Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
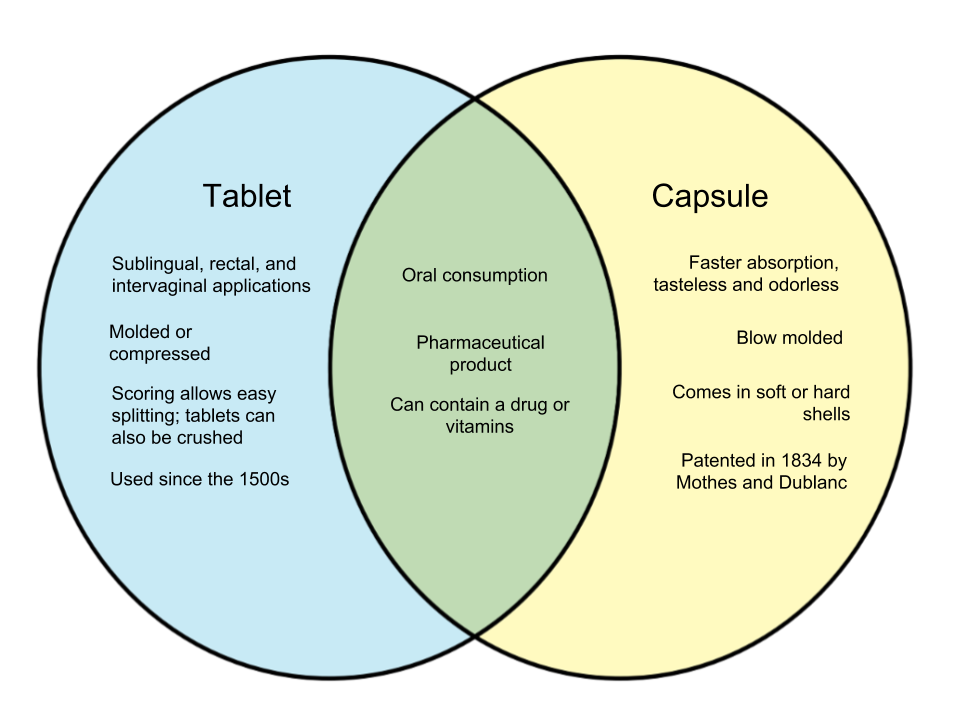
Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. There is evidence from case reports that gabapentin capsules may be subject to misuse in certain populations, particularly those with histories of substance abuse or dependency. It is conceivable, however, that gabapentin tablets would also be subject to intranasal misuse since the tablets can be crushed and the resulting powder inhaled. Drug Interactions: A total of 270 drugs are known to interact with Gabapentin: 28 major drug interactions (148 brand and generic names) 232 moderate drug interactions (1026 brand and generic names) 10 minor drug interactions (52 brand and generic names) A total of 270 drugs are known to interact with Neurontin: Tablets and capsules are similar but have some key differences, including price. Both are pills that you take by mouth. And, since they both pass through your digestive tract, they generally enter your system the same way. The active ingredient in gabapentin is same for human and animal formulations. So, the effects and benefits should be similar. Still, there may be differences in dosing instructions and methods between humans and pets. Vets are trained to decide the ideal dosage for an animal depending on factors like weight, health, and condition. Although tablets and capsules work in a similar way, they have some key differences, too. And, in some cases, one form may be better suited for you than the other. Here’s a look at the The core difference between gabapentin used for dogs and gabapentin used for humans lies not in the active ingredient itself, but primarily in the formulation and potential added ingredients. Both human and veterinary gabapentin utilize the same active pharmaceutical ingredient (API): gabapentin. This drug, primarily an anticonvulsant, is Each tablet contains 600mg or 800mg of gabapentin. If you're taking gabapentin as a liquid, 2ml is usually the same as taking a 100mg tablet or capsule. Always check the label. The usual dose for: The usual dose to treat nerve pain in adults is 900mg to 3,600mg a day, split into 3 doses. TITLE: Gabapentin Tablets Versus Capsules: A Review of the Evidence Regarding Appropriate Use . DATE: 13 April 2010. CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Gabapentin is approved by Health Canada as an antiepileptic agent and it is also widely used off-label in the treatment of pain and in the management of several psychiatric conditions, As mentioned, the fundamental element, gabapentin itself, is chemically identical in medications for both humans and animals. There is no unique “animal gabapentin molecule.” The difference comes into play in the following areas: Formulation Differences. Human Gabapentin: Typically available in capsules, tablets, and liquid solutions. These Label: Neurontin- gabapentin capsule Neurontin- gabapentin tablet, film coated Neurontin- gabapentin solution. DailyMed. Label: Gralise- gabapentin tablet, film coated Gralise- gabapentin kit. Food and Drug Administration. Lyrica CR (pregabalin extended-release tablets) label. Prescribers' Digital Reference. Neurontin (gabapentin) - drug summary. Though similar, there are some essential distinctions between capsules and tablets. Some notable differences include the following: Capsules usually don't have a taste; however, uncoated tablets taste bitter. Capsules are easier to swallow than tablets. Yes, gabapentin is the generic name for neurontin. Gabapentin's name is derived from the word "gaba" which is the chemical in your brain that is improved by this medication. Valium works by improving the brain's "gaba" chemicals also. yes it is its just the generic name for it. hope you feel better. Yes. It's the generic version. Is there a difference between gabapentin tablets and capsules? Tablets have a longer shelf life and come in a variety of forms. They can also accommodate a higher dose of an active ingredient than a capsule. They tend to be slower acting and, in some cases, may disintegrate unevenly in your body. Capsules act quickly and most, if not all, of Is There a Difference Between Veterinary Gabapentin and Human Gabapentin? The short answer is: No, the active ingredient, gabapentin itself, is the same in both veterinary and human formulations. The difference lies primarily in how the medication is prepared and the specific ingredients it contains. While the core molecule responsible for the Driving performance studies conducted with a prodrug of gabapentin (gabapentin enacarbil tablet, extended-release) indicate that gabapentin may cause significant driving impairment. Prescribers and patients should be aware that patients' ability to assess their own driving competence, as well as their ability to assess the degree of somnolence *The dose is normalized to 1,000 mg equivalent (mg-eq) of gabapentin. t max is presented as median (minimum, maximum). b.i.d. = twice daily; q.d. = once daily; t.i.d. = 3 times daily; C max = maximum plasma concentration over the last dosing day; t max = time to reach maximum concentration over the dosing interval in which the C max was observed (if the maximum value occurred more than once in Gabapentin Capsules or Tablets Gabapentin is a medication that treats nerve pain by calming overactive nerves in your body. It may also prevent and control seizures in people with epilepsy. If you’re considering using gabapentin for treating a medical condition, you may be wondering if there is a difference between taking it in capsule form or as a tablet. While both options contain the same active ingredient, gabapentin, there are some slight variations in how they are formulated and delivered. During the controlled epilepsy trials in patients older than 12 years of age receiving doses of gabapentin up to 1,800 mg daily, somnolence, dizziness, and ataxia were reported at a greater rate in patients receiving gabapentin compared to placebo: i.e., 19% in drug versus 9% in placebo for somnolence, 17% in drug versus 7% in placebo for
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |