Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 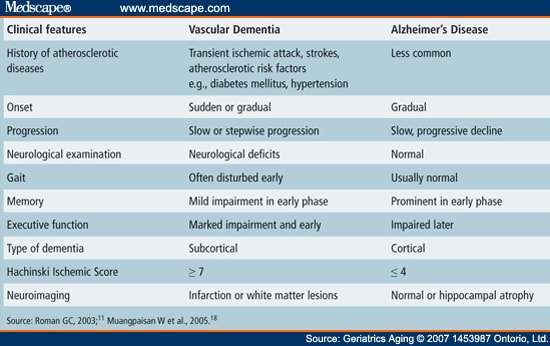 |
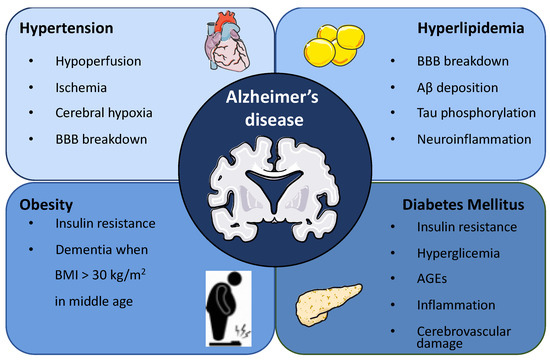
In a seminal trial on pain following shingles (post-herpetic neuralgia), the target dose of gabapentin was 900 mg four times daily. It often takes weeks or months to build up to this dose so that Gabapentin, also known by its brand name Neurontin, is primarily used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain. However, recent studies have shown a potential link between gabapentin use and memory problems, leading to questions about its safety and long-term effects on cognitive function. Key Takeaways: We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. In this study, we discovered a significant association between cumulative exposure to gabapentin and pregabalin and the risk of dementia. Particularly, individuals <50 years and those with higher accumulative dose were more susceptible. Although previous studies have established a link between chronic pain and elevated risk of cognitive dysfunction, including dementia (Kao et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2023; Cao et al., 2019), the literature is sparse on gabapentin's potential role in dementia onset. We estimated the yearly prevalence of gabapentin use, both overall and within subgroups defined by cognitive status [normal, mild cognitive impairment, and dementia] and demographics [age and sex] for participants aged 65+. Especially in older adults, gabapentin is prescribed to treat behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) (Kim et al., 2008). Several studies have reported that gabapentin has a deleterious effect on cognition (Leach et al., 1997; Meador et al., 1999; Shem et al., 2018). There’s mounting evidence supporting a connection between certain medications (anticholinergics and benzodiazepines) and dementia. An expert discusses the latest research and what to do if you Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to investigate the associations between exposure to gabapentin or pregabalin and the quartiles of cDDDs of gabapentin or pregabalin exposure and the risk of dementia, adjusting other potential confounders and estimating the hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Can Gabapentin Cause Dementia? Exploring the Link and Risks. The Evidence: Gabapentin, Cognitive Decline, and Dementia. Gabapentin and Memory Impairment; Gabapentin and Dementia Risk; Long-Term Effects of Gabapentin; FDA Warnings and Lawsuits; Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Gabapentin and Cognitive Effects. 1. Does gabapentin always And since treatment options for dementia are limited, prevention is key. Dementia risk is tied to common things like diabetes, high blood pressure, and physical inactivity. But some common medications are associated with dementia risk, too. Here are four common drug classes linked to dementia, and what the research says about your risk. 1. Long-term Gabapentin therapy for chronic pain is not associated with a differential risk of dementia across dosage levels, irrespective of age or gender. Further study into its potential cognitive impacts is essential. Gabapentin has been increasingly prescribed to older adults for off-label indications, and accumulating evidence suggests potential for gabapentin misuse and related adverse events. However, the relation between gabapentin initiation and longer-term neurocognitive changes is not well understood. 9. What is the connection between gabapentin and dementia? Studies have shown a link between cumulative exposure to gabapentin and pregabalin and the risk of dementia, particularly in individuals under 50 and with higher cumulative doses. 10. Can gabapentin cause liver or kidney damage? The authors describe the use of gabapentin in the treatment of 4 outpatients with dementia-associated agitation. On the basis of clinical case reports and the Overt Agitation Severity Scale, all 4 patients had reduced agitation with gabapentin. Three of 4 patients were successfully titrated to a full dose of 2,400mg/day. These findings suggest a possible role for gabapentin in the behavioral Gabapentin use was significantly associated with decline in cognitive and functional status among older adults with initially normal cognition. Further studies are needed to examine the association. Benzodiazepines and drugs with strong anticholinergic effects have been linked to Alzheimer’s disease in people who take them. There are alternatives to both types. Objective: Previous studies have shown that gabapentin or pregabalin use is associated with cognitive decline. Herein, we aimed to evaluate the association between gabapentin or pregabalin use and the risk of dementia. Methods: In this retrospective, population-based matched cohort stu In a recent population-based cohort study, Huang et al. identified a notable association between cumulative use of gabapentin and pregabalin and an increased risk of dementia, notably in younger demographics and those on higher dosages (Huang et al., 2023). This contrasts with our findings, which did not demonstrate significant differences in While gabapentin and pregabalin serve crucial roles in managing various medical conditions, the emerging link between these drugs and dementia raises serious concerns. Given the evidence of potential cognitive decline, particularly with long-term use and high cumulative doses, a cautious and well-informed approach is necessary.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |