Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
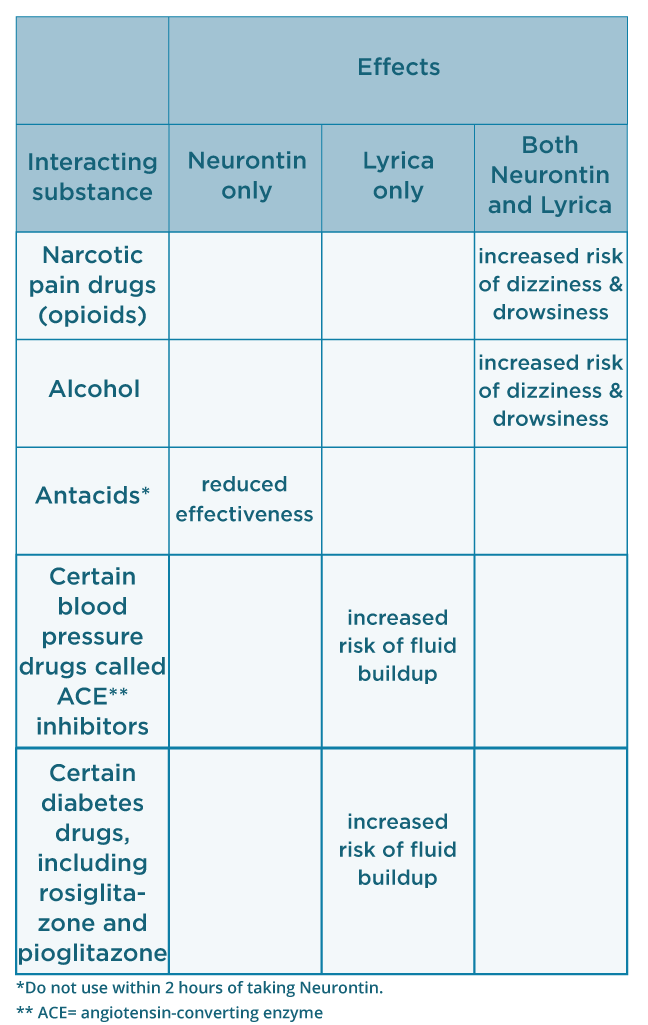
Gabapentin is prescribed for long-term pain control. It isn't used to treat short-term pain. Researchers aren't sure exactly how it works, but it may change how your body feels and reacts to pain. Duloxetine effects begin from the first weeks, while gabapentin effects begin gradually with the best at the end of the third month. Key points: • Medical treatment is used for releiving pain in knee osteoarthritis. • Gabapentin and duloxetine are both effective in reducing pain in knee osteoarthritis. Objective: Gabapentin can treat neuropathic pain syndromes and has increasingly been prescribed to treat nociplastic pain. Some patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA) suffer from both nociceptive and nociplastic pain. We examined the cost-effectiveness of adding gabapentin to knee OA care. While inflammation is a significant driver of arthritis pain, especially in the initial stages, chronic arthritis can often lead to nerve pain as well. This is where gabapentin proves beneficial. It’s particularly helpful in managing chronic, neuropathic pain that can develop as a result of arthritis-related changes in the joints and This suggests that gabapentin can be an effective option for long-term pain management in knee OA. Mechanisms of Gabapentin in Arthritis Pain Relief. Gabapentin's role in pain relief extends beyond its central nervous system effects. Research on an arthritis rat model demonstrated that gabapentin can modulate pain by affecting the dorsal root Method: We used the Osteoarthritis Policy Model, a validated Monte Carlo simulation of knee OA, to examine the value of gabapentin in treating knee OA by comparing three strategies: 1) usual care, gabapentin sparing (UC-GS); 2) targeted gabapentin (TG), which provides gabapentin plus usual care for those who screen positive for nociplastic pain NSAIDs are effective in treating the nociceptive arthritis-related pain. However, safety concerns of NSAIDs may cause clinicians to undertreat arthritis-related pain. In this context, combination therapy may be more appropriate to manage the different pain mechanisms involved. Neurontin (gabapentin), generally prescribed for the treatment of nerve pain, is sometimes used to relieve severe pain caused by knee osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthritis, also known, as wear-and-tear arthritis, can often become so severe that joint replacement surgery is needed. Gabapentin can treat neuropathic pain syndromes and has increasingly been prescribed for nociplastic pain, which some knee osteoarthritis patients can feel along with nociceptive pain. Some studies have also tried to determine whether gabapentin can have anti-inflammatory effects, but nothing conclusive has been found so far. By targeting specific nerve pathways, gabapentin could potentially reduce pain and inflammation in the joints. Researchers believe that gabapentin may also help slow down the progression of OA by reducing oxidative stress and promoting joint repair. Gabapentin and duloxetine were found to provide comparable analgesia and improvement in functional status in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA) after 3 months of treatment, according to a study published in Clinical Rheumatology. Over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve) can help relieve occasional pain triggered by activity your muscles and joints aren't used to — such as gardening after a winter indoors. Prescriptions for gabapentin, which is effective against nociplastic pain and neuropathic pain syndromes, have been on the rise. Knee osteoarthritis (OA) patients sometimes experience both nociceptive and nociplastic pain. Adding gabapentin to treatment for knee OA was analyzed for its cost-effectiveness. Drug Class: Anticonvulsants Brand Names: Gralise, Horizant, Neurontin. 1,200 to 3,000 mg daily in two or three doses. Dizziness; dry mouth; fatigue; high blood pressure; sleepiness; swelling of hands or feet. Do not take an antacid for at least 2 hours after taking this drug. Research on an arthritis rat model demonstrated that gabapentin can modulate pain by affecting the dorsal root ganglia. Specifically, gabapentin was shown to increase the paw withdrawal mechanical threshold (PWMT), indicating reduced pain sensitivity. We know that pain makes does more anxious, and anxiety makes pain worse, so reducing anxiety is an important part of controlling arthritis pain. While gabapentin is often prescribed for dogs with arthritis, there is actually no research that has been done to show that gabapentin is effective or safe in dogs with arthritis. A 2017 study of 150 patients with rheumatoid arthritis found that gabapentin reduced pain and improved sleep quality compared to placebo3. However, these studies have some limitations, such as Gabapentin, brand name drugs include Neurontin and Gabarone, is an anticonvulsant used to treat nerve pain and seizures. Gabapentin is also used in adults to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. So it is not used for arthritis. No its used for nerve pain. rheumatoid arthritis, gabapentin. In cats, gabapentin is most often used as a pain medication for chronic pain, such as from arthritis.. Gabapentin is also recognized as beneficial in reducing the fear responses that a kitty may have to the stress of handling and being examined at the vet. The of Gabapentin for Arthritis Pain Relief. One of the main benefits of Gabapentin for arthritis is its ability to provide pain relief. Chronic arthritis pain can be debilitating and significantly impact a person's quality of life. Gabapentin has been shown to reduce pain intensity and frequency in individuals with arthritis.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |