Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
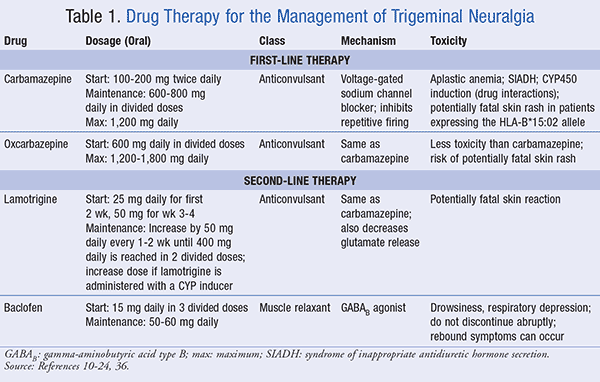
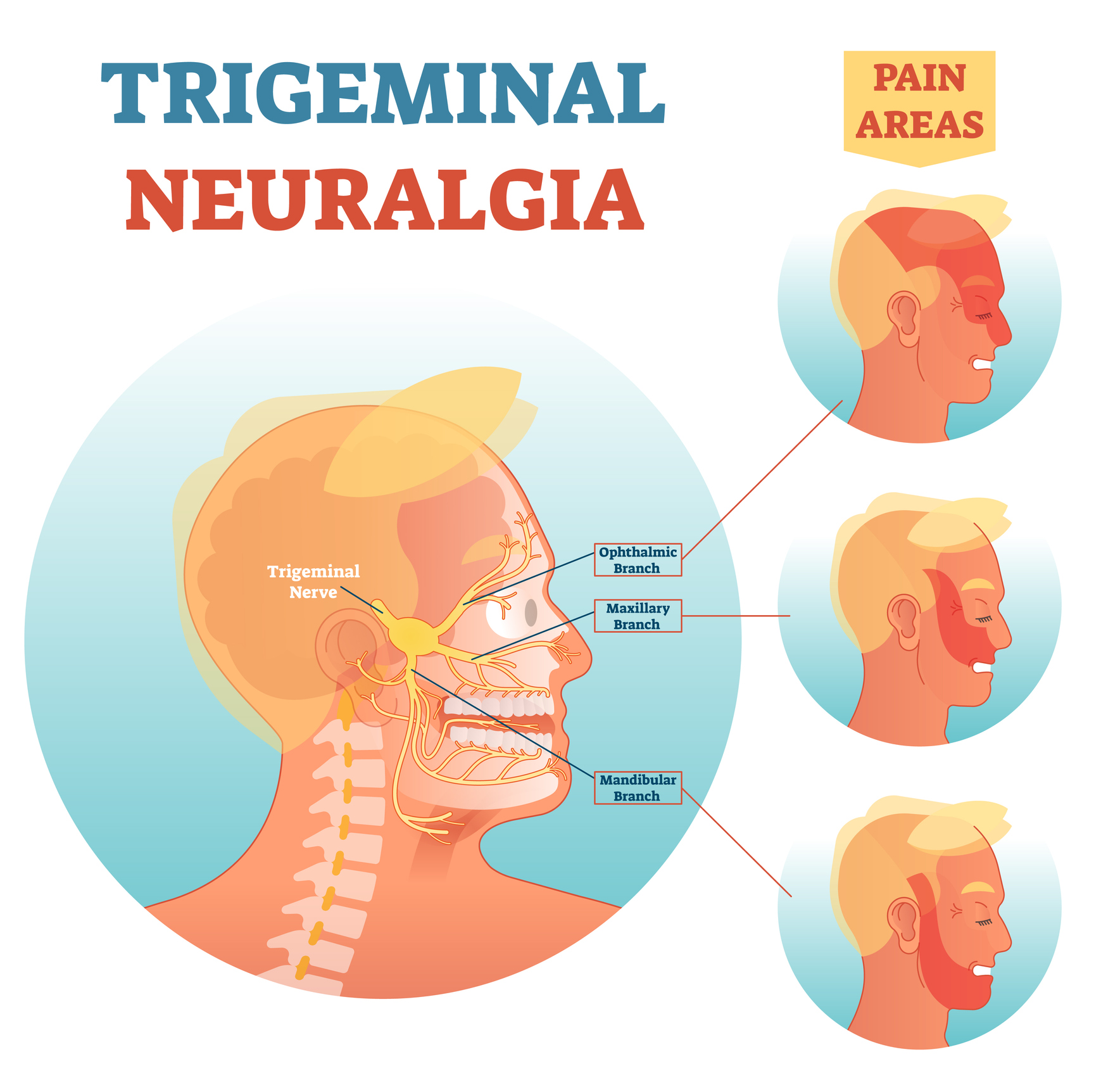
In addition, in patients with concomitant continuous pain, the efficacy of these drugs may drop, thus suggesting the opportunity to test the efficacy of different drug categories. The aim of this review is to provide current, evidence-based, knowledge about the use of gabapentin and other α2δ ligands in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Cost. Because patients with trigeminal neuralgia will be using medications for years, perhaps decades, their cost is relevant. Generic carbamazepine is the cheapest; costs vary widely for the other agents, depending on the source, but approach a 4-fold increase for generic gabapentin (GBP), 8-fold for lamotrigine (LTG), 10-fold for topiramate (TPM), and 20-fold for oxcarbazepine (OCB) in A. Introduction Today, trigeminal neuralgia is usually treated with drugs called anti-convulsants, which include carbamazepine (Tegretol®), phenytoin (Dilantin®), oxycarbazepine (Trileptal®), and gabapentin (Neurontin®). Phenytoin was first introduced in 1942, and in 1962 carbamazepine became the most commonly used drug. Baclophen (Lioresal Trigeminal neuralgia is an uncommon disorder characterized by recurrent attacks of lancinating pain in the trigeminal nerve distribution. Typically, brief attacks are triggered by talking, chewing Most patients respond well to pharmacotherapy; carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine are first line therapy, while lamotrigine and baclofen are considered second line treatments. Other drugs such as topiramate, levetiracetam, gabapentin, pregabalin, and botulinum toxin-A are alternative treatments. The combination of “gabapentin”, “carbamazepine”, and “primary trigeminal neuralgia” used the Boolean operator “AND” to carry out the specific search. Language restrictions and publication status were not considered in our literature search. Other procedures may be used to treat trigeminal neuralgia, such as a rhizotomy. In a rhizotomy, your surgeon destroys nerve fibers to reduce pain. This causes some facial numbness. In this review, based on a systematic search of relevant literature, we aim to provide current, evidence-based, knowledge about the use of gabapentin and other α 2δ ligands in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Reviews and ratings for Gabapentin when used in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. 38 reviews submitted with a 7.5 average score. I am currently on 1800 mg/day of gabapentin, but am still having a fair amount of pain. On a scale of 1 to 10, the background level is about a 2 with occasional flares to a level of 5 or 6. Does anyone have luck with gabapentin, and if so, what dosages? In addition, in patients with concomitant continuous pain, the efficacy of these drugs may drop, thus suggesting the opportunity to test the efficacy of different drug categories. The aim of this review is to provide current, evidence-based, knowledge about the use of gabapentin and other α2δ ligands in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with trigeminal neuralgia (TN) advocate for a multidisciplinary team approach to improve the care of patients with acute and chronic TN. Evidence-based discussions and decisions are encouraged to establish care pathways for prompt diagnosis and treatment, and long-term outcomes data collection to improve care. The guidelines include Drug therapy is the most commonly used treatment for primary trigeminal neuralgia (PTN), in which carbamazepine is the first-line drug. Recently, the anti-epileptic drug gabapentin has also been widely used in patients with PTN, but whether it can be used as a substitute for carbamazepine still needs to be verified. Most people with trigeminal neuralgia will be prescribed medicine to help control their pain, although surgery may be considered for the longer term in cases where medicine is ineffective or causes too many side effects. Medicine. As painkillers like paracetamol are not effective in treating trigeminal neuralgia, you'll usually be prescribed an The present study suggests that gabapentin can be effective as first or second line treatment of trigeminal neuralgia, even in cases resistant to traditional treatment modalities. Gabapentin does have support for use in treating other neuropathic pain conditions, particularly multiple sclerosis. Despite a lack of RCT data, observational evidence supports the use The aim of this systematic review was to determine the efficacy of gabapentin (GBP) in the treatment of pain of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia (TN). Low-dose gabapentin combined with either lamotrigine or carbamazepine can be useful therapies for trigeminal neuralgia in multiple sclerosis. Eur Neurol . 2000;44(1):45–48. doi: 10.1159/000008192 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ] The preferred treatment for trigeminal neuralgia consists of antiepileptic drugs. Among them, gabapentin has shown promise in relieving some forms of neuropathic pain. This retrospective review examined 194 consecutive cases of trigeminal neuralgia, many of whom had paroxysmal facial pain resistant to previous surgical interventions or treatment with multiple medications. Of the 92 who had The first-line pharmacologic treatment for TGN is the anticonvulsant carbamazepine, with oxcarbazepine utilized for its similar mechanism but milder adverse-effect profile.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |