Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |
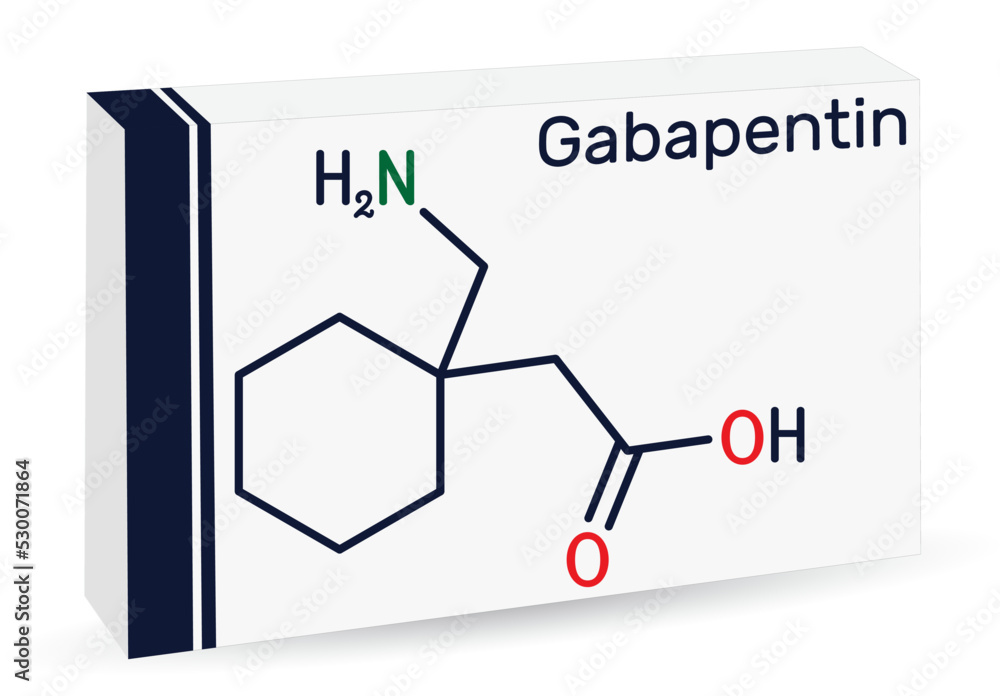
Gabapentin use in pediatric patients with epilepsy 3 to 12 years of age is associated with the occurrence of CNS related adverse reactions. insomnia, nausea, pain USES: Gabapentin is used with other medications to prevent and control seizures. It is also used to relieve nerve pain following shingles (a painful rash due to herpes zoster infection) in adults. Gabapentin is available as Gralise, Neurontin, and generic gabapentin in the following dosage forms that are taken by mouth. 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg oral capsules 250 mg/5 mL oral solution Gabapentin has been associated with a discontinuation syndrome when abruptly stopped. Symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain, and sweating. It should be tapered off slowly under a doctor's advice. The dosage of gabapentin needs to be reduced for kidney disease. Rarely do hypersensitivity reactions occur. Gabapentin is fairly safe when you use it correctly. It does come with some possible side effects, though. People who misuse this drug are also at risk of additional side effects. Gabapentin is For healthcare professionals. Applies to gabapentin: compounding powder, oral capsule, oral solution, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release. General adverse events. The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of this drug were dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Permanent side effects are rare, but they can occur, particularly with long term use of gabapentin, or in cases of misuse. These lasting effects may include: Cognitive impairment: Prolonged gabapentin use has been linked to memory loss and concentration issues. Some people may find it difficult to focus or retain information, and these problems Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin’s main clinical use is in the treatment of neuropathic pain where its binding to neuronal alpha-2/delta subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs) is critical to its mechanism of action. Over the past 10 years, there have been several reports of gabapentin also having anti-nausea and anti-emetic effects in conditions including postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV Gabapentin's main clinical use is in the treatment of neuropathic pain where its binding to neuronal alpha-2/delta subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs) is critical to its mechanism of action. Over the past 10 years, there have been several reports of gabapentin also having anti-nausea and anti-emetic effects in conditions including postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV Out of 33 clinical trials reviewed, 12 assessed nausea and/or vomiting (N/V) associated with gabapentin therapy as primary outcome measures. These 12 studies provided a Grade A recommendation for gabapentin use in treating PONV, a Grade B recommendation for use in treating CINV, and a Grade C recommendation for use in treating HG. Gabapentin side effects are usually mild, and they may be less common with gabapentin ER forms. Examples of mild side effects that can happen include: Vertigo (dizziness) Feeling fatigued or sleepy. Fluid retention. Trouble balancing or controlling movement. Diarrhea or constipation. Nausea and vomiting. Brain fog. Headache. Weight gain. Dry mouth Chronic unexplained nausea and vomiting (CUNV) refers to a symptom complex defined by nausea and/or vomiting with normal diagnostic testing, including anatomic assessments (including upper endoscopy) and measures of upper gut function (e.g. gastric emptying testing). The main symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal are nausea, anxiety, headaches, and seizures. According to the study titled “Gabapentin Withdrawal Syndrome” by Tran et al., published in Pharmacotherapy in 2005, gabapentin withdrawal occurs in patients who abruptly discontinue the medication, particularly after long-term use or high doses When you stop taking gabapentin, you'll need to reduce your dose gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor. Talk to your doctor if you're concerned about becoming physically dependent on gabapentin. Other side effects. These are not all the side effects of gabapentin. Gabapentin is also sometimes used to relieve the pain of diabetic neuropathy (numbness or tingling due to nerve damage in people who have diabetes), and to treat and prevent hot flashes (sudden strong feelings of heat and sweating) in women who are being treated for breast cancer or who have experienced menopause (''change of life'', the end of monthly menstrual periods). What is gabapentin and what is it used for? Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles , and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Given the effects of gabapentin on the reduction of nausea and vomiting following anesthesia and surgery, it can be used as an alternative therapy in order to control CINV. Owing to the increasing lifespan, prevalence of cancer and chemotherapy, CINV has become an issue of importance for health and treatment.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |