Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
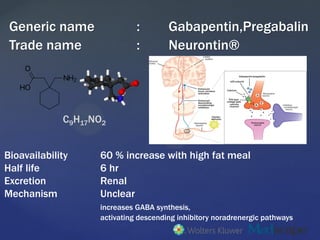
Neurontin (gabapentin) is an anti-eleptic medication used to treat seizures that occur with epilepsy, as well as nerve pain associated with shingles. Learn side effects, dosage, drug interactions, warnings, patient labeling, reviews, and more. The chemical structure of gabapentin (Neurontin) is derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin prevents seizures in a wide variety of models in animals, including generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures. Gabapentin has no activity at We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. 가바펜틴(Gabapentin)는(상품명으로 '뉴론틴' 등이 사용된다) 1973년 미국 화이자사가 개발하여, 뇌전증 및 신경성 통증에 사용되어, 약물과의 상호 작용이 적은 삶의 질을 높이는 항경련제이다. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. FARMACOCINÉTICA Y FARMACODINAMIA: Propiedades farmacodinámicas: La gabapentina está estructuralmente relacionada con el neurotransmisor GABA (ácido g-aminobutírico), pero su mecanismo de acción difiere del de otros varios fármacos que interactúan con las sinapsis del GABA como valproato, barbitúricos, benzodiazepinas, inhibidores de la GABA transaminasa, inhibidores de la captación Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. Gabapentin (Neurontin) Carisoprodol (Soma) Diazepam (Valium) Alprazolam (Xanax) Lorazepam (Ativan) There are also herbs and amino acids available without a prescription that can be used as GABA surrogates: Valerian root. Ashwagandha. Taurine. Brahmi. Bacopa. Glutamine: GABA’s Precursor Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Neurontin (gabapentin) is used to treat seizures and nerve pain caused by the herpes virus. Includes Neurontin side effects, interactions and indications. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] . Structure of GABA: gabapentin and pregabalin. 10. Pharmacokinetics. The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake. They undergo facilitated transport across cell membranes through system l-amino acid transporters (LAT) as both drugs are structurally similar to the amino acid leucine. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Des réactions allergiques et des réactions cutanées, rares mais parfois graves, ont été rapportées avec la gabapentine. En cas de gonflement du visage (lèvres, paupières) ou d'une autre région du corps ou de survenue d'une éruption cutanée sans cause évidente (varicelle, moustiques, orties), prenez d'urgence un avis médical. Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Gabapentin (3-cyclohexyl-GABA) is designed as a lipophilic analogue of GABA for blood-brain barrier penetration and closely resembles pregabalin. Although gabapentin does not directly modify GABA-A receptor function, it may indirectly increase tonic inhibition via enhanced expression of extrasynaptic receptors in specific brain regions Gabapentin is structurally related to GABA. However, it does not bind to GABA A or GABA B receptors, and it does not appear to influence synthesis or uptake of GABA. High affinity gabapentin binding sites have been located throughout the brain; these sites correspond to the presence of voltage-gated calcium channels specifically possessing the Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |