Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 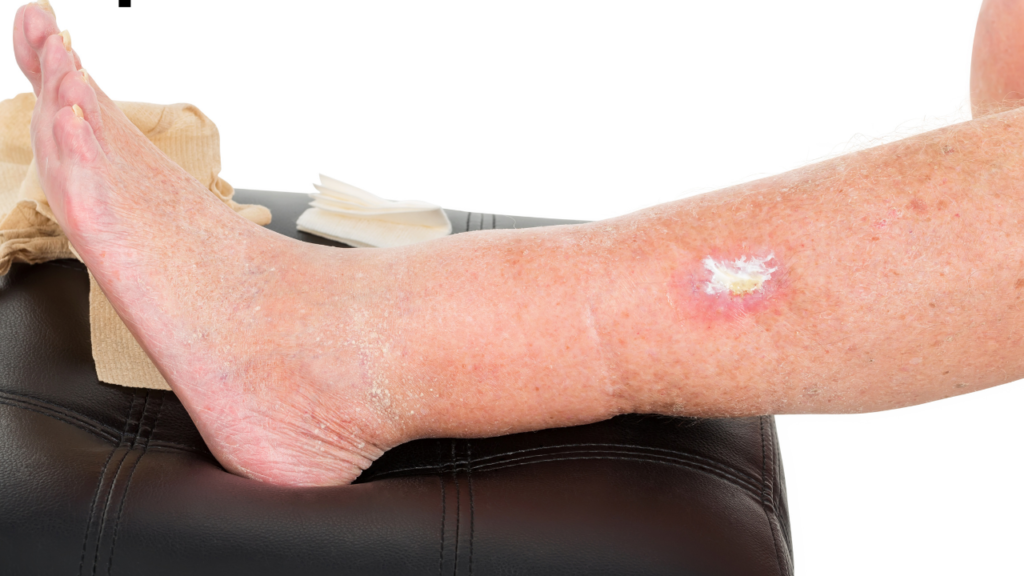 |
Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. On the sunny side of things, many users report feeling a sense of calm washing over them. It’s like gabapentin sprinkles a bit of zen dust on their anxiety, helping them feel more relaxed and at ease. Some even describe a subtle lift in their mood, as if the medication is gently nudging them towards a more positive outlook. Overall, while Gabapentin can be highly beneficial in treating various conditions, it must be used responsibly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to minimize potential risks and adverse effects. In the context of the question, "can Gabapentin cause depression?", there is no direct evidence linking Gabapentin to depression. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Drugs such as gabapentin have been linked in rare cases to an increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors. If you take gabapentin, you or your family should tell the doctor about any unusual changes in your mood, such as agitation, violence, aggression, depression, or talking about wanting to hurt yourself. Neurontin - also known as Gabapentin - is a drug that is sometimes prescribed to those who experience anxiety especially in situations where the anxiety is co-occurring with bipolar disorder. This article explores the usage of Neurontin, as well as the benefits, weaknesses, and side effects for those looking to learn more about this medication Gabapentin, while initially developed for treating epileptic seizures, has become a valuable option in mental health care due to its unique benefits. Many healthcare providers consider it a good alternative to traditional psychotropic medications for specific conditions. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA approved to treat seizure disorder and nerve pain from shingles. But it’s also used off-label to treat many other conditions, including anxiety, nerve pain from diabetes, and hot flashes. Gabapentin may be effective for anxiety, but it’s usually not a first-choice medication for this use. While studies don’t typically show effectiveness for improving symptoms of depression, there is evidence that gabapentin may have some benefit for anxiety disorders. A rat study found that gabapentin produced behavioral changes suggestive of anxiolysis, or feelings of calmness. As we delve into the complexities of gabapentin’s psychological effects, it’s crucial to understand both its benefits and potential risks. Gabapentin, a medication that sounds like it could be the name of a quirky robot sidekick in a sci-fi flick, is actually a serious player in the world of pain management and neurological disorders. Some reports suggest that gabapentin can exacerbate mood issues and has been linked to depressive symptoms, highlighting a complex relationship between the medication and mental health. According to a 2020 review, about 1 to 10% of people may experience a sense of euphoria when taking gabapentin, which may increase the likelihood of misuse.And data suggest that 40-65% of people This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of Gabapentin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. What are the brand names of gabapentin? Gabapentin is available as both a brand name product and a generic product (chemically the same, usually lower cost than the brand name product). Brand names of gabapentin include Horizant®, Gralise® and Neurontin®. Neurontin (gabapentin) is used to treat pain you may have from shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). It is also used with other seizure medicines for partial onset seizures in patients 3 years and older. Gralise (gabapentin) is only used for pain after having shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). It should not be used for any other medical condition. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and relieve pain for certain conditions in the nervous system. It is not used for routine pain caused by minor injuries or arthritis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is a prescription drug. It comes as an oral capsule, an immediate- or extended-release oral tablet, and an oral solution. Depression. Using this drug increases your risk Balancing the benefits and risks of gabapentin use for mental health is an ongoing process. As with any medication, it’s about weighing the potential improvements against the possible side effects. It’s a delicate balance, but one that can lead to significant improvements in quality of life for many individuals struggling with mental health Gabapentin may be effective for treating depression and anxiety, among other things. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. Gabapentin is available as Gralise, Neurontin, and generic gabapentin in the following dosage forms that are taken by mouth. 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg oral capsules 250 mg/5 mL oral solution
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |