Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 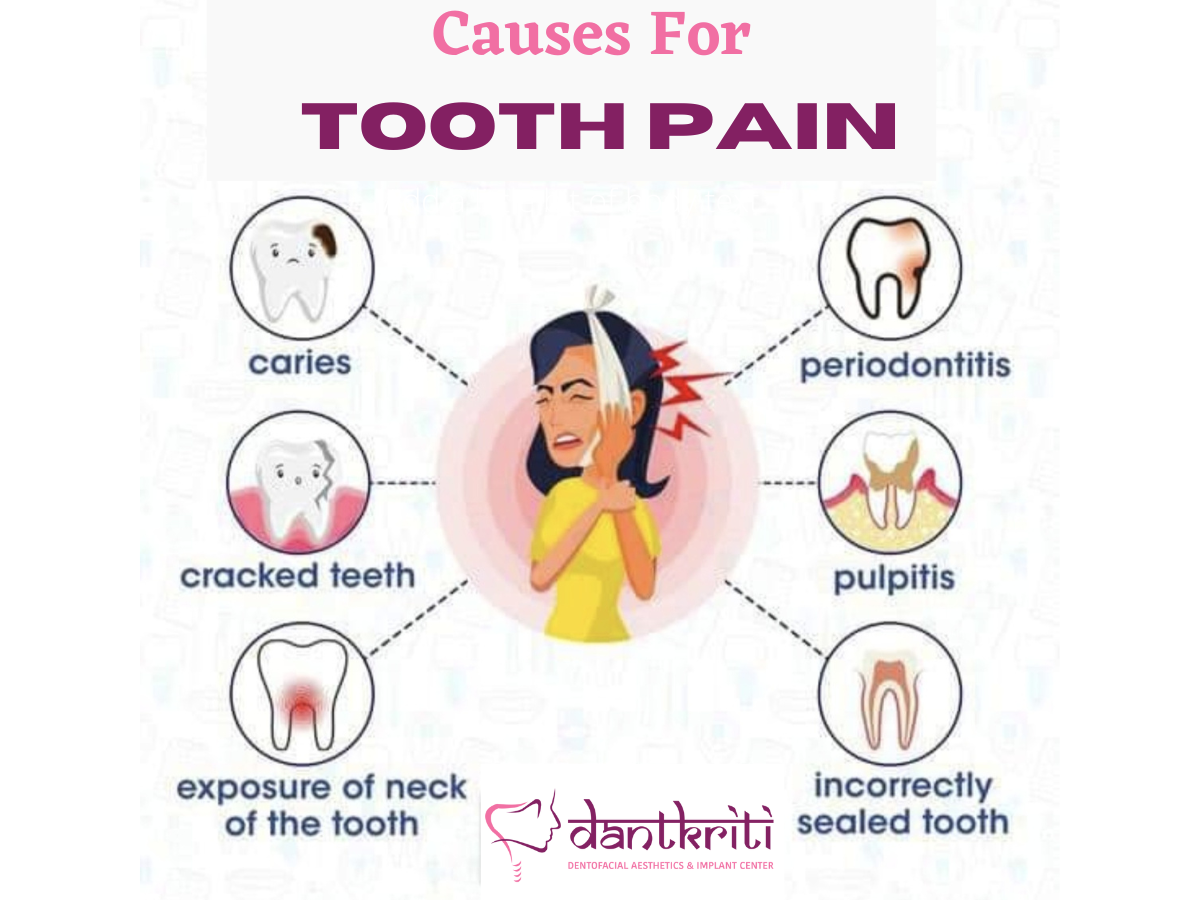 |
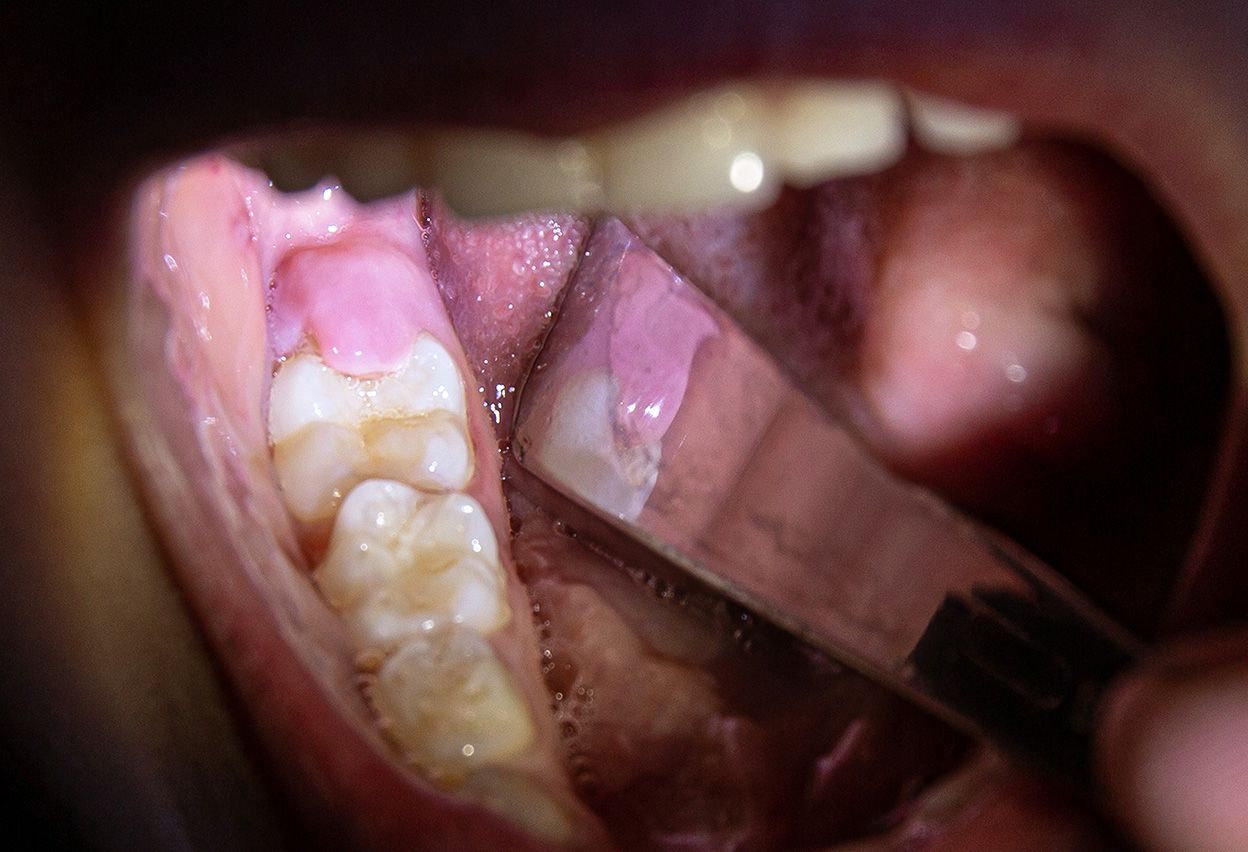
Gabapentin, a medication most commonly used to treat epilepsy and nerve pain, has been linked to tooth decay in certain cases. While not a universally recognized side effect, some patients have reported notable tooth problems after long-term Gabapentin use. Careful dental hygiene and routine dentists' visits may aid in minimizing this risk. Gabapentin didn’t do anything for my tooth pain. However I HIGHLY recommend taking 2 Tylenol and 2 Motrin at the same time. It knocks my tooth pain completely out. Moved Permanently. The document has moved here. “We hypothesized that using a combination of the non-opioid pain medications and adding gabapentin to the mix for pain would be an effective strategy to minimize or eliminate opioids for dental pain,” said Yanfang Ren, DDS, PhD, MPH, professor and clinical chief, Howitt Urgent Dental Care. Tooth pain or pain at the site of a tooth extraction. More often in molars and in maxilla. Continuous or almost continuous. Usually localized to tooth at onset. Can spread to wider area of face or neck. Moderate severity. Deep, poorly localized. Dull, aching. Occasional sharp pain. Mechanical stimulation or pressure to site of pain. The best pain reliever for a tooth ache, or really any transient pain is ibuprofen. (I worked with a dentist for 15 years.) If you don't already take Gabapentin, no one is going to prescribe it for you for a tooth ache. A long-term study that took place at a New York dental clinic makes the strong case that giving patients nonopioid painkillers for dental pain is as effective as opioids, echoing a growing body of work—and messaging—that dentists should minimize prescribing opioids for pain. Unbelievable how fast my teeth deteriorated while continuing to see a dentist it was absurd. I first put $17,000 out of pocket into my mouth trying to save my own teeth in my mid to late 30's. I continually wad told dental work is expensive, but like that. I'm 42 with a full upper denture, and 7 teeth remaining on the bottom. While primarily known for managing nerve pain associated with conditions like postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy, studies indicate that gabapentin can offer analgesic effects for dental pain, particularly in reducing postoperative endodontic pain. Gabapentin is thought to be particularly effective for tooth pain because it can specifically target neuropathic pain, which is pain caused by damage or dysfunction of the nerves. Many dental conditions can lead to nerve damage in the teeth, such as tooth decay, infection, or dental trauma. However, most dental operatory patients experience persistent pain; hence, the correct term is pretreatment rather than preemptive in the dental scenario. The root canal procedure can trigger prostaglandin production due to trauma from severing the pulp and irritation of the periodontal ligament after establishing patency, cleaning, and shaping PubMed Central (PMC) is a free digital repository that archives publicly accessible full-text scholarly articles in the biomedical and life sciences. In terms of tooth pain, especially when caused by nerve irritation or damage—such as after a dental procedure or from an abscess—gabapentin can help alleviate discomfort by addressing the underlying nerve issues rather than just masking the symptoms. Gabapentin, a medication originally developed to treat epilepsy, has gained recognition for its effectiveness in managing nerve-related pain, including toothaches. This medication works by modulating the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, reducing the transmission of pain signals. How Gabapentin Works to Provide Toothache Relief? 2020 in dental clinics affiliated to US dental schools7,15, though considerable evidence demonstrates that non-opioid analgesics, such as NSAIDs or a combination of NSAIDs such as ibuprofen with acetaminophen (N-acetyl-para-aminophenol, or APAP), are superior to opioids for dental pain after dental extractions, including third molar surgeries16-18 This study showed a shift in prescribing in our clinic from opioids and single-medication analgesics to nonopioids and multimodal analgesia to manage postoperative dental pain. Hi Cleo, do you think the gabapentin is doing something for you in terms of enhancing pain medication or in relation to epilepsy, the reason I'm asking is because I was taking gabapentin to enhance my pain medication supposedly, My doctor weaned me off gabapentin my pain levels did not increase or become worse, however, I did notice that my A combination of analgesics prescribed with gabapentin after dental procedures was shown to be just as effective for treating pain as opioids, researchers reported in JAMA Network Open. In a new study at the University of Rochester Medical Center’s Eastman Institute for Oral Health (EIOH), researchers found that gabapentin, when combined with ibuprofen or acetaminophen, was more effective than opioids in relieving pain after tooth extractions.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |