Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
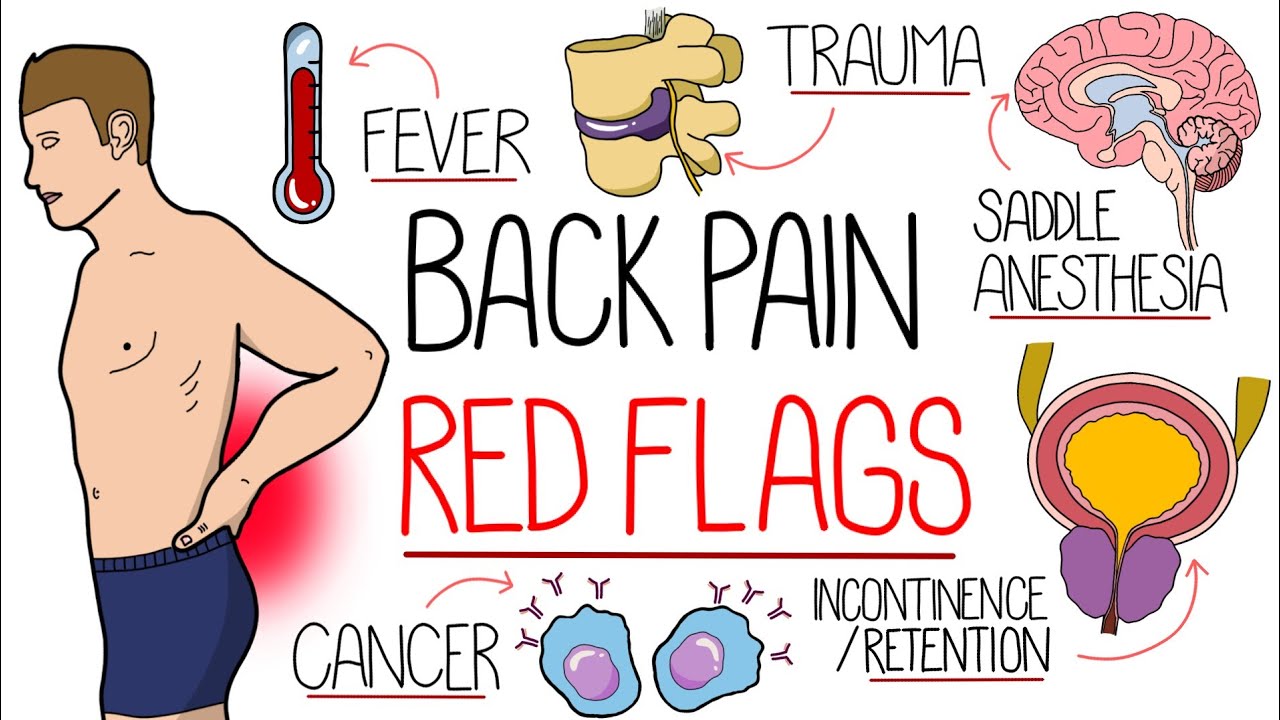
Gabapentin can be very effective in treating various types of back pains, including: Gabapentin for Sciatica: Sciatica, marked by sciatic nerve compression, presents as lower back pain radiating down one or both legs. In recent years—especially as concern over the opioid epidemic has increased—doctors have turned to prescribing the gabapentinoids pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin, others), which have demonstrated benefit for neuropathic pain conditions but not for nonspecific CLBP. In people experiencing nerve pain after having had shingles, gabapentin is thought to change the way pain signals are sent through the body and brain. It's not entirely clear how gabapentin works to treat restless legs syndrome. Side effects of gabapentin. Common side effects of gabapentin include: drowsiness or dizziness; headache or blurred Chronic Low Back Pain (CLBP) is very common, with a lifetime prevalence between 51% and 80%. In majority, it is nonspecific in nature and multifactorial in etiology. Pregabalin (PG) and Gabapentin (GB) are gabapentinoids that have demonstrated Background Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is a global health problem, and gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in the treatment of patients without associated radiculopathy or neuropathy. Therefore, determining their efficacy and safety is of enormous value. Lyrica, Neurontin and other anti-convulsant drugs are ineffective for treating low back pain and may even be harmful to patients, according to a new study published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal. Gabapentin is a remedy for nerve pain that’s also prescribed for back pain. See how it works and if it can help back pain from sciatica, shingles, and more. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. I have also been on 300 mg Gabapentin for about one month (for sleep) and suddenly have developed lower back pain. I have never had an issue with back pain. Extra Strength Tylenol has minimal effect upon the discomfort. I am wondering if the individual who posted on April 11, 2021 continued to have lower back pain while using Gabapentin or if Gabapentin is most effective in relieving neuropathic pain conditions caused by disk herniation, spinal stenosis, diabetic neuropathy, and postherpetic neuralgia. It provides limited sciatica and fibromyalgia relief, and is ineffective for reducing arthritis-related chronic low back pain. Gabapentin (GB) and Pregabalin (PG) have been shown to be helpful in neuropathic pain conditions, such as diabetic neuropathy. Despite no clear rationale, their use for CLBP has significantly increased. A 2016 double-blind RCT (N = 108) investigated gabapentin as a treatment for chronic low back pain with and without a radicular component. 2 This RCT was included in the 2017 meta-analysis but is Despite its many uses, Gabapentin is particularly effective at treating neuropathic (nerve-related) pain. According to research, Gabapentin can often alleviate back problems caused by a herniated disc or spinal stenosis. Spinal herniation occurs when a disc between adjacent spinal vertebrae slips out of place and pinches a nerve. Back pain has an impact on daily life and drives individuals to seek effective treatments, leading many healthcare providers to turn to gabapentin. Originally designed as an anti-seizure medication, gabapentin has found application beyond its initial purpose, addressing not only back pain but also nerve pain, postsurgical discomfort, and People with radiating chronic spine pain may be prescribed gabapentin or pregabalin to treat their nerve-related neck, back and/or leg pain. If you’re taking either of these medications, please Background and objective: Chronic Low Back Pain (CLBP) is very common, with a lifetime prevalence between 51% and 80%. In majority, it is nonspecific in nature and multifactorial in etiology. Pregabalin (PG) and Gabapentin (GB) are gabapentinoids that have demonstrated benefit in neuropathic pain conditions. Gabapentin is prescribed for analgesia in chronic low back pain, yet there are no controlled trials supporting this practice. This randomized, two-arm, 12-week, parallel group study compared gabapentin (forced titration up to 3600 mg daily) to inert placebo. Prescribing gabapentin for chronic, non-specific low back pain is not recommended. Patients who suffer from nerve pain, numbness, and tingling in the legs from sciatica or have diabetic neuropathy One was a small study of high-dose gabapentin (3,600 mg per day) in 43 patients with lumbar radicular pain, and the other was a study of topiramate (300 mg per day) in 96 patients with low back pain. Gabapentin for treatment of radicular low back pain. American Family Physician. Mathieson, S., et al. (2017). Trial of Pregabalin for Acute and Chronic Sciatica. The New England Journal of Medicine. Medicine Optimisation. (2020). Back pain & sciatica – NICE warn against benzos, gabapentinoids & opioids. MedlinePlus. (2020). Capsaicin topical
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |