Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
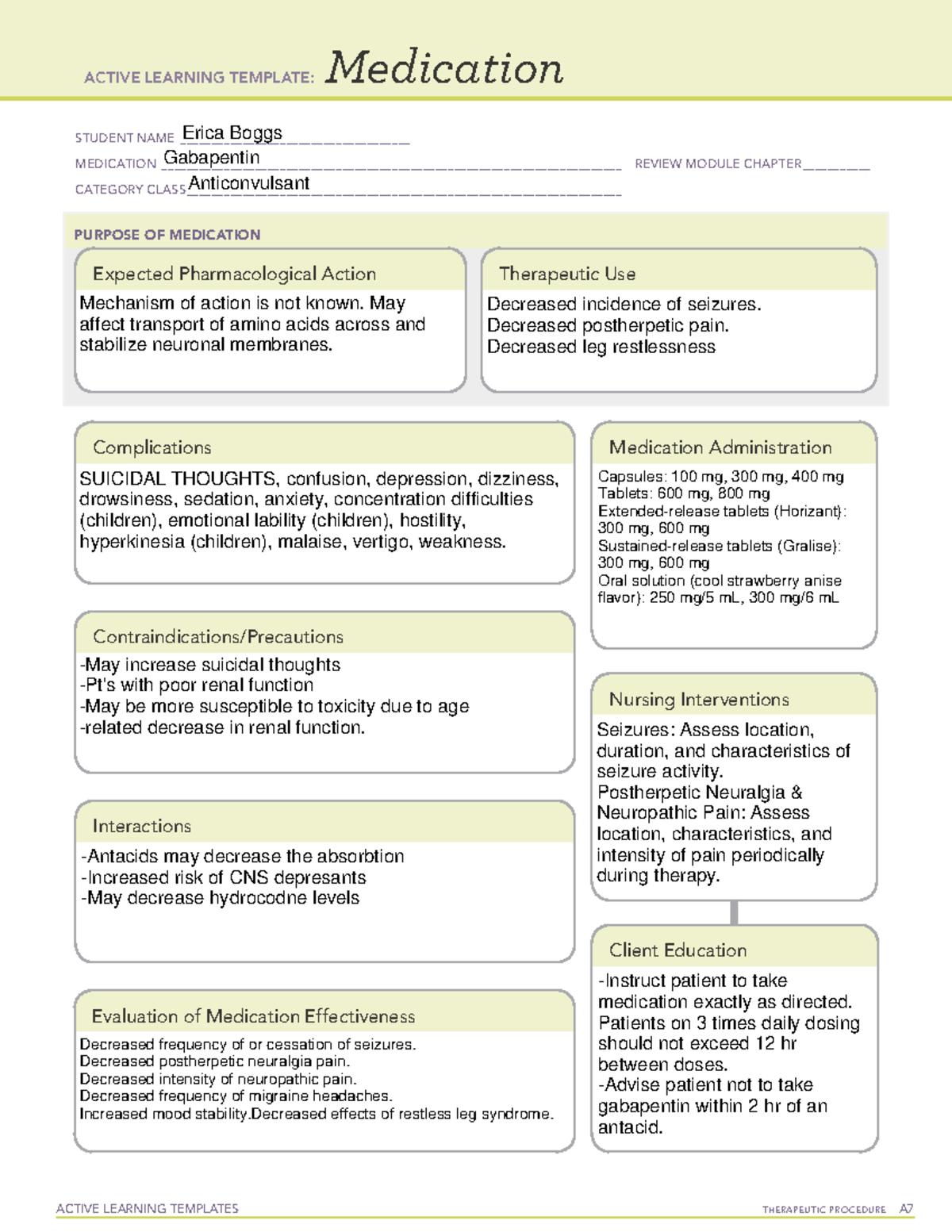
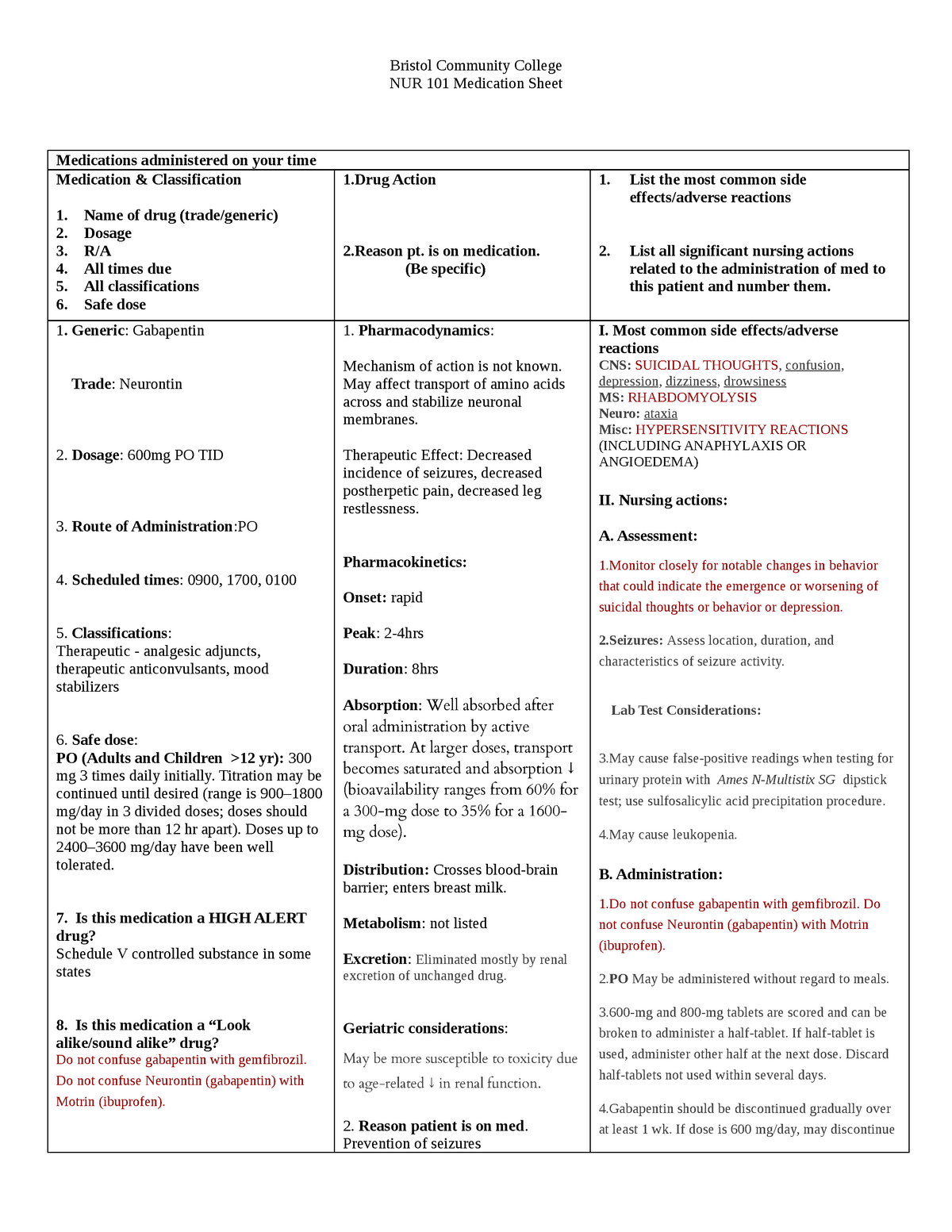
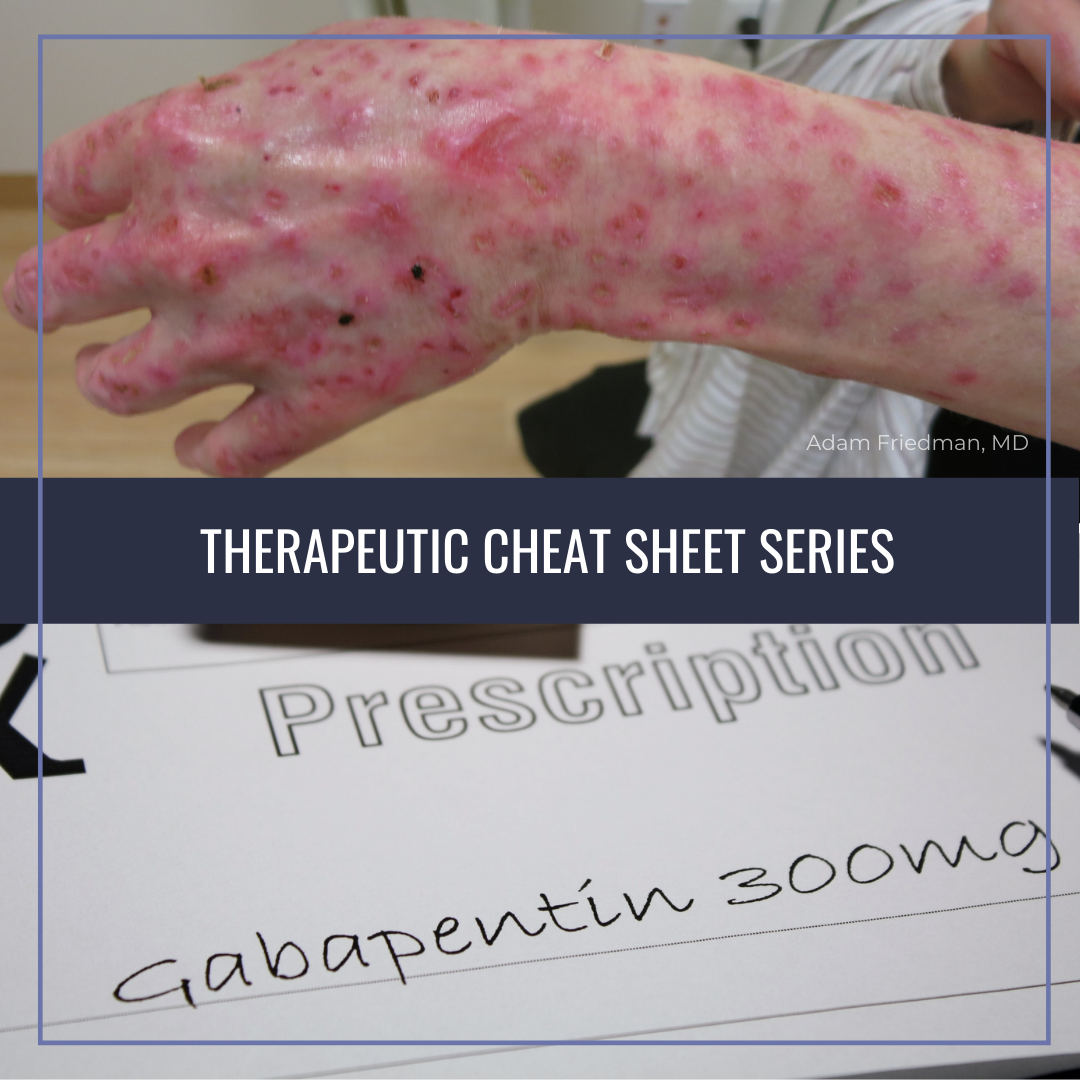
Grab our free cheatsheet covering the 50 most commonly prescribed medications right here: to all the episodes at: Gabapentin is structurally related to the neurotransmitter GABA but is neither a GABA agonist nor antagonist. Gabapentin-binding sites have been identified throughout the brain tissues e.g. neocortex and hippocampus. However, the exact mechanism of action is still unknown. ANTIEPILEPTICS, PART 2: DRUG NAME: vigabatrin (Sabril) gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise) CLASS: GABA inhibitors: GABA analogues: MECHANISM OF ACTION: Prevent GABA reuptake into presynaptic neurons; ↑ GABA concentration in synapse; ↓ seizure activity NCLEX Review: Gabapentin (Neurontin) - Mechanism of Action, Uses, Side effects, Contraindications, and Nursing considerationsAction: 0:20Uses: 0:29Side effec In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Nursing Considerations Therapeutic Effects Side/Adverse Effects; Anticonvulsant: gabapentin: Administer first dose at bedtime to decrease dizziness and drowsiness Monitor for worsening depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior Taper dose; do not stop abruptly: Decreased neuropathic pain or seizures Report to Physician or nurse if any of those side effect / adverse reaction occurs. Tylenol Teaching 2619 SN to educate patient concerning the use of gabapentin is to increased pain relief affects by using the CNS to decrease symptoms of pain and assist Tramadol or other prescribed pain medications, even Tylenol ER in ultimate pain relief. We use Gabapentin for the prevention of seizures for peripheral neuropathy, for neuropathic pain and for the prevention of migraines. So some of the side effects that we see with Gabapentin are things like drowsiness, facial edema, hypertension, and confusion. Gabapentin (brand name Neurontin) is classified therapeutically in a few different ways. As an anticonvulsant, an analgesic adjunct, and a mood stabilizer. Since the exact mechanism is unknown, Gabapentin is one of those drugs that aren’t in a pharmacologic class. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. Generic name: Gabapentin. Brand names: Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant, Gabarone. Pharmacologic class: Anticonvulsant, Antiepileptic. Therapeutic class: Anticonvulsant, Analgesic for neuropathic pain. gabapentin (ga-ba- pen -tin) Neurontin. Therapeutic: analgesic adjuncts, therapeutic, anticonvulsants, mood stabilizers. Partial seizures (adjunct treatment). Postherpetic neuralgia. Unlabeled Use: Chronic pain. Prevention of migraine headache. Bipolar disorder. Anxiety. Mechanism of action is not known. Antiseizure agents (also known as antiepileptic drugs or as anticonvulsants) are drugs used to manage epilepsy, the most prevalent neurological disorder. Antiseizure agents of choice depends on the type of epilepsy, age of the patient, patient tolerance, and specific patient characteristics. Table of Common Drugs and Generic Names Here is a table of commonly encountered antiseizure agents Pain Management: Gabapentin Page 2 _____6. Which of the following patients is at highest risk for serious adverse effects of Neurontin: A. 32-year old nursing mother B. 60-year old woman with hypertension C. 75-year old man with emphysema D. 49-year old man who is immunocompromised _____7. Abrupt discontinuation of Neurontin is likely to cause: Gabapentin works by affecting the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, specifically targeting calcium channels. By modulating these channels, it helps to reduce the excessive electrical activity in the brain that can lead to seizures in individuals with epilepsy. Gabapentin (Neurontin) Nursing Considerations Created Date: 3/23/2022 10:18:38 PM Assess location, characteristics, and intensity of pain periodically during therapy. Monitor frequency and intensity of pain on pain scale. Restless Leg Syndrome: Assess frequency and intensity of restless leg syndrome prior to and periodically during therapy. Lab Test Considerations: Gabapentin (Neurontin) Nursing Considerations Created Date: 3/23/2022 10:18:38 PM gabapentin (gab ah pen' tin)Neurontin . Pregnancy Category C . Drug class. Antiepileptic . Therapeutic actions. Mechanism of action not understood; antiepileptic activity may be related to its ability to inhibit polysynaptic responses and block posttetanic potentiation. SN instructed patient about Gabapentin ( Neurontin ). It is a medication used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain and hot flashes. It is also used for restless leg syndrome. It is a first line agent for the treatment of neuropathic pain arising from diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, and central neuropathic pain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |