Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
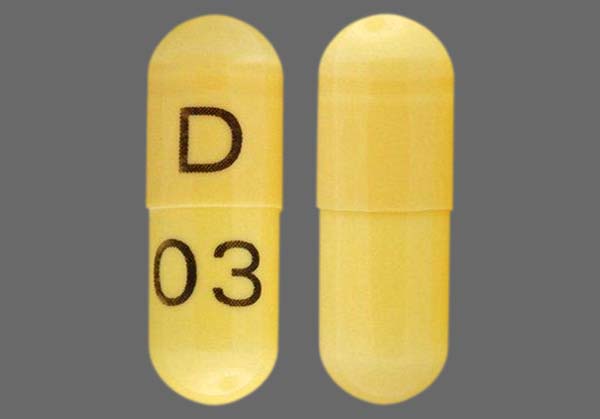
Could gabapentin be more than just an anticonvulsant? As it turns out, the answer is a resounding yes. Today, gabapentin is frequently prescribed off-label for various mental health conditions, joining the ranks of other mood-stabilizing medications like lamotrigine, which has shown promise in treating bipolar disorder and depression. In cases of depression, Neurontin works as a mood stabilizer. How do I take it? Prescribing information states that Neurontin should be taken three times a day. Neurontin comes in tablet, capsule, and liquid solution forms. Neurontin - also known as Gabapentin - is a drug that is sometimes prescribed to those who experience anxiety especially in situations where the anxiety is co-occurring with bipolar disorder. This article explores the usage of Neurontin, as well as the benefits, weaknesses, and side effects for those looking to learn more about this medication The relationship between gabapentin, depression, and suicidality remains an ongoing area of research, with many advocating for comprehensive treatment strategies that prioritize mental health alongside pharmacological interventions. It is crucial to monitor any changes in mood or depression while taking the medication and seek medical attention if necessary.Additionally, gabapentin can interact with other medications, including opioids and certain stomach acid medications, so it is important to inform healthcare providers about all medications being taken. Gabapentin was significantly more effective than lamotrigine and carbamazepine in reducing depressive symptoms on the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory-2 (MMPI-2) depression subscale (50 Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Gabapentin works by mimicking a neurotransmitter in the brain called GABA. GABA has a calming effect on the brain and impaired functioning of GABA has been linked to various mental health conditions such as panic disorder and depression. It’s important to note that the medication gabapentin isn’t a synthetic or lab-made form of GABA. Gabapentin in the treatment of anxiety and depression: Gabapentin is sometimes prescribed off-label for patients with bipolar disorder to reduce anxiety levels or for anxiety disorders. Clinicians have also used it for patients who have anxiety and depression. While studies don’t typically show effectiveness for improving symptoms of depression, there is evidence that gabapentin may have some benefit for anxiety disorders. A rat study found that gabapentin produced behavioral changes suggestive of anxiolysis, or feelings of calmness. Gabapentin has less likely benefit adjunctively for bipolar disorder. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. Background: Previous studies in predominantly bipolar patients have suggested that gabapentin may be useful in treating mood disorders. This report describes its efficacy and tolerability as an adjunctive agent in treatment-resistant depression. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. Limitations of available data include variation in dosing between studies, gabapentin as monotherapy or adjunctive treatment, and differing primary outcomes between trials. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. In 2019, the FDA added a warning and precaution about the possibility of respiratory depression that states: “There is evidence from case reports, human studies, and animal studies associating gabapentin with serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression when coadministered with CNS depressants, including opioids, or in the Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal. Gabapentin has less likely benefit adjunctively for bipolar disorder. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. According to a 2020 review, about 1 to 10% of people may experience a sense of euphoria when taking gabapentin, which may increase the likelihood of misuse.And data suggest that 40-65% of people
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |