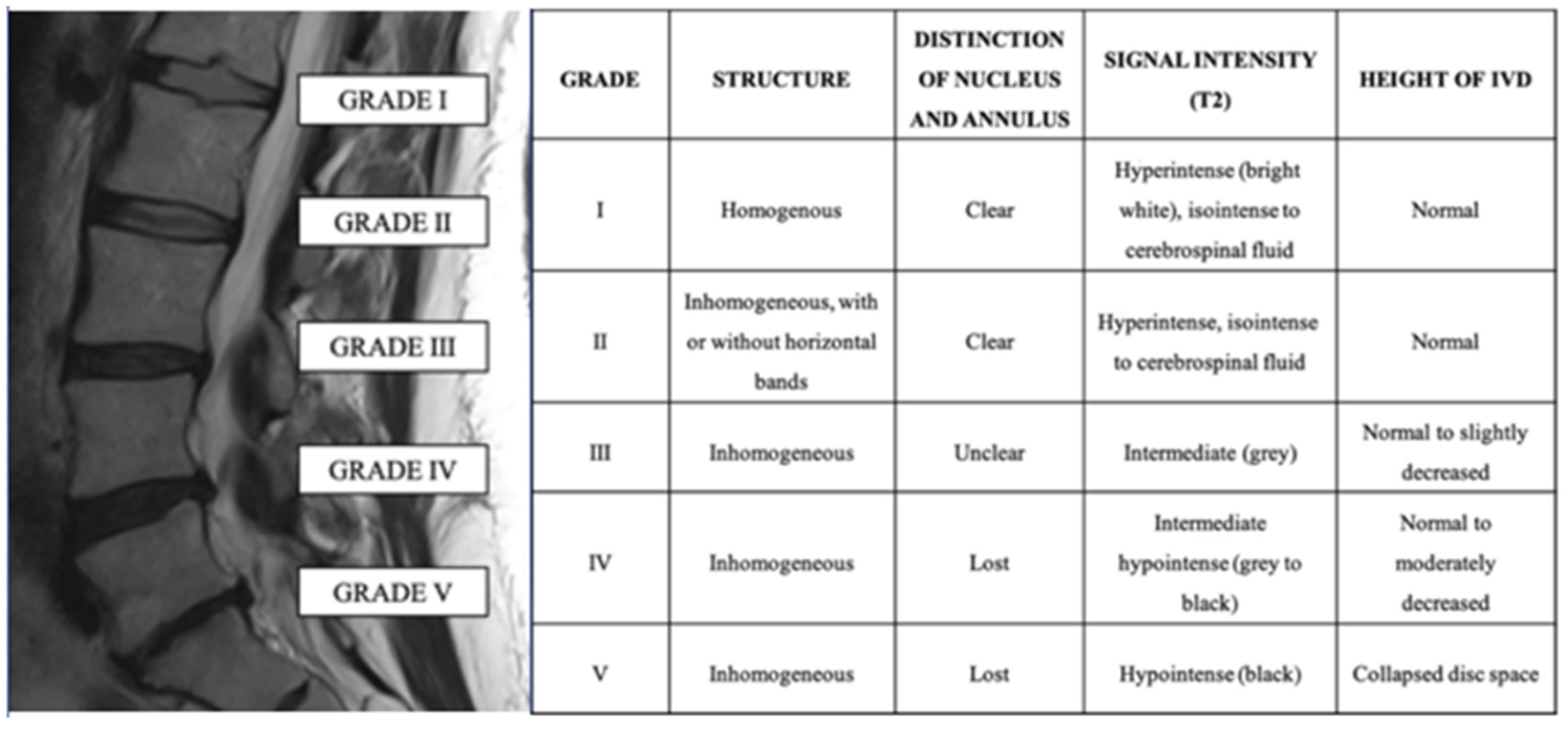
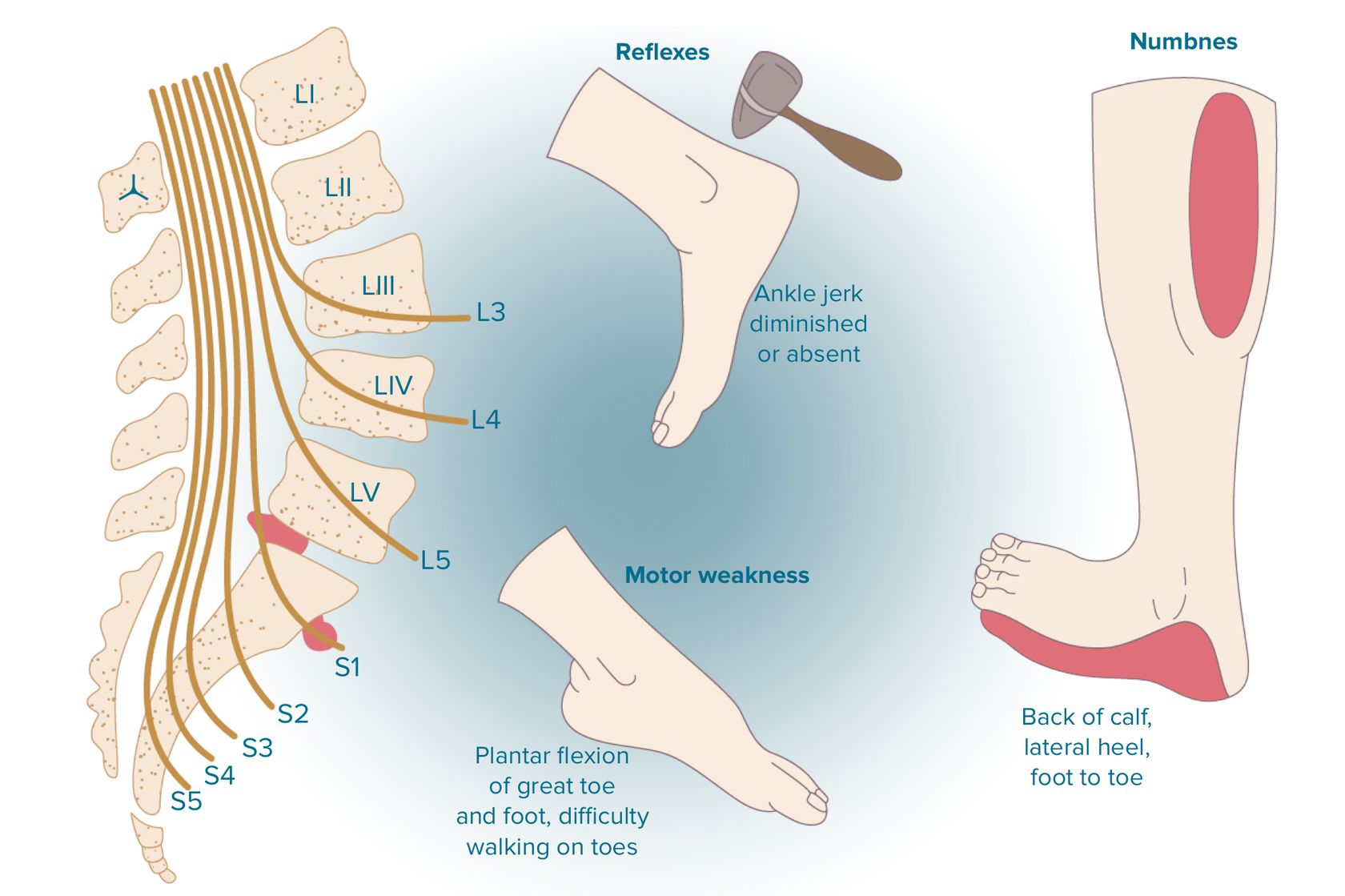
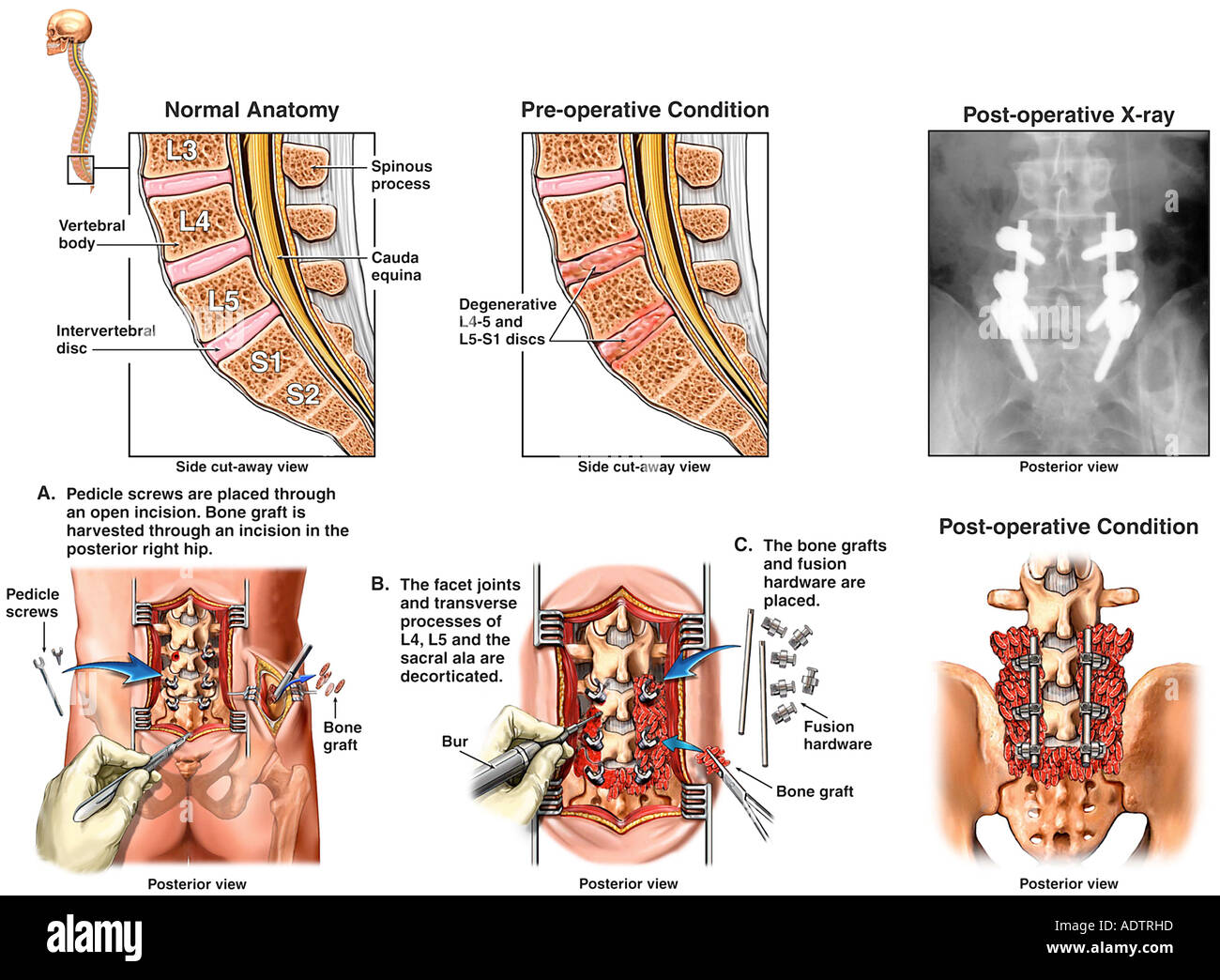
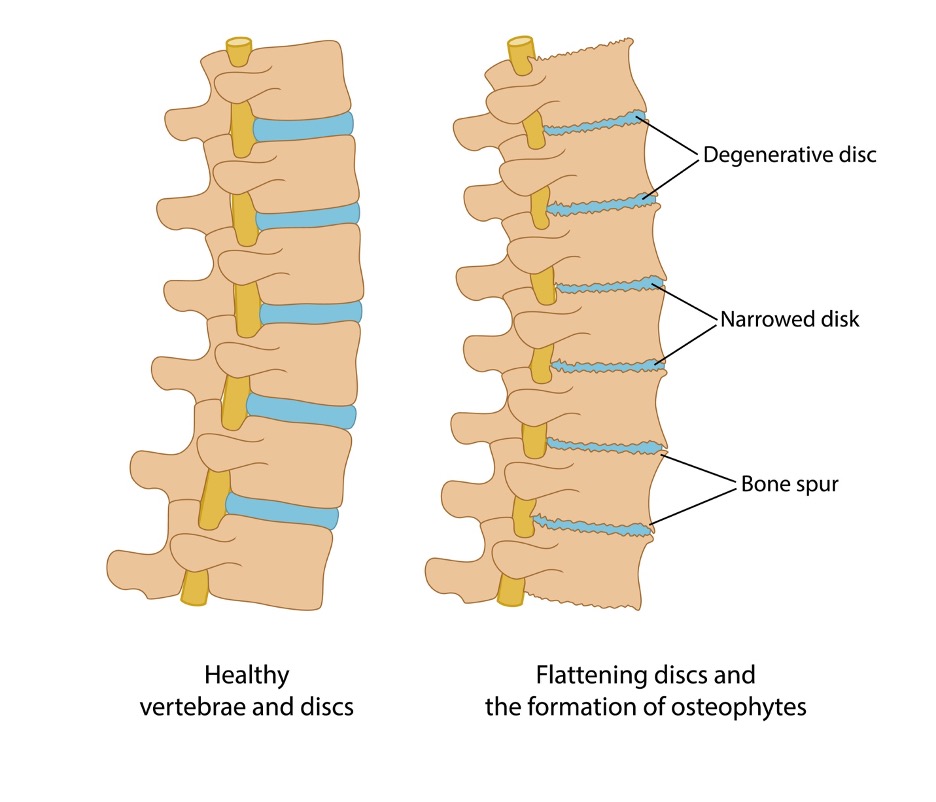
The most common spine surgery for degenerative disc disease is a discectomy—complete removal of the disc along with spinal fusion—or a disc replacement. Alternative treatments The bad news is that many people do not find adequate symptom relief from conservative medical treatments. Gabapentin, FDA-approved for seizures and nerve pain after shingles, is often used off-label for nerve pain from degenerative disc disease. It may affect calcium channels in the nervous system. Dosage varies based on individual factors and kidney function. Gabapentin is prescribed for analgesia in chronic low back pain, yet there are no controlled trials supporting this practice. This randomized, two-arm, 12-week, parallel group study compared gabapentin (forced titration up to 3600 mg daily) to inert placebo. Gabapentin is most effective in relieving neuropathic pain conditions caused by disk herniation, spinal stenosis, diabetic neuropathy, and postherpetic neuralgia. It provides limited sciatica and fibromyalgia relief, and is ineffective for reducing arthritis-related chronic low back pain. Clinically this is seen as a progressive or booster response. These injections can also be used to help in more clearly diagnosing the cause of the pain when there are several levels of degenerative disc disease. Surgery: Many different types of surgical procedures are offered for the treatment of degenerative disc disease. In conclusion, the present review showed that there is still no quality information to support the use of pregabalin or gabapentin for the treatment of nociceptive/mechanopostural CLBP without radiculopathy or neuropathy, although the results suggest that the gabapentin may be a viable option. Ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil) and naproxen (Aleve) are staples in the treatment of cervical disc disease because they reduce both pain and inflammation. Like acetaminophen, many NSAIDs are available Research suggests that combining gabapentin with epidural steroid injections yields enhanced pain relief, particularly following spinal disc surgery. This combination has shown effective results compared to relying solely on injections and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). An expert research librarian used terms related to neuropathic pain and spinal disorders, disc herniation, stenosis, and spinal cord injury to search in MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane CENTRAL for primary research from January 2000 to October 2015. What is degenerative disc disease? Degenerative disc disease isn't really a disease. It's a term used to describe the normal changes in your spinal discs as you age. Spinal discs are small, spongy discs that separate the bones (vertebrae) that make up the spine. The discs act as shock absorbers for the spine. They let your spine flex, bend, and Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is the deterioration of the discs in the spine. These medications, such as gabapentin (Neurontin) block specific nerve pain Examples of anticonvulsants that are used to treat chronic pain include: Gabapentin (Neurontin) Pregabalin (Lyrica) Carbamazepine (Tegretol) Lamotrigine (Lamictal) Topiramate (Topamax) Anticonvulsants are commonly used to manage chronic back pain caused by conditions such as radiculopathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and spinal cord injury. They This is called degenerative disc disease or discogenic pain. It’s more likely to occur in the neck (cervical spine) and low back (lumbar spine) than the mid back. Treatment options are available, and research is underway on many others. Here, we’ll cover degenerative disc disease, its symptoms, and how to find the right treatment for you. The most commonly prescribed pain medicines for degenerative disc disease include the following: Oral steroids are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that may be an effective treatment for low back pain from degenerative disc disease. Neurontin (gabapentin) is an example. In the most extreme cases, and only under careful supervision, your doctor may prescribe an opioid. Vicodin is an example of an opioid, also called a The efficacy of gabapentin monotherapy was investigated against both acute or chronic radicular pain caused by lumbar disk hernia (LDH) or lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). Seventy-eight patients with radicular pain, 10 males and 68 females aged 23 to 76 years (mean 49.4 years), caused by LSS in 45 pati Recently, many prescribers have reached for gabapentin to treat back pain and a range of off-label uses. Gabapentin was originally developed as an anti-seizure medication. But healthcare professionals don’t just prescribe it for back pain. It’s also used for nerve pain, postsurgical pain, and occasionally anxiety. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Paired t test was used to examine scores of the cases before and after gabapentin treatment. Results were considered significant at P < 0.05, and 95% confidence interval was calculated. Results: Mean visual analog scale score was 9.3 in the pretreatment period, and reduced to 5, 2.6, and 1.3 on posttreatment days 1, 7, and 30, respectively (P Clinically this is seen as a progressive or booster response. These injections can also be used to help in more clearly diagnosing the cause of the pain when there are several levels of degenerative disc disease. Surgery: Many different types of surgical procedures are offered for the treatment of degenerative disc disease.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |