Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
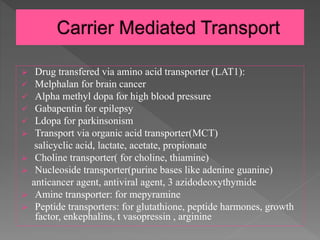
Ligands of auxiliary α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) decrease elevated L-type VDCCs surface expression in arterial myocytes and arterial constriction in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). However, their effect on blood pressure (BP) is unclear. In this study, we investigated the hemodynamic response to acute and chronic administration of gabapentin, a ligand of Gabapentin is also used off-label to treat conditions such as anxiety and nerve pain from diabetes. It may also be used to treat alcohol use disorder. Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects too. Knowing about gabapentin side effects in advance can help you manage them if they happen to you. The phase IV clinical study analyzes which people have High blood pressure when taking Gabapentin, including time on the drug, (if applicable) gender, age, co-used drugs and more. It is created by eHealthMe based on reports of 313,421 people who have side effects when taking Gabapentin from the FDA, and is updated regularly. Can gabapentin cause high blood pressure? Yes, abruptly stopping gabapentin can lead to rebound hypertension , a withdrawal symptom. Additionally, while not a direct cause, the cardiovascular risks associated with long-term use can indirectly affect blood pressure. What is gabapentin and what is it used for? Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles , and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. Research on rats has shown that gabapentin may lower blood pressure in those with high blood pressure (hypertension). Research suggests that gabapentin can lower blood pressure by reducing the body’s production of certain hormones that can increase blood pressure. It may also help to relax blood vessels, making it easier for blood to flow through them. For medications that do not improve longevity, do not lower blood pressure (BP) and that are used long-term, such as androgens, corticosteroids (when used to treat non-life-threatening conditions), mineralocorticoids, pramipexole and ropinirole, patients and clinicians need to know if there is an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. 1. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH): Gabapentin is primarily prescribed for treating PAH, a condition where high blood pressure in the lungs makes it difficult for the heart to pump blood efficiently. 2. Secondary Raynaud’s Phenomenon (Off-label Use): In some cases, Gabapentin is used to reduce the frequency and severity of Raynaud's Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. This study aims to But that doesn’t mean one can suffer high blood pressure when taking gabapentin. Here’s what happens. When an individual withdraws abruptly from gabapentin and uses the drug for nerve pain regulation, there’s a chance the pain could return. Severe pain alone can drive up one’s blood pressure. Brand names of gabapentin include Horizant®, Gralise® and Neurontin®. What is gabapentin approved for? Gabapentin is used to: Prevent and control partial seizures. Gabapentin can be used in adults and children age 3 and older who have partial seizures. Relieve nerve pain following shingles in adults. losartan, a medication used to treat high blood pressure ; ethacrynic acid (Edecrin), The use of gabapentin, even when used correctly, may cause some side effects. Usually, the side effects The risk of stomach bleeding tends to be lower if you take a COX-2 inhibitor, but bleeding can still occur. This is true especially at higher doses. And COX-2 inhibitors can lead to headaches, dizziness, high blood pressure, kidney problems, fluid retention and high blood pressure. These medications may increase the risk of a heart attack or Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous system. While gabapentin is not a controlled substance or considered a drug with a high potential for abuse, there have been reports of people abusing it to experience a more intense high from opioids such as methadone. 2. Side Effects of Gabapentin. The use of any medication, including gabapentin, can create a number of various side effects. 1. Can I take gabapentin with high blood pressure medication? Studies have shown that gabapentin can actually be effective in attenuating the hypertensive response to laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation, which suggests it can be used with treated hypertensive patients, but it’s important to discuss your medication regimen with your doctor. 2. Yes, it can cause High Blood Pressure (hypertension) Cardiovascular side effects including hypertension have been reported to occur in more than one percent of patients taking gabapentin. Read more at: I suggest you contact your Dr. asap. Thanks! I will do that tomorrow! Brenda. Not everyone who takes gabapentin will experience changes in blood pressure. However, certain factors may increase your risk, including: * Age: Older adults may be more susceptible to blood pressure changes. * Existing blood pressure issues: If you already have high or low blood pressure, gabapentin may exacerbate these issues.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |