Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
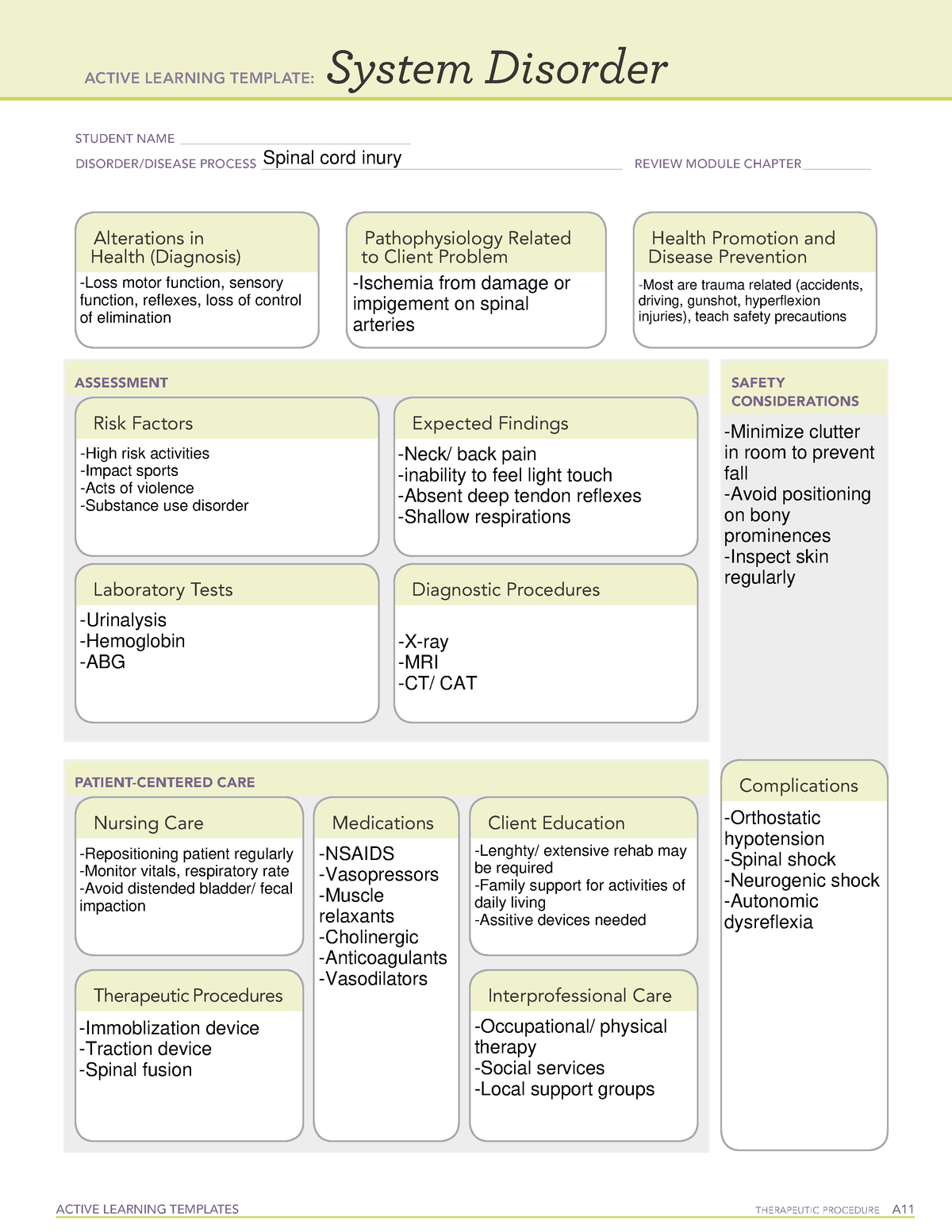
Gabapentin is most effective in relieving neuropathic pain conditions caused by disk herniation, spinal stenosis, diabetic neuropathy, and postherpetic neuralgia. It provides limited sciatica and fibromyalgia relief, and is ineffective for reducing arthritis-related chronic low back pain. Gabapentin, which has been used in the treatment of neuropathic pain, may be effective in the treatment of symptoms associated with LSS. Methods: Fifty-five patients with LSS, who had NIC as the primary complaint, were randomized into 2 groups. Gabapentin could be an option in the conservative management of acute or chronic radicular pain. The efficacy of gabapentin monotherapy was investigated against both acute or chronic radicular pain caused by lumbar disk hernia (LDH) or lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). Gabapentin is a commonly tried drug for spinal stenosis, but effectiveness varies among individuals. 4.0% of members reported high effectiveness, while 44.0% reported no effect. Common combinations include paracetamol (acetaminophen) and physiotherapy. However, it's best to take it at night, as one of the most frequent side effects of gabapentin is drowsiness. Most people will end up taking gabapentin three times daily. However, to ensure a consistent level of gabapentin throughout the day, it's recommended to take the medication at even intervals, approximately every eight hours. Gabapentin for spinal stenosis. Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the space between the bones of your back (vertebrae) and the spinal cord. This can happen as the spine collapses with age or from spine arthritis. As the space narrows, the bones or discs in the spine can compress the spinal cord and cause pain and nerve symptoms. eHealthMe is studying from 322,815 Gabapentin users for the drug's side effects, drug interactions, effectiveness and more. Check Gabapentin in the real world. What is Spinal stenosis? Spinal stenosis (narrowing of spinal column) is found to be associated with 546 drugs and 186 conditions by eHealthMe. Check our latest studies of Spinal stenosis. Pregabalin and gabapentin are antiepileptic drugs that decrease presynaptic excitability. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the use of pregabalin and gabapentin is effective in the symptomatic management of spinal stenosis, compared to other drugs, by using pain and disability rating scales. Certain medications are safer and more effective than others for treating spine pain in older adults, according to a recent study. Among these are the over-the-counter drugs acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil) and some nerve pain drugs, muscle relaxants, and antidepressants. Spinal stenosis is painful because as the spinal cord narrows, it puts pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots. When these nerves become compressed, it causes pain, cramping, weakness, and/or tingling that can radiate from the back to the buttocks and down the legs. One open label study concluded that compared to usual care, gabapentin reduced pain intensity and improved walking distance in lumbar spinal stenosis, a condition associated with neurologic intermittent claudication, manifest as symptoms of leg pain, numbness, and cramping precipitated by standing or walking . In any event he inclusion of non Lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) is a narrowing of the spinal canal that often occurs as a result of disk degeneration or herniation, subluxation of the vertebrae, overgrowth of the facets, or thickening of the ligaments. Additional, less common causes of narrowing include tumor, infection, fracture and epidural lipomatosis. Gabapentin (Neurontin) has been used quite successfully for patients with neuropathic (nerve) pain in the hands and feet. In this study, patients with neurologic intermittent claudication (NIC) from lumbar spinal stenosis were given gabapentin. Class Summary. Use of certain antiepileptic drugs, such as the GABA analogue Neurontin (gabapentin), has proven helpful in some cases of neuropathic pain. [] These agents have central and peripheral anticholinergic effects, as well as sedative effects, and block the active reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin. Keywords: lumbar spinal stenosis, pregabalin, gabapentin, gabapentinoids, treatment. 1 Introduction. Lumbar Spinal Stenosis (LSS) is a degenerative condition that affects the spine’s structures, leading to compression of the thecal sac and nerve structures in the spinal cord and cauda equina. This study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of pregabalin and gabapentin in managing spinal stenosis symptoms compared to other drugs, using pain and disability rating scales. It also aimed to evaluate the improvement in ambulation ability and safety profile associated with their use. Limitations: Variation in degree of spinal stenosis, small sample size. Conclusions: Gralise demonstrated moderate efficacy with reduced pain intensity and increased sleep and was well tolerated in spinal stenosis patients with radicular symptoms. Key words: Spinal stenosis, gabapentin, Gralise®, radicular pain, neuropathic pain As an adjunctive treatment, gabapentin demonstrated efficacy in improving neuropathic pain when added to standard care for lumbar spinal stenosis [75]. The trial included patients up to the age of Injecting a steroid medicine into the space around the pinched nerve may help reduce the swelling and relieve some of the pain. However, steroid shots may not be the best choice for spinal stenosis. Some studies have shown that combined injections of steroids and a numbing medicine relieve back pain no better than shots of numbing medicine alone. If you have lumbar spinal stenosis and have nerve pain in your legs that is reducing your ability to walk, your doctor may prescribe a neuropathic agent, such as gabapentin (Neurontin).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |