Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
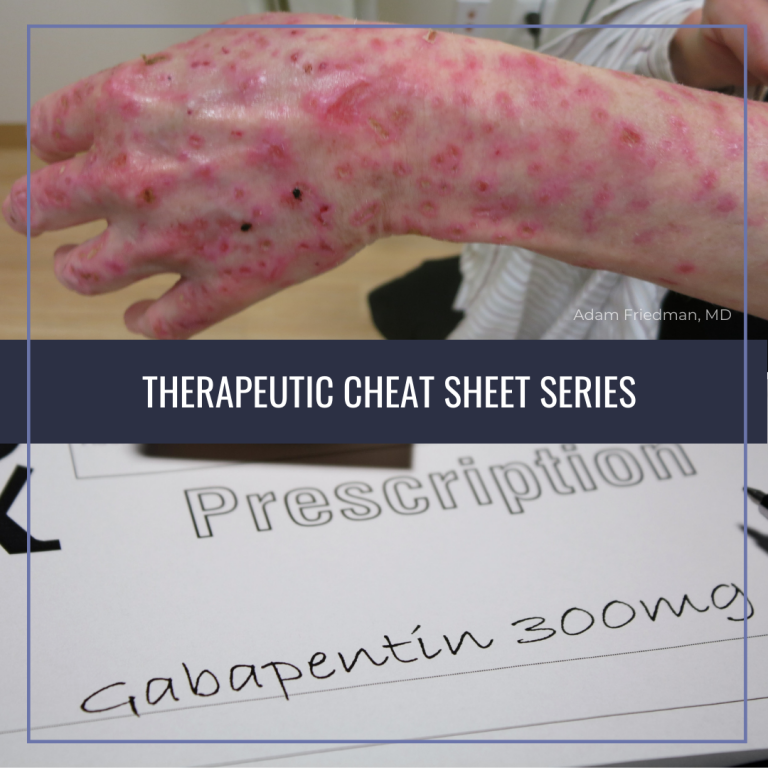
Several mechanisms of gabapentin have been proposed after neuropathy including an inhibition of NMDA receptors, inhibition of sodium currents and reducing β4a subunit mediated VGCC trafficking (Hara and Sata 2007; Mich and Horne 2008; Yang et al. 2009). Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related compounds with recognized efficacy in the treatment of both epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The pharmacological mechanisms by which these agents exert their clinical effects have, until recently, remained unclear. The interaction of gabapentin and pr Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related compounds with recognized efficacy in the treatment of both epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The pharmacological mechanisms by which these agents exert their clinical effects have, until recently, remained unclear. The present review discusses the effectiveness of gabapentin in different types of neuropathic pain in preclinical as well in clinical settings and also discusses the possible mechanism of action at different levels including at dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and dorsal horn neurons along with at supra-spinal centres. Gabapentin (Trade name: Neurontin) is an anticonvulsant.It is commonly also used off-label for anxiety disorders, restless leg syndrome, and in alcohol use disorder.It is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Although the exact mechanism of action with the GABA receptors is unknown, researchers know that gabapentin freely passes the blood-brain barrier and acts on neurotransmitters. Gabapentin has a cyclohexyl group to the structure of the neurotransmitter GABA as a chemical structure. Mechanism of action of gabapentinoids Site of action The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake.21 They were originallydesigned as g aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogues but do not have any effects on GABA receptors. Gabapentin binds to a 2d receptors with greater affinity to the a 2d-1 subtype.22 Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin is structurally related to GABA. However, it does not bind to GABA A or GABA B receptors, and it does not appear to influence synthesis or uptake of GABA. High affinity gabapentin binding sites have been located throughout the brain; these sites correspond to the presence of voltage-gated calcium channels Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic agent but now it is also recommended as first line agent in neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post herpetic neuralgia. α2δ-1, an auxillary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, has been documented as its main target and its specific bindin Mechanism of Action The mechanism by which gabapentin exerts its analgesic action is unknown, but in animal models of analgesia, gabapentin prevents allodynia (pain-related behavior in response to a normally innocuous stimulus) and hyperalgesia (exaggerated response to painful stimuli). In 1 This label may not be the latest approved by FDA. Gabapentin was first conceptualised in the early 1970s during efforts to discover drugs for treating neurological disorders. 7 Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) was known to be a key inhibitory neurotransmitter, whose inhibition could cause seizures. Mechanism of action of Gabapentin (Neurontin) Gabapentin, also known as Neurontin, is a GABA analogue that works by modulating the release of neurotransmitters in the brain. GABA, or γ-aminobutyric acid, is a neurotransmitter that inhibits nerve transmission in the brain and plays a crucial role in regulating neuronal excitability. Results with human and rat brain NMR spectroscopy indicate that gabapentin increases GABA synthesis. Gabapentin increases non-synaptic GABA responses from neuronal tissues in vitro. In vitro, gabapentin reduces the release of several mono-amine neurotransmitters. This activity outlines the indications, mechanisms of action, administration, significant adverse effects, contraindications, monitoring, and characteristics of gabapentin toxicity. This activity also provides clinicians with the necessary skills and tools to treat various types of muscular, neurological, and psychiatric medical conditions Although the cellular mechanisms of pharmacological actions of gabapentin (Neurontin) remain incompletely described, several hypotheses have been proposed. It is possible that different mechanisms account for anticonvulsant, antinociceptive, anxiolytic and neuroprotective activity in animal models. Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related compounds with recognized efficacy in the treatment of both epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The pharmacological mechanisms by which these agents exert their clinical effects have, until recently, remained unclear. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10] [7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] Mechanism of action. The precise mechanism through which gabapentin exerts its therapeutic effects is unclear. 16,17 The primary mode of action appears to be at the auxillary α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (though a low affinity for the α2δ-2 subunit has also been reported). 10,8,14 The major function of these subunits is Busch et al. reported that antacids reduce the bioavailability of gabapentin by ≈ 20% when given concomitantly with, or up to 2 h post, gabapentin administration . Mechanism of action. Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Although the cellular mechanisms of pharmacological actions of gabapentin (Neurontin ®) remain incompletely described, several hypotheses have been proposed. It is possible that different mechanisms account for anticonvulsant, antinociceptive, anxiolytic and neuroprotective activity in animal models.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |