Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
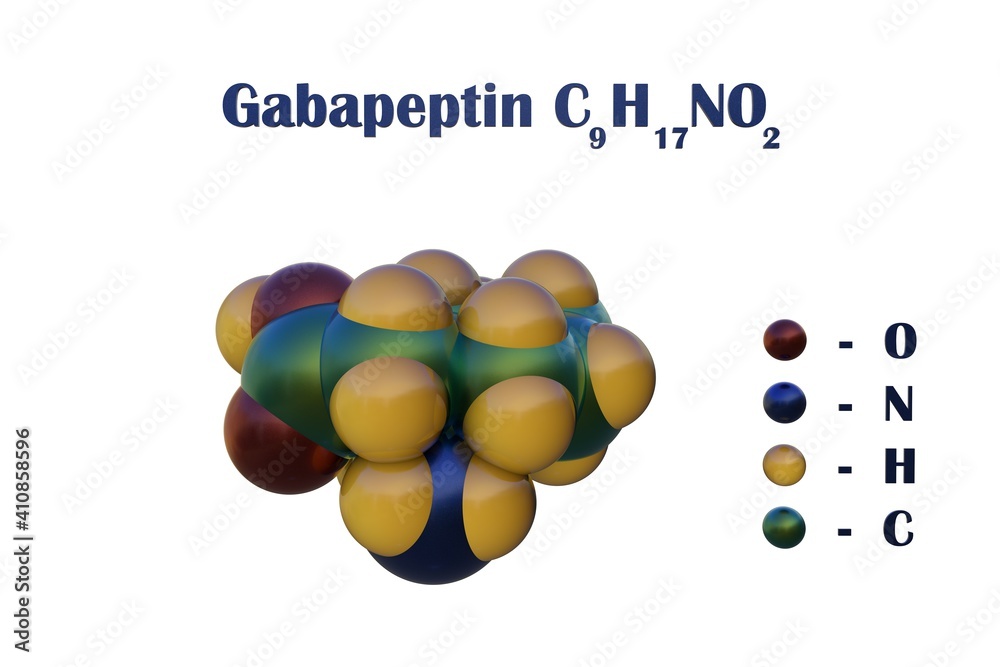
Gabapentin (Neurontin) has been approved by the FDA as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of focal onset seizures. Neurontin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It affects chemicals and nerves in the body that are involved in the cause of seizures and some types of pain. Neurontin is used in adults to treat neuropathic pain (nerve pain) caused by herpes virus or shingles (herpes zoster). Gabapentin is 1 of many antiseizure medications available for the treatment of epilepsy in adults; however, there are potential risks associated with its use. Therefore, it is important to determine the place of therapy of gabapentin in the treatment of epilepsy. What Did We Do? Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. There was a statistically significant difference in seizure frequency from the baseline to the treatment phase between participants receiving placebo and gabapentin 1200 mg, in whom seizure frequency decreased 57%. Gabapentin 900 mg appeared to be ineffective. There was a close relationship between serum gabapentin concentrations and gabapentin Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy: Class IV studies showed that GBP may trigger or exacerbate absence seizures, and myoclonic seizures. 43. According to the USA guidline for epilepsy treatment, the patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy can be treated with gabapentin. 19. Seizure in stroke patients. One of the complications of stroke in adults is Reports that employed gabapentin doses and titration schedules were selected for review. Results: Our review of this literature suggests improved seizure control at higher gabapentin maintenance dosages (< or =3600 mg/d) than are used today in clinical practice (1800 mg/d) without an increase in the incidence of adverse reactions. Most of the Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. Gabapentin (gab-ah-PEN-tin) is the generic name (non-brand name) of the seizure medicine Neurontin (nur-ON-tin) used in the United States, Canada, the UK, and some other countries. Another commonly used name for gabapentin is GBP. Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. For individuals with epilepsy, neurontin can help to control seizures, improving their quality of life and reducing the risk of complications. For those suffering from debilitating neuropathic pain, it can provide much-needed relief, enhancing their ability to function and participate in daily activities. The efficacy of gabapentin (Neurontin), in generalized seizures was evaluated in this 14 week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, add-on, multicenter study. A total of 129 patients with refractory generalized seizures were randomized to receive either placebo or 1200 mg/day gabapentin Gabapentin for partial seizures: According to the guidelines from the American Epilepsy Society, clinicians might consider gabapentin as a potential option for patients aged 60 and older with new-onset focal epilepsy, as it could be similarly effective and better tolerated compared to carbamazepine. Currently, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends gabapentin use for postherpetic neuralgia in adults, and as an adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures with and without secondary generalisation in adults and paediatric patients three years of age or older with epilepsy (U.S. Food and Drug Administration Gabapentin for dogs is commonly prescribed for pain, anxiety, or seizures. It's generally safe, but there are some known side effects to be aware of. Veterinarians commonly prescribe gabapentin to treat pain, seizures, and anxiety in dogs. Gabapentin is a human medication, and its use in veterinary medicine is “off-label,” meaning it is not FDA-approved for pets. Sedation is the main potential side effect of gabapentin, and the level of sleepiness varies from patient to patient. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Neurontin (gabapentin) is an anti-eleptic medication used to treat seizures that occur with epilepsy, as well as nerve pain associated with shingles. Learn side effects, dosage, drug interactions, warnings, patient labeling, reviews, and more. Gabapentin has efficacy as an add-on treatment in people with drug-resistant focal epilepsy, and seems to be fairly well-tolerated. However, the trials reviewed were of relatively short duration and provide no evidence for the long-term efficacy of gabapentin beyond a three-month period. The results Gabapentin should not be abruptly discontinued after long-term use as seizures can be precipitated. Instead, gabapentin should be gradually tapered off over a couple of weeks. Many commercially prepared gabapentin oral liquids are sweetened with xylitol, which has toxic properties in the dog. The issue can be avoided by having liquid
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |