Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-103265210-56a8fbb73df78cf772a27c25.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
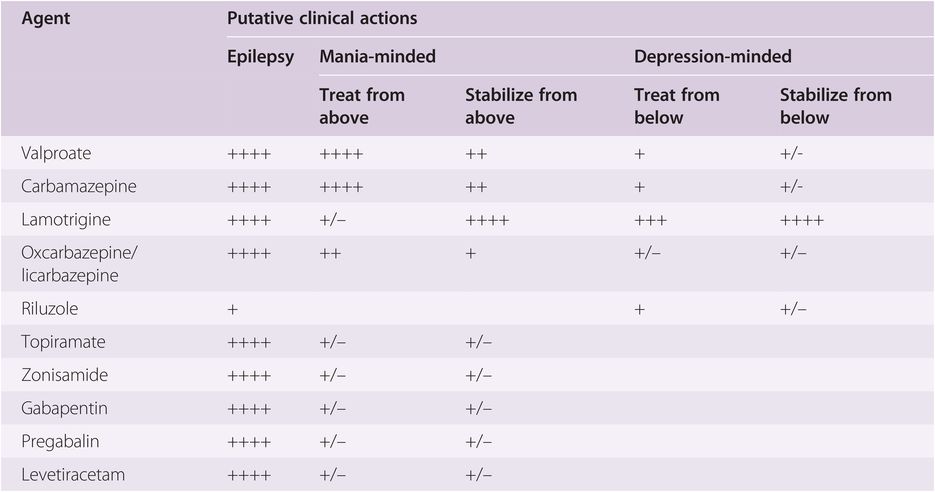
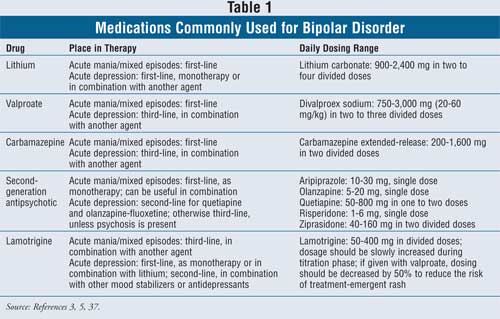
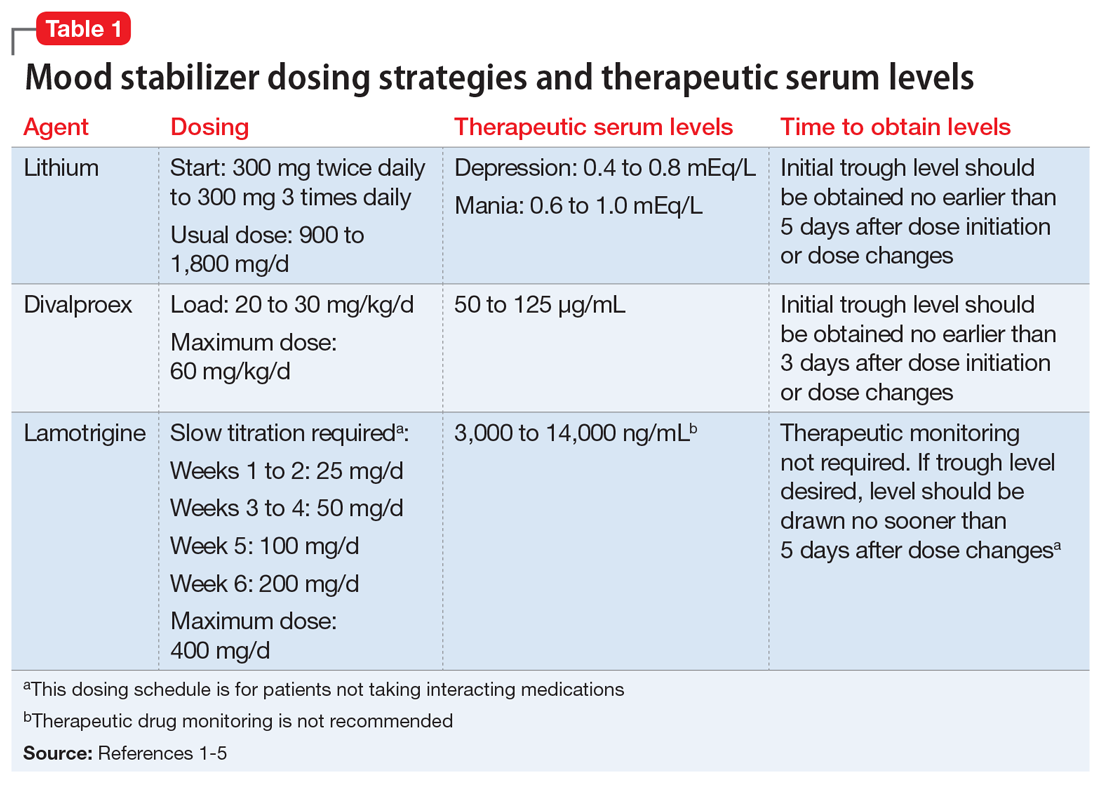
medications, mood stabilizer use and dosage, evidence regarding poor response to standard mood stabilizers be-fore gabapentin use, evidence regarding whether during gabapentin treatment mania or hypomania occurred, ad-verse events, maximum and maintenance gabapentin dose and duration of treatment, indications for treatment Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use disorder. There is sufficient evidence to consider gabapentin as a third-line treatment for social anxiety disorder and severe panic disorder. Gabapentin (Neurontin) Primer Gabapentin (Trade name: Neurontin) is an anticonvulsant. It is commonly also used off-label for anxiety disorders, restless leg syndrome, and in alcohol use disorder. It is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Gabapentin is licensed for use in the USA for the treatment of focal seizures and post-herpetic neuralgia [1] and in the UK for focal seizures and peripheral neuropathic pain [2]. Pregabalin For 1 year, 13 patients received adjunctive gabapentin with standard mood stabilizers and 12 patients received adjunctive placebo. On the basis of the CGI-BP, gabapentin-treated patients showed significant improvement from baseline to month 12. Adjunctive therapy of gabapentin to stable doses of mood stabilizers or atypical antipsychotics, initiated at 300 mg at bedtime and increased by 300 mg every four nights until symptom relief or adverse effects were noted. Final GBP dose was clinically determined. Maximum dose 3600 mg per day in divided doses (range 600 mg to 3300 mg). Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. American Psychological Association: Gabapentin has been “largely discredited as a mood stabilizer for bipolar disorder.” Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance : Gabapentin “was used frequently for treatment of bipolar disorder, but controlled studies found it was no more effective than a placebo.” By affecting neurotransmitters, gabapentin might help improve mood and overall emotional well-being. Bipolar Disorder. Gabapentin is also used to manage bipolar disorder, mainly when mood stabilizers or antipsychotic medications are not sufficient. Gabapentin binds to voltage-gated calcium channels. If used as a mood stabilizer or anti-depressant, the dose is usually between 900 and 2,000 mg a day. But, it may also be increased for better results. Off-label gabapentin (Neurontin) got a bad rep when it missed the mark in bipolar disorder, but there may be something worth salvaging in this drug. Here, we weigh its pros and cons for anxiety, substance use disorders, sleep, pain, and hot flashes, and compare it to its underutilized cousin, pregabalin (Lyrica). After receiving gabapentin 600–3,600 mg/d for 10 weeks, mood scale scores were no different between treatment groups. 19 In a double-blind, randomized, crossover series (N = 31), 20 patients with refractory bipolar and unipolar mood disorder received three 6-week monotherapy treatments of lamotrigine, gabapentin, or placebo. Gabapentin use in elderly patients. Gabapentin can be used in elderly patients, but caution should be exercised due to age-related changes in renal function. A lower starting dose may be necessary to prevent overdose and accumulation of the drug in the body. Monitoring of kidney function is recommended. Gabapentin use in pediatric patients According to Psycom, gabapentin for depression may follow a different dosage pattern. Dosage of between 900 and 2,000 mg a day works as a mood stabilizer or antidepressant. Some people experience improvement within a week after treatment initiation, others need more time to feel significant symptom relief. Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. These results should be confirmed in randomized clinical trials. When I finally met the doctor who diagnosed my bipolar disorder, he prescribed gabapentin as a mood stabilizer, as well as a sleeping aid (Ambien), and Zoloft (the only antidepressant that ever worked for me). I have been on this regimen for almost 3 years now and I fully believe it has saved my life!"
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-103265210-56a8fbb73df78cf772a27c25.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |