Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
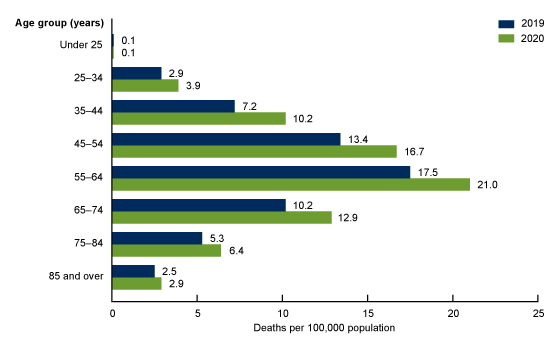
Taking alcohol and gabapentin together is a type of drug abuse that can lead to more rapid development of physical dependence. It can also lead to more severe withdrawal symptoms when you try to quit, feeding into the addiction cycle. Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. They can provide guidance on managing food interactions effectively to ensure the safe and effective use of gabapentin. Alcohol Interactions. Mixing gabapentin with alcohol can be dangerous and should be avoided. Both gabapentin and alcohol are central nervous system depressants, meaning they slow down brain activity. Gabapentin is a common prescription drug used to relieve nerve pain, restless leg syndrome, and other conditions. Consuming alcohol while taking gabapentin can be dangerous. This article will explore the risks of mixing alcohol and gabapentin. You will learn: If you or someone you love struggles with drug or alcohol abuse, you are not alone. Risks of Combining Gabapentin and Alcohol. Side effects of either substance can become worsened when alcohol and gabapentin are combined. As a result, the following side effects may occur or become heightened when mixing alcohol and gabapentin: Dizziness; Loss of coordination; Drowsiness; Fatigue; Anxiety; Nausea, vomiting, and headaches Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-misuse, and drug-related harms. Results are statistically significant unless indicated. Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. Gabapentin increases the abuse liability of alcohol alone and in combination with oxycodone in participants with co-occurring opioid and alcohol use disorder. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 173482. Recent cross-sectional studies of opioid abuse samples in the US and UK estimated gabapentin misuse to be between 15–22% (42, 44, 45) and gabapentin abuse with a prescription ranged from 40–65% (44, 45, 47, 49). There was little evidence of gabapentin abuse among those with a positive history of alcohol abuse or dependence. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Gabapentin carries a significant risk when mixed with alcohol. Both substances act as depressants, and their combined effects can lead to serious health complications. It's crucial to understand the dangers and potential consequences of combining these substances to make informed decisions about your health and well-being. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Conducted by scientists supported by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), part of the National Institutes of Health, the study found that alcohol dependent patients using gabapentin were more likely to stop drinking or refrain from heavy drinking than those taking placebo. The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Alcohol abuse is a huge problem in the United States, with 5.6% of adults dealing with an alcohol use disorder and more than 414,000 teenagers with the same condition in 2019. As a country, there are about 95,000 deaths annually with alcohol as a contributing factor . Gabapentin And Alcohol Gabapentin And Alcohol Gabapentin And Alcohol . Some patients are advised to avoid or limit the consumption of alcohol while taking medication because of the likelihood of side effects. Keep your doctor informed of your alcohol consumption before taking prescription or non-prescription medications. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Mixing Neurontin with drugs or alcohol can be dangerous. According to case reports, Neurontin is often abused with other substances. For example, it is sometimes taken with quetiapine (an antipsychotic medication used to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression) for a sedating, euphoric high. Is Gabapentin an Effective Treatment for Alcohol Withdrawal? Studies suggest that gabapentin may be effective in treating alcohol withdrawal and promoting alcohol abstinence. 1,5 In a randomized clinical trial by a study published in the Journal of American Medical Association, 41% of gabapentin participants reached total abstinence. 1
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |