Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
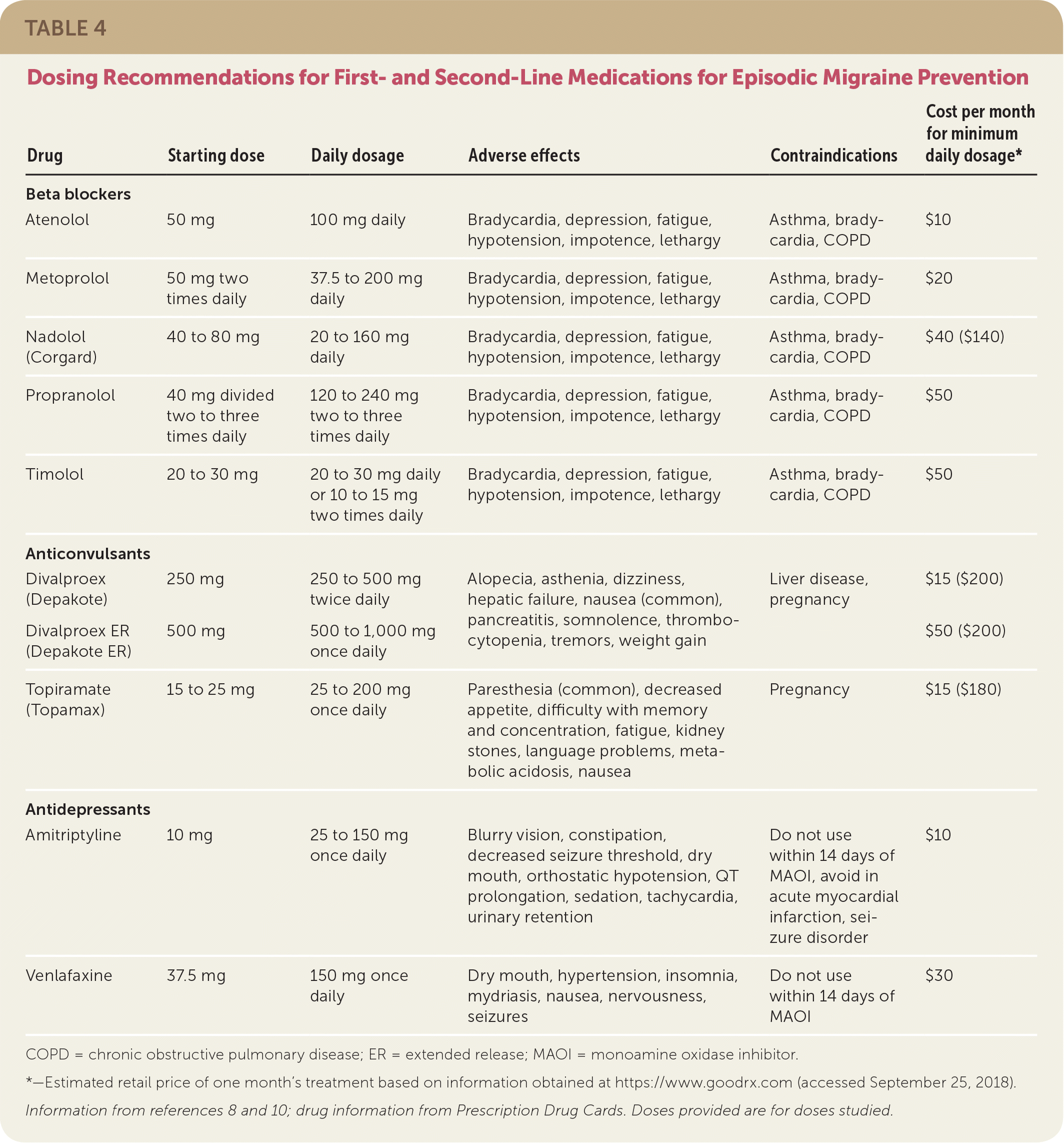
The abortive (symptomatic) therapy of migraine ranges from the use of simple analgesics such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen to triptans, antiemetics, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antagonists, lasmiditan, and dihydroergotamine. According to the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention (AMPP) Study, 38.8% of patients with migraine should be considered for (13.1%) or offered (25.7%) preventive migraine therapy.16 Unfortunately, the underutilization of migraine preventive medications is underscored by the fact that only 13% of all patients with migraine currently use Many drugs can effectively help migraine by treating active symptoms or preventing new episodes from occurring as often or severely. Medication options to help relieve a migraine include triptans, antiemetics, and ergots. Medications that can help prevent migraine include certain blood pressure medications, antiepileptics, and antidepressants. "This medication, gabapentin, was a lifesaver for migraines. I had very bad headaches along with gum and tooth pain, and just after two days of taking this med, my pain is gone and I’m a new person. It has helped my anxiety tremendously, as well as my sleep. I am so thankful. Please don’t lose hope. Just try it, and it might work for you. Certain anti-seizure medications can prevent migraine. Topiramate (Topamax®) is an anti-seizure medication that also has uses for migraine prevention. Some anti-epilepsy drugs make birth control pills or oral contraceptives (OCPs) less effective. Discover the potential of gabapentin for preventing migraine attacks and headaches. While not a first-line treatment, it can be effective in combination with other options. American Migraine Foundation® is a recognized public charity under Internal Revenue Code section 501(c)(3) status. Donations to the American Migraine Foundation are tax-deductible to the extent permitted by law. The American Migraine Foundation EIN is 85-2527027. In the past several years, the FDA has approved many drugs developed specifically to treat migraine. These medicines target calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), a protein that can cause inflammation and pain associated with migraine. They are available as tablets, injections or infusions and are taken daily, monthly or once every three months. A 2016 study found that gabapentin showed some benefits for migraine headaches. However, it concluded that there wasn't enough evidence to recommend it as a primary therapy. Another study review in 2023 found that gabapentin was no more effective than a placebo in reducing monthly migraine days. Drugs for migraine headaches can relieve the pain and symptoms of a migraine attack and help prevent further migraine attacks. Migraines can be treated with two types of drugs: abortive and The 2021 American Headache Society consensus guideline recommends that preventive pharmacologic therapy should be considered for patients with 4 or more migraine headache days per month or those with 2 or more migraine headache days per month that are associated with substantial disability despite use of acute medication. 2 Preventive treatment Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used off-label to help prevent migraine attacks. Learn about why it’s used and how it works. Objective While there are several trials that support the efficacy of various drugs for migraine prophylaxis against placebo, there is limited evidence addressing the comparative safety and efficacy of these drugs. We conducted a systematic review and network meta-analysis to facilitate comparison between drugs for migraine prophylaxis. Methods We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, CENTRAL, and Objective: To compare gabapentin with placebo for use as a prophylactic agent in patients with migraine (with or without aura). STUDY DESIGN AND TREATMENT: After screening, a 4-week, single-blind, placebo baseline period was followed by a 12-week, double-blind, treatment period. Does gabapentin (Neurontin) help prevent episodic migraine? Evidence-Based Answer Gabapentin does not decrease the frequency of migraine headaches and is not recommended for prophylactic There is limited evidence for nebivolol, bisoprolol, pindolol, carbamazepine, gabapentin, fluoxetine, nicardipine, verapamil, nimodipine, nifedipine, lisinopril, and candesartan. Acebutolol, This review considers the evidence for the efficacy and tolerability of the antiepileptic drugs gabapentin and pregabalin for preventing episodic migraine in adults. The prophylactic treatment of migraine in children is the subject of a separate Cochrane review (Victor 2003). Gabapentin is used "off-label" for migraine prevention and treatment, including migraines with or without aura, vestibular migraines. It reduces the frequency of headaches, pain intensity, and the use of symptomatic medications 1 , 2 . Many medications claim to relieve migraine pain, but some are more helpful than others. In a large study looking at real-world data on 25 drugs, migraine sufferers rated the most and least helpful options. • Effective migraine preventive medications include candesartan, telmisartan, lisinopril, oral magnesium, topiramate, propranolol, erenumab, fremanezumab, and galcanezumab. •
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |