Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
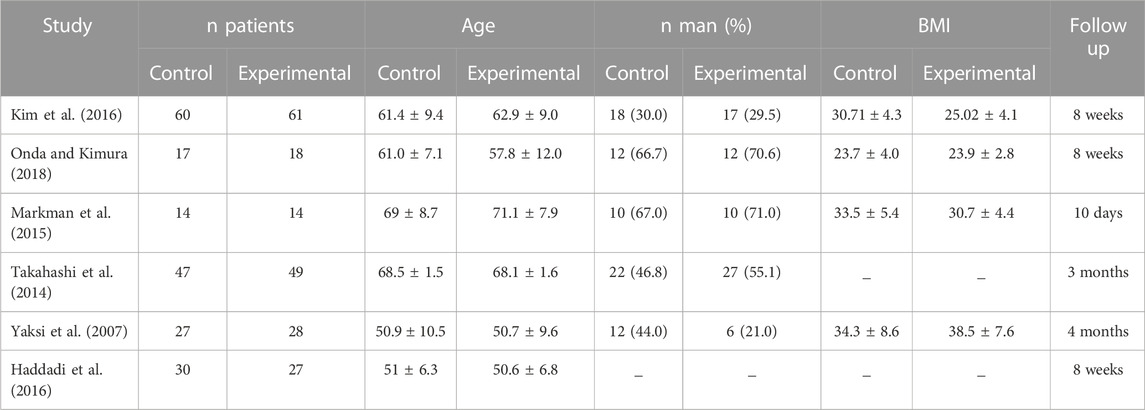
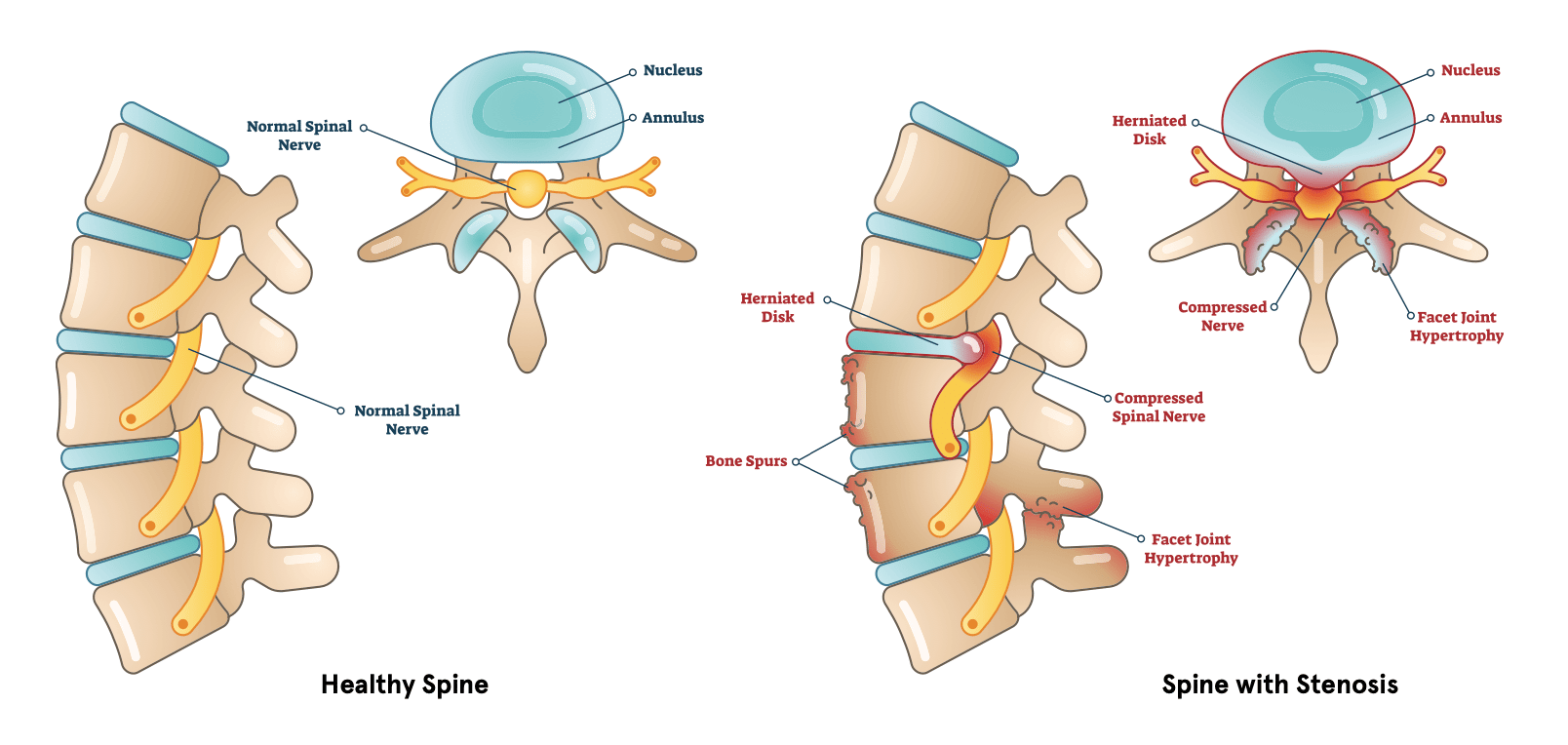
The inclusion criteria were studies that compared pregabalin or gabapentin to a control group in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. We included randomized clinical trialsand a comparative About 5% to 10% of people with low back pain have sciatica, 2 in which the leg pain follows the sciatic nerve and can be accompanied by strength, sensory and reflex changes in the leg. 3 A smaller proportion of people have neurogenic claudication, in which the leg pain is associated with spinal stenosis and symptoms are exacerbated with differ in patients with spinal stenosis (2). Patients with congenital spinal stenosis usually suffer from pain early in life (3). Many people may have spinal stenosis with-out being aware of the condition (2). Many patients undergo back surgery because of spinal stenosis and the cost of these procedures exceeds one billion dollars per year (1,6-8). Objectives: To investigate the efficacy of treatment with gabapentin on the clinical symptoms and findings in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). Summary of background data: LSS is a syndrome resulting from the narrowing of the lumbar nerve root canal, spinal canal, and intervertebral foramen, causing compression of the spinal cord. Gabapentin helps manage pain from spinal stenosis by reducing the excitability of nerve cells. By dampening these pain signals, patients often experience less burning, shooting, or stabbing sensations. Certain medications are safer and more effective than others for treating spine pain in older adults, according to a recent study. Among these are the over-the-counter drugs acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil) and some nerve pain drugs, muscle relaxants, and antidepressants. Keywords: Lumbar Spinal Stenosis, Nonsurgical Treatment, Epidural Steroid Injection, Interspinous Lumbar Decompression, Minimally Invasive, Algorithmic Approach. Introduction. Lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) is described as a condition in which there is diminished space available for the neural and vascular elements in the lumbar spine . LSS may If you have lumbar spinal stenosis and have nerve pain in your legs that is reducing your ability to walk, your doctor may prescribe a neuropathic agent, such as gabapentin (Neurontin). Gabapentin (Neurontin) has been used quite successfully for patients with neuropathic (nerve) pain in the hands and feet. In this study, patients with neurologic intermittent claudication (NIC) from lumbar spinal stenosis were given gabapentin. Spinal stenosis is painful because as the spinal cord narrows, it puts pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots. When these nerves become compressed, it causes pain, cramping, weakness, and/or tingling that can radiate from the back to the buttocks and down the legs. Healthcare professionals sometimes prescribe gabapentin as an off-label use for spinal stenosis. But there’s not much evidence that it provides long-term pain relief. A recent clinical practice guideline didn’t recommend gabapentin for spinal stenosis treatment. Gabapentin is most effective in relieving neuropathic pain conditions caused by disk herniation, spinal stenosis, diabetic neuropathy, and postherpetic neuralgia. It provides limited sciatica and fibromyalgia relief, and is ineffective for reducing arthritis-related chronic low back pain. One open label study concluded that compared to usual care, gabapentin reduced pain intensity and improved walking distance in lumbar spinal stenosis, a condition associated with neurologic intermittent claudication, manifest as symptoms of leg pain, numbness, and cramping precipitated by standing or walking . In any event he inclusion of non Membrane-stabilizing anticonvulsants, such as gabapentin and carbamazepine, may reduce neuropathic radicular pain from lateral recess stenosis. These agents have central and peripheral eHealthMe is studying from 322,815 Gabapentin users for the drug's side effects, drug interactions, effectiveness and more. Check Gabapentin in the real world. What is Spinal stenosis? Spinal stenosis (narrowing of spinal column) is found to be associated with 546 drugs and 186 conditions by eHealthMe. Check our latest studies of Spinal stenosis. Introduction: In Japan, conservative therapy for patients with lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), prostaglandin E1, tramadol, physical/exercise It really depends on how severe the stenosis is in your back. Now there’s two types of stenosis, you can have stenosis in the middle of the spine where the spinal cord runs inside the bone. That’s called Central stenosis. And then you can have lateral stenosis, also called foraminal stenosis, where these nerves come out on the sides of the spine. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the use of pregabalin and gabapentin is effective in the symptomatic management of spinal stenosis, compared to other drugs, by using pain and disability rating scales. Keywords: lumbar spinal stenosis, pregabalin, gabapentin, gabapentinoids, treatment. Citation: Martínez T, Mariscal G, de la Rubia Ortí JE and Barrios C (2023) Efficacy and safety of pregabalin and gabapentin in spinal stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 14:1249478. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1249478 The efficacy of gabapentin monotherapy was investigated against both acute or chronic radicular pain caused by lumbar disk hernia (LDH) or lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). Seventy-eight patients with radicular pain, 10 males and 68 females aged 23 to 76 years (mean 49.4 years), caused by LSS in 45 pati
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |