Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
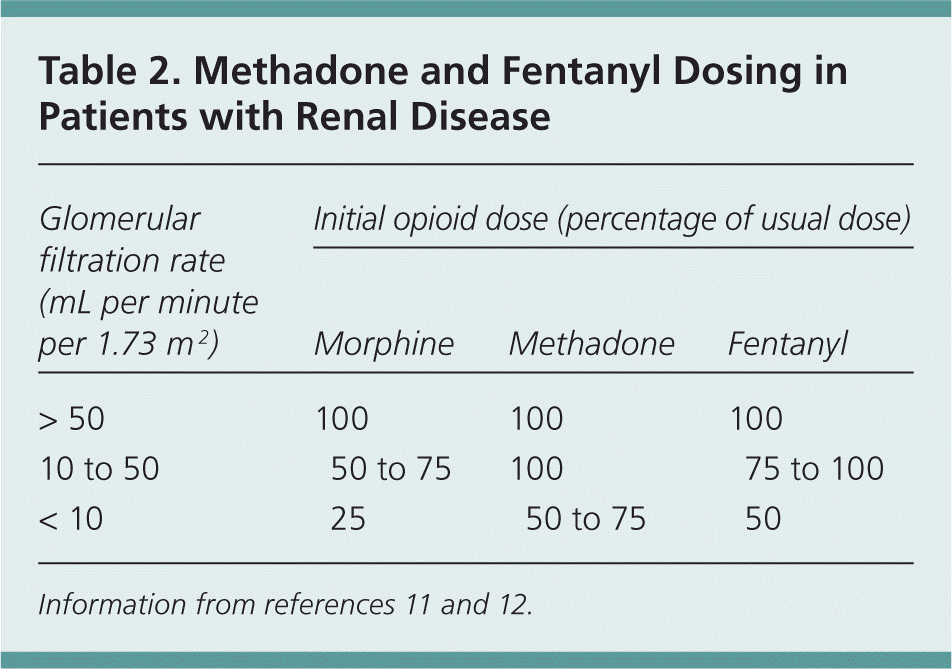
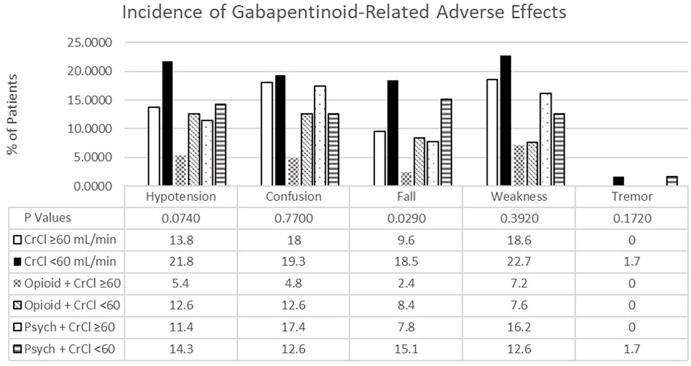
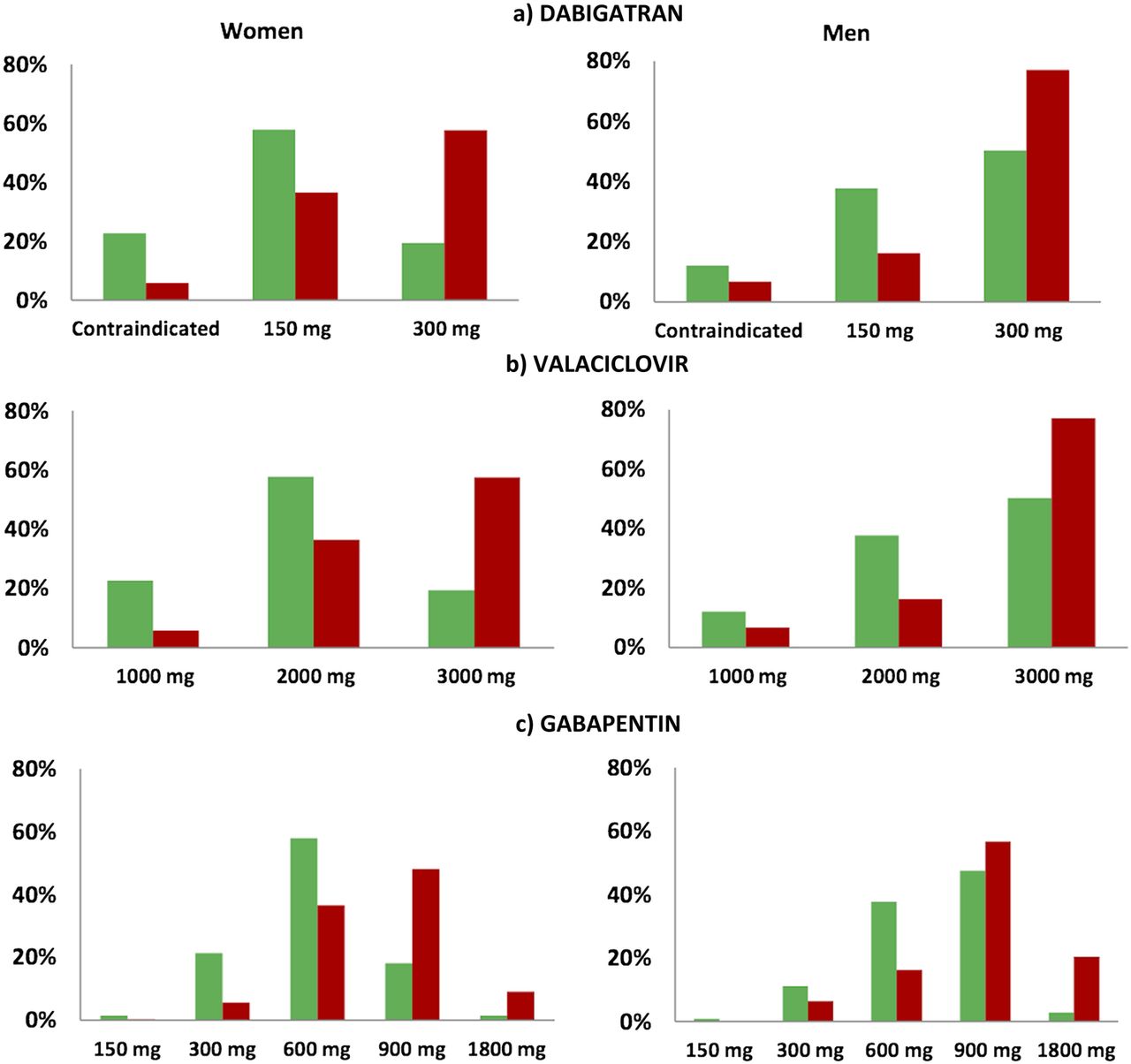
Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. the kidney, and pharmacokinetic studies show a stepwise prolongation in the elimination half-life of gabapentin and pregabalin as kidney function declines.9,10 Gabapentinoids should therefore be started at lower doses in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD; guidelines are summarized in Table S1).1-3,11 Although the risk of gabapentinoid Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Take 900-1200 gabapentin daily over past 20 years. Experiencing severe side effects of gabapentin that Im beginning to think correlate with decreased kidney function. It’s becoming cyclic. Take normal dose of gabapentin until start to become confused and lethargic. Taper gabapentin and start to return to normal. Twice a day helps neuropathy, also helps blood sugar and protects the kidney. When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. This study evaluated GP prescribing patterns and whether excessive dosing was associated with increased incidence of gabapentinoid-related Why is Kidney Function Important When Considering Gabapentin? Gabapentin’s reliance on renal excretion is the crux of the problem. Unlike many drugs metabolized by the liver, gabapentin’s primary pathway out of the body is through the kidneys. The half-life of gabapentin immediate-release formulation is 5–7 hours in patients with normal renal function and is prolonged up to 52 hours in patients with CrCl<30 mL/min. 26 The half-life of pregabalin is 16.7 hours in patients with CrCl 30–59 mL/min, 25 hours in patients with CrCl 15–29 mL/min, and 48.7 hours in patients with CrCl<15 Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. This elderly patient had been on a dose of (Neurontin) gabapentin 600 mg three times daily for peripheral neuropathy. Over time, the patient’s kidney function had been declining and was diagnosed with chronic kidney disease. Family had begun to notice that the patient was becoming more lethargic and dizzy. The patient had also made the [] Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. In individuals with normal renal function, gabapentin clearance is 100 ml/min, which is equivalent to a normal creatinine clearance. On the other hand, in patients with ESRD and on HD, gabapentin clearance with HD is approximately 142 ml/min with an elimination half-life of about four hours with HD, which makes HD an effective treatment option Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |