Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
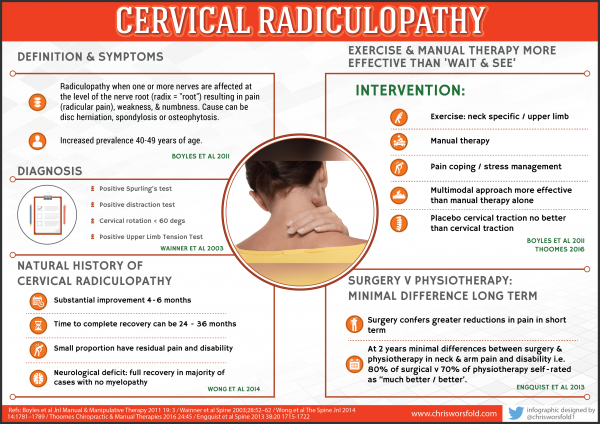
What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin has active ingredients of gabapentin. It is often used in neuralgia. eHealthMe is studying from 322,815 Gabapentin users for the drug's side effects, drug interactions, effectiveness and more. Check Gabapentin in the real world. What is Cervical radiculopathy? Studies of the use of carbamazepine in other peripheral neuropathic conditions have produced variable results. Although gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related to GABA, they do not bind to GABA A or GABA B receptors. Instead, gabapentin and pregabalin are calcium channel blockers with α 2 /δ 1 subunits. The most significant One common cause of neck pain is nerve pain, which can occur due to various reasons such as herniated discs, pinched nerves, or cervical radiculopathy. While gabapentin is commonly used to treat nerve pain, there are alternative treatment options available that can provide relief and improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from Gabapentin and epidural steroid injections used to treat lumbosacral radicular pain both resulted in modest improvements in pain and function, which persisted through three months. Although some differences favored epidural steroid injections, these tended to be small and transient. Methods: Thirty-five patients with radicular pain and diagnosed as L4, L5 or S1 radiculopathy were treated with oral gabapentin from a total of 300 mg per day once up to a total of 1800 mg per day divided in 3 doses for eight-week trial period. Is gabapentin (Neurontin) effective for the treatment of radicular low back pain? Evidence-Based Answer Gabapentin is not effective for the treatment of radicular low back With regards to use in radiculopathy, in one placebo controlled study of 50 patients with lumbosacral radiculopathy found that when compared to placebo, those who received Gabapentin had improved motor and sensory function, lumbar flexion range of motion, and pain . Anticonvulsant medicines with similar modes of action were grouped together; e.g., gabapentin and pregabalin. 23 Where appropriate, data were pooled and treatment effects were quantified using mean differences (MDs; if the same scale was used) or standardized mean differences (SMDs; if different scales were used) for continuous outcomes (pain The efficacy of gabapentin monotherapy was investigated against both acute or chronic radicular pain caused by lumbar disk hernia (LDH) or lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). Objective To evaluate whether an epidural steroid injection or gabapentin is a better treatment for lumbosacral radiculopathy. Design A multicenter randomized study conducted between 2011 and 2014. Computer generated randomization was stratified by site. Patients and evaluating physicians were blinded to treatment outcomes. Settings Eight military, Veterans Administration, and civilian In conclusion, the present review showed that there is still no quality information to support the use of pregabalin or gabapentin for the treatment of nociceptive/mechanopostural CLBP without radiculopathy or neuropathy, although the results suggest that the gabapentin may be a viable option. But it’s also commonly used off-label to treat other types of nerve pain, including back pain. Although healthcare professionals often prescribe gabapentin, high-quality studies show that gabapentin doesn’t work well to treat all types of back pain. Evidence suggests that gabapentin works best for nerve pain caused by diabetes and shingles. This meta-analysis was conducted on patients with lumbar radiculopathy. Gabapentin was used as an intervention, and pregabalin as a comparison. As outcomes, pain rating scales including visual analog scale (VAS) and numeric pain rating scale (NRS), and number of adverse events (dizziness and sedation) were obtained. The most common medication class recommended by the CPGs for lumbar radiculopathy was antidepressants. No CPGs recommended prescribing acetaminophen, benzodiazepines, muscle relaxants, or antibiotics. There was very little agreement between the CPGs, and all the medication classes had at least one CPG recommended against its use. Yildirim, K, Deniz, O, Gureser, G, et al. Gabapentin monotherapy in patients with chronic radiculopathy: the efficacy and impact on life quality. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 2009;22:17-20 Crossref Background: Gabapentinoids are commonly prescribed to control neuropathic pain of lumbar radiculopathy. Few trials have compared the efficacy of gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB). Therefore, the authors conducted a meta-analysis to compare the difference in effect between GBP and PGB in lumbar radiculopathy patients. This review finds good evidence that these drugs are not an effective treatment for low back pain with or without radiculopathy, and are associated with an increased risk of There is moderate- to high-quality evidence that anticonvulsants are ineffective for treatment of low back pain or lumbar radicular pain. There is high-quality evidence that gabapentinoids have a higher risk for adverse events. PROSPERO-CRD42016046363. Medications that include gabapentin and pregabalin are frequently used to relieve radiculopathy related pain symptoms. These medications work differently than anti-inflammatory medications. (They are also used, though less frequently, for patients suffering seizure disorders.) Gabapentin could be an option in the conservative management of acute or chronic radicular pain. The efficacy of gabapentin monotherapy was investigated against both acute or chronic radicular pain caused by lumbar disk hernia (LDH) or lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |