Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 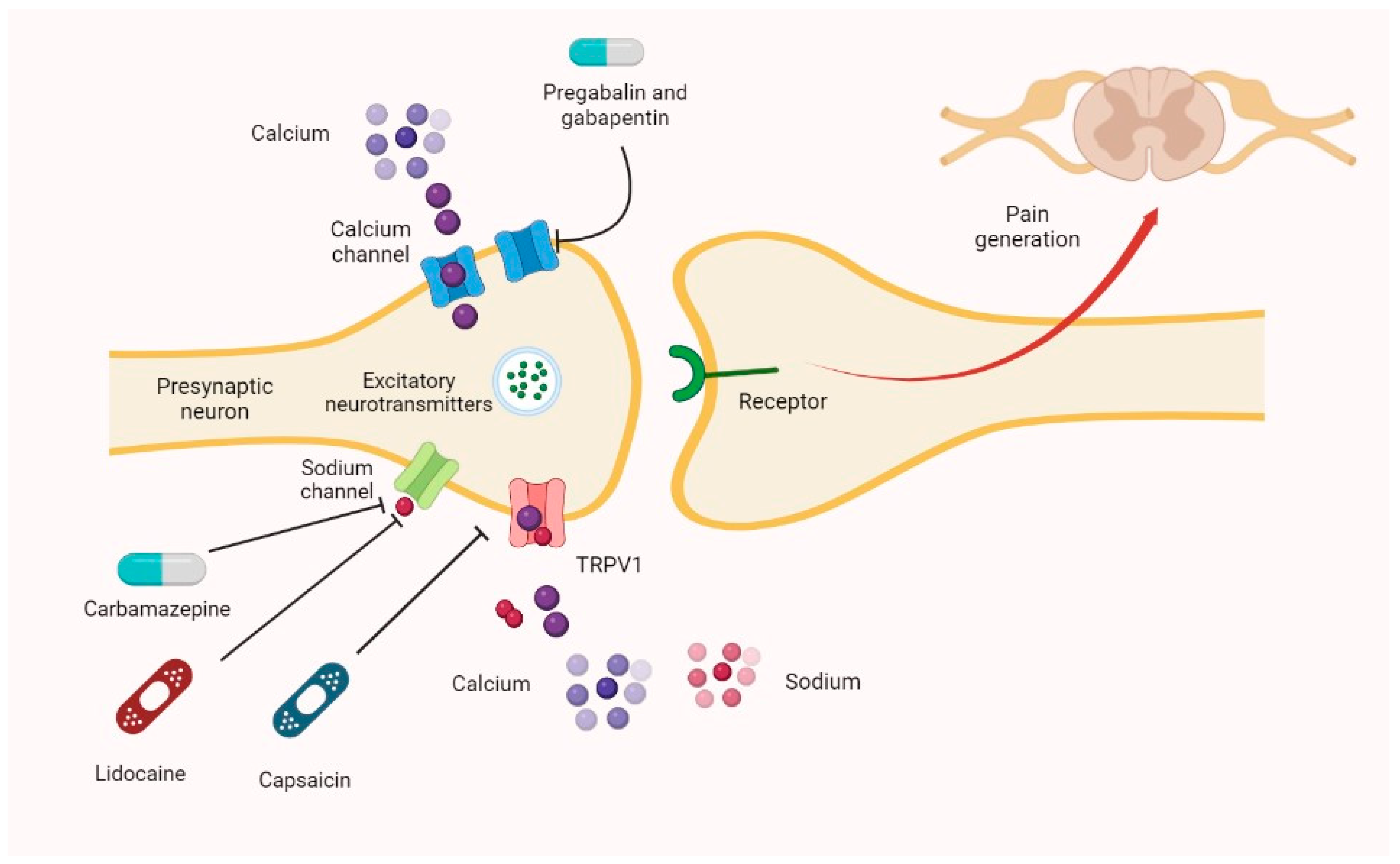 |
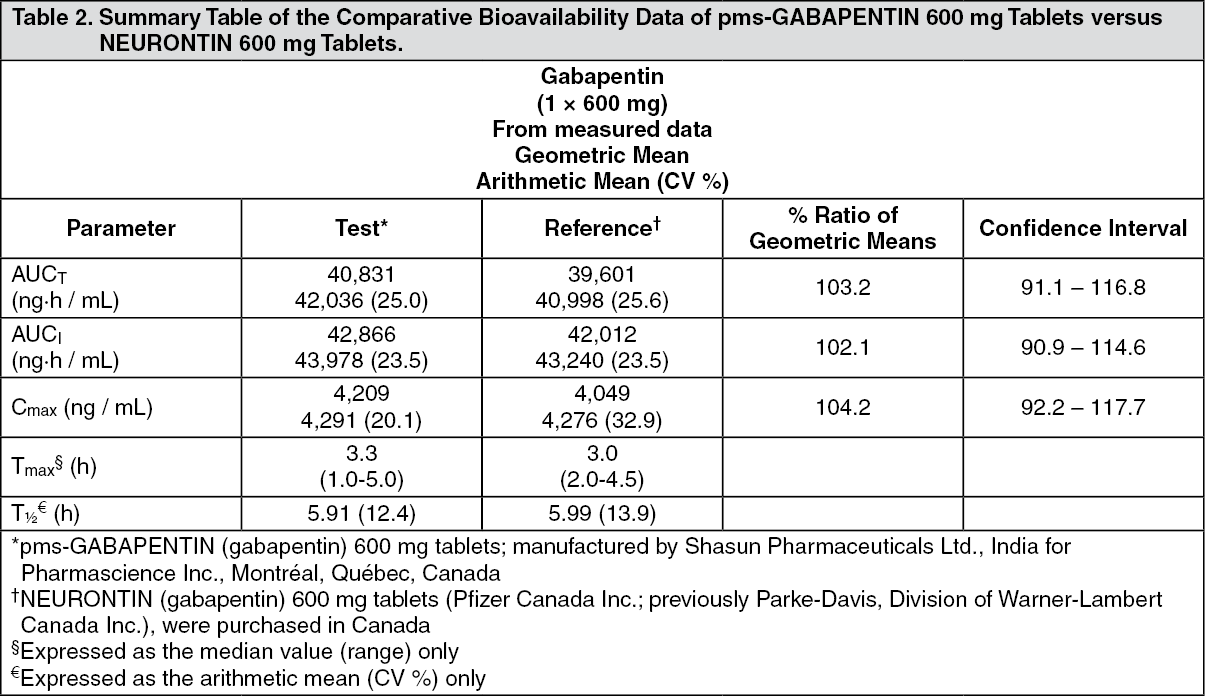
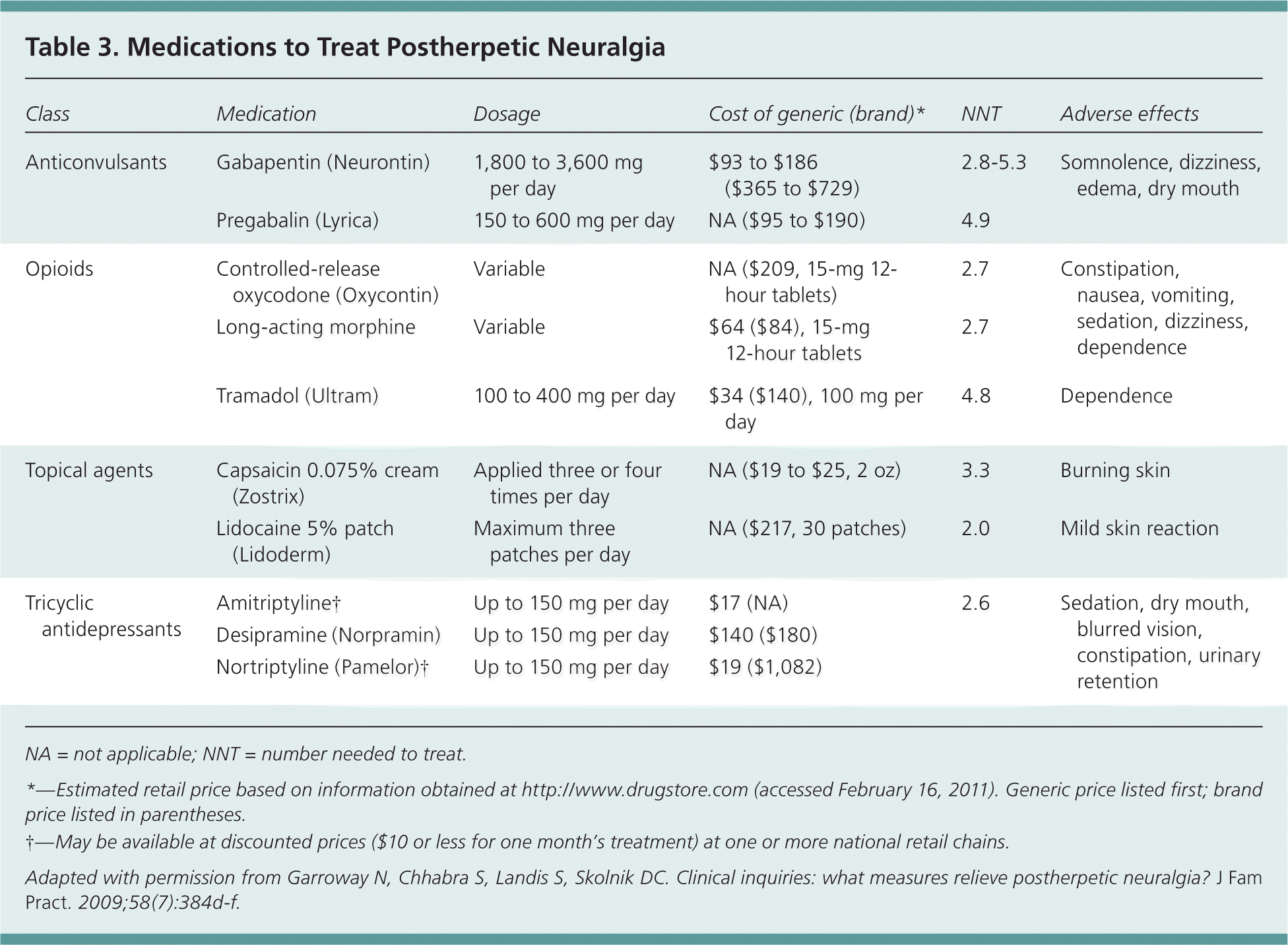
The duration of gabapentin's effectiveness can vary based on several factors, including the dose, the condition being treated, and individual patient characteristics. Typically, gabapentin's effects can last between 5 to 7 hours for immediate-release forms. Neurontin requires three times daily administration because of its short duration of effect. Only effective for partial-onset seizures, not other types of seizure disorders. Note: In general, seniors or children, people with certain medical conditions (such as liver or kidney problems, heart disease, diabetes, seizures) or people who take other Mechanism of action. Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. Pregabalin and gabapentin share a similar mechanism of action, inhibiting calcium influx and subsequent release of excitatory neurotransmitters; however, the compounds differ in their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics. Gabapentin is absorbed slowly after oral administration, with m If you have impaired kidney function, taking a lower dose or spacing out the dosing time is essential to prevent unwanted side effects.; Taking gabapentin with opioids (e.g., morphine, hydrocodone) can cause respiratory depression and sedation, and lead to fatal outcomes. Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant medication that inhibits the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, allowing for its use against pathologic neurotransmission such as that seen in neuropathic pain and seizure disorders. 16,19 It has a wide therapeutic index, with doses in excess of 8000 mg/kg failing to cause a fatal reaction in rats. 21 Neurontin: Treats pain from shingles (postherpetic neuralgia) and, when combined with other seizure medications, treats partial-onset seizures in adults and children over 3 years old. Gralise: Specifically for postherpetic neuralgia (pain after shingles) and should not be used for any other conditions. Administer NEURONTIN three times a day using 300 mg or 400 mg capsules, or 600 mg or 800 mg tablets. The maximum time between doses should not exceed 12 hours. The starting dose range is 10 mg/kg/day to 15 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses, and the recommended maintenance dose reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days. Gabapentin generally takes about 3 to 4 hours to reach maximum plasma concentrations after oral administration. For pain relief, significant effects can be observed within a few days to a week, while its anticonvulsant effects can be seen relatively quickly, even within the first few days of treatment. Gabapentin (1200-2400 mg per day) is safe and effective for the treatment of pain and other symptoms associated with fibromyalgia. In a 12-week, randomized, double-blind study a significantly greater proportion of gabapentin-treated patients achieved response than placebo-treated patients (51% versus 31%). Time course of action: Mechanism of action: gabapentin reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters (mostly noradrenaline, dopamine and serotonin), and Gabapentin binds to a 2d receptors with greater affinity to the a 2d-1 subtype.22 Mutations of a 2d-1 or a 2d-2 block the neuronal actions of gabapentin by prevent-ing its binding, but not mutations in a 2d-3, indicating that the effects are mediated by a 2d subunits of VGCCs.23 Several other sites of action have been described, such as NMDA Gabapentin has a half-life of 5 to 7 hours and a duration of action of 6 to 8 hours. It should be taken consistently for optimal effect, not on an 'as needed' basis. The time for “onset of action” is how long it takes for you to feel the drug’s effects. “Half-life” is a measure of how long it takes until half of the drug becomes inactivated. Since several of the benzos are metabolized into other benzos, to understand the full impact of a benzo, you must include its active (benzo-like) metabolites Mechanism of Action . The mechanism by which gabapentin exerts its analgesic action is unknown, but in animal models of analgesia, gabapentin prevents allodynia (pain-related behavior in response to a . Reference ID: 2998182 This label may not be the latest approved by FDA. Absorption of gabapentin is solely dependent on LAT that are easily saturable, resulting in dose-dependent pharmacokinetics. As the dose of gabapentin increases, the area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC) does not increase proportionally. This activity outlines the indications, mechanisms of action, administration, significant adverse effects, contraindications, monitoring, and characteristics of gabapentin toxicity. This activity also provides clinicians with the necessary skills and tools to treat various types of muscular, neurological, and psychiatric medical conditions Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that can treat nerve pain, seizures, and restless legs syndrome. It may take up to 4 weeks to reach its full effect, depending on the condition and the dose. Shorter duration of action: Though some individuals prefer pregabalin’s longer duration of action (8 to 14 hours) over gabapentin’s shorter duration of action (5 to 8 hours) – others prefer the opposite. For example, persons who use gabapentinoids “as needed” for intermittent and/or short-term management of medical symptoms might only Gabapentin is a medication used to treat various conditions, such as epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. It has a variable absorption, a long half-life, and no known metabolism. The dosage and duration of action depend on the indication, formulation, and renal function.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |