Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
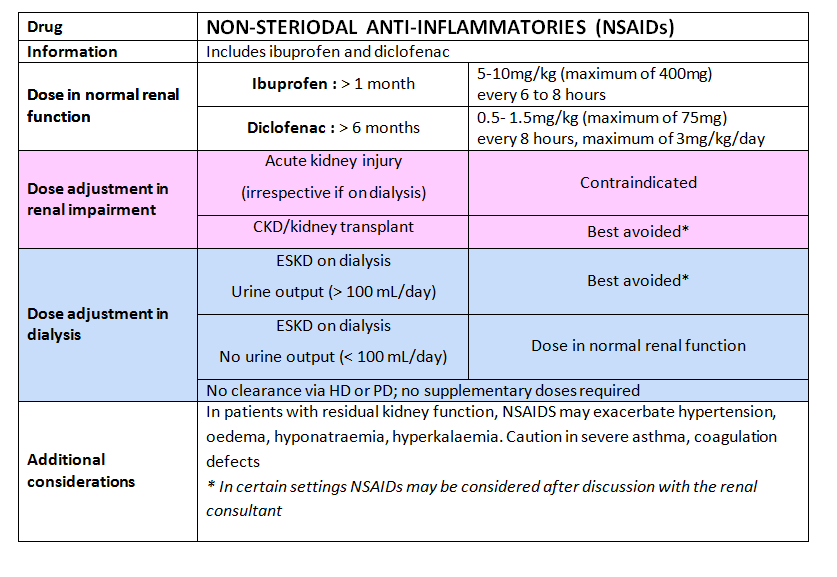
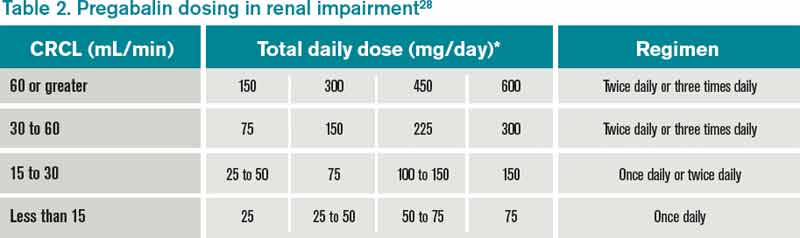
Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Rare cases of liver and kidney damage have been reported with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions may be at a higher risk. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential while taking Gabapentin. It is not reviewed for medical accuracy and should not replace professional medical advice. Not necessarily unless you have chronic kidney disease, then it can cause toxicity. gabapentin, kidney. Still looking for answers? Try searching for what you seek or ask your own question. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Some of its most common side effects include the following: ataxia, nystagmus, drowsiness, headaches, diplopia, fatigue and myoclonic twitches. 1 All of these effects appear quite often in patients with chronic kidney disease, especially if they are undergoing dialysis and their doses are not adjusted to their glomerular filtration rates. 2 We However, in stage 3 kidney disease, where kidney function is moderately reduced (typically with an eGFR between 30 and 59 ml/min/1.73 m²), the kidneys’ ability to clear gabapentin is diminished. Potential Risks of Gabapentin Buildup Majority drugs, including Gabapentin, are eliminated by the kidneys and will accumulate to a toxic level in renally compromised patients as in this case. Per Lexicomp, Gabapentin’s recommended dose in patients with renal impairment is as follows: CrCl >15 to 29 mL/minute: 200 to 700 mg once daily. CrCl 15 mL/minute: 100 to 300 mg once daily Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. Is Gabapentin Hard on Cats’ Kidneys? A Comprehensive Guide. The question of whether gabapentin is harmful to cats’ kidneys is complex and requires a nuanced answer. The short answer is: gabapentin does not directly cause kidney damage in most cases. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its well recieved pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Gabapentin may interact with certain types of substances and cause negative side effects. For example, mixing alcohol and gabapentin can cause people to feel dizzy or tired. Despite the risk of bad side effects of using gabapentin, it can be more dangerous to stop using it. Gabapentin use can cause physical dependence. Is gabapentin hard on Medications can impact your kidneys, especially with chronic kidney disease. Learn which drugs may need adjustments to protect your kidney health. Medications save and improve lives, but it can be easy to overlook their risks and side effects, especially if you don't think they apply to you. NSAIDs have the most potential for risk when it comes to your kidneys. The best pain med for you depends on a variety of factors, including kidney health. Let's discuss: Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. Gabapentin and Cirrhosis of the Liver - Fatty Liver Disease
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |