Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
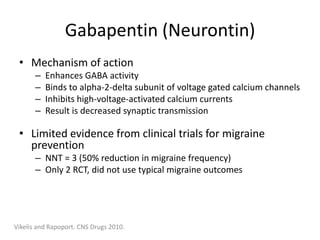
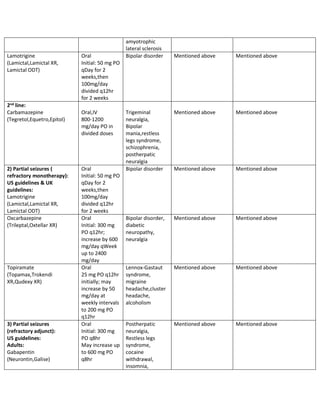
The studies showed that neither gabapentin nor gabapentin enacarbil was more effective than placebo at reducing the frequency of migraine headaches. Gabapentin commonly caused side effects, especially dizziness and somnolence (sleepiness). No studies of pregabalin were identified, and research on this drug is desirable. Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. Gabapentin shows to have an effective therapeutic action in the prophylactic treatment of migraine. Our observations indicate that gabapentin is well tolerated by patients and that reduces headache frequency and use of symptomatic drugs in both groups. Migraine is a common episodic disorder, the hallmark of which is a disabling headache generally associated with nausea and/or light and sound sensitivity. The acute treatment of migraine in adults is reviewed here. Preventive treatment of migraine in adults is discussed separately. (See "Preventive treatment of episodic migraine in adults".) Gabapentin for migraine prevention can be taken with or without food and comes in an extended release tablet, an immediate release tablet, or an oral solution. Objective: Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. To describe and assess the evidence from controlled trials on the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin/gabapentin enacarbil or pregabalin for preventing migraine attacks in adult patients with episodic migraine. In 2022, a trial (Head-to-Head Study of Erenumab Against Topiramate in Patients with Episodic and Chronic Migraine [HERMES]) comparing erenumab and topiramate for the prevention of migraine was published. 38 The HER-MES study was a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in adults (n = 777); most patients had The recommendations on what information and self-care advice should be given to people with migraine are based on clinical guidelines National headache management system for adults [], Headaches in over 12s: diagnosis and management [], Primary care management of headache in adults [Becker, 2015] and Pharmacological management of migraine [], the American Headache Society updated consensus Petasites is established to be effective in migraine prevention. 64, 65 CoQ10 is possibly effective for migraine prevention, 27 while riboflavin is probably effective. 66 Percutaneous estradiol is possibly effective for migraine prevention, 67 as is a combination of soy isoflavones (60 mg), dong quai (100 mg), and black cohosh (50 mg). 67 Migraines. Gabapentin is used "off-label" for migraine prevention and treatment, including migraines with or without aura, vestibular migraines. It reduces the frequency of headaches, pain intensity, and the use of symptomatic medications 1, 2. However, gabapentin is not helpful for migraine aura, vertigo, or other accompaing symptoms. Gabapentin is an anti-seizure drug that is sometimes prescribed to help prevent migraines. However, there is conflicting research on whether it's effective for this use. It may also be prescribed for conditions such as diabetic neuropathy, restless leg syndrome, and fibromyalgia. Discover the potential of gabapentin for preventing migraine attacks and headaches. While not a first-line treatment, it can be effective in combination with other options. This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter study in patients with migraine (with or without aura) was conducted to determine the efficacy and safety of gabapentin in migraine prophylaxis. We found moderate certainty evidence that beta-blockers, valproate, and amitriptyline increase the proportion of patients who experience a 50% or more reduction in monthly migraine days, and low certainty evidence that gabapentin may not be different from placebo. However, little evidence is available on the effects and mechanisms of action of gabapentin during the migraine attack period. Gabapentin's analgesic effect may result from the antagonism of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and central nervous system calcium channels[5,6]. Migraine is a common, multifactorial neurovascular disorder. GBP has some efficacy in migraine headache, but not sufficient evidence to suggest primary therapy. When primary headache treatments fail, a GBP trial may be considered in the individual patient. Gabapentin , Headache , Migraine , Chronic Daily Headache Gabapentin or pregabalin for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013(6):CD010609. Xu XM, Liu Y, Dong MX, Zou DZ, Wei YD. Acute migraines respond to nonsteroidal medications and triptans. Ibuprofen appears to be slightly more effective than naproxen, aspirin, and acetaminophen. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is minimally Does gabapentin (Neurontin) help prevent episodic migraine? Evidence-Based Answer Gabapentin does not decrease the frequency of migraine headaches and is not recommended for
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |