Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
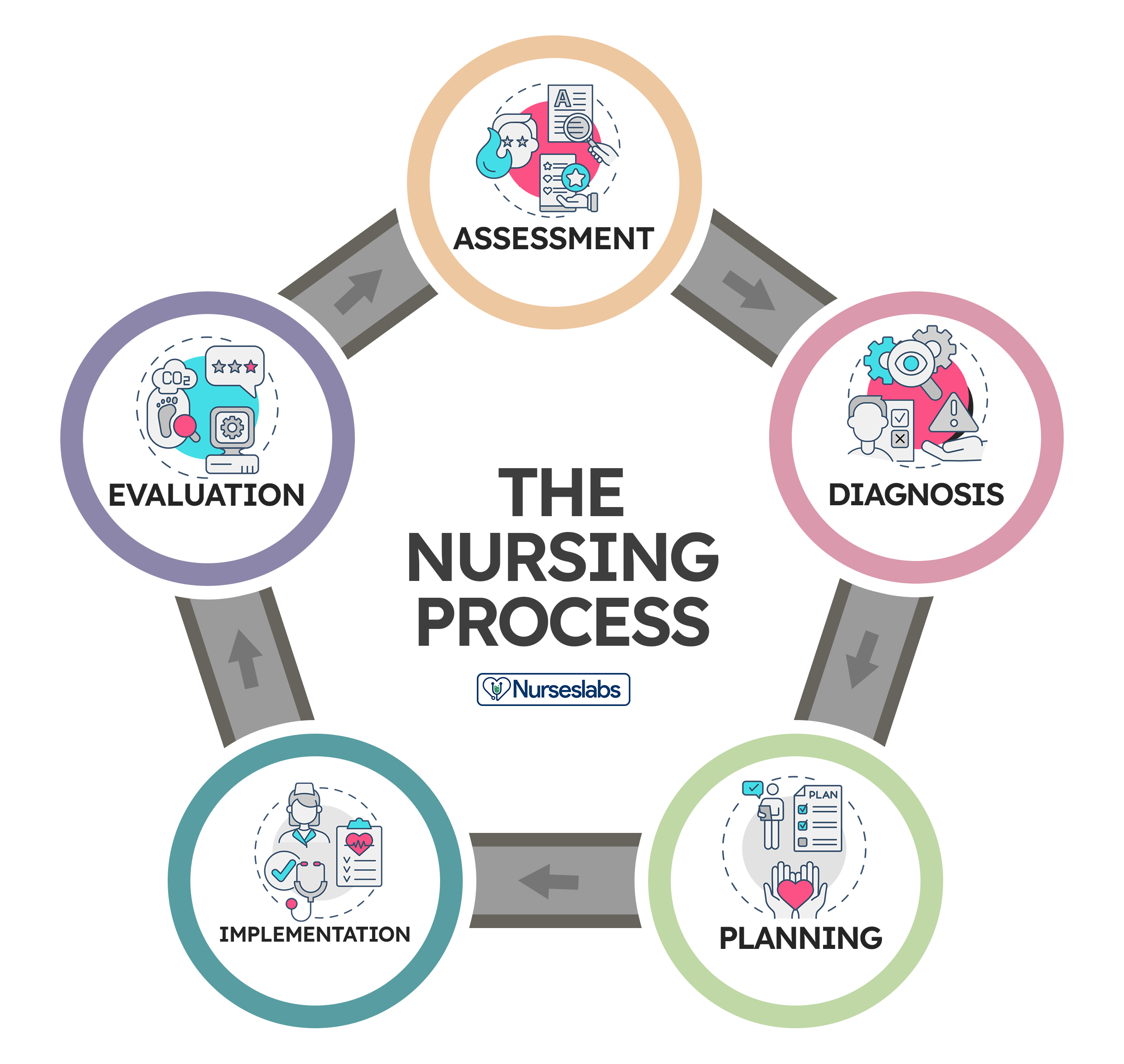
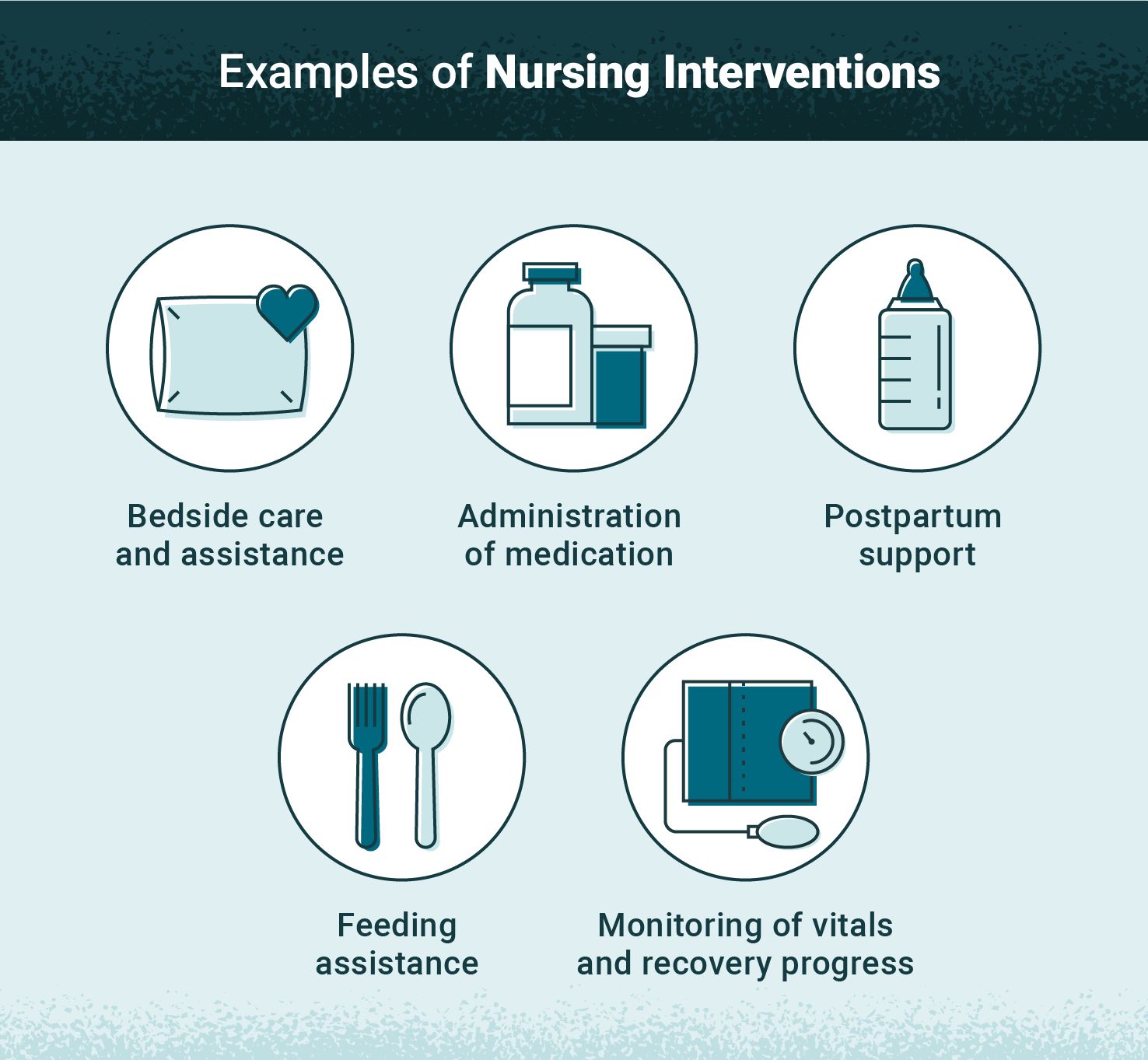
What is the generic name? GABAPENTIN. What is the Trade Name for GABAPENTIN? Neurontin. What are the Indications for GABAPENTIN? 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE NEURONTIN ¬Æ is indicated for: Management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in adults and pediatric patients 3 years and older with Antiseizure agents (also known as antiepileptic drugs or as anticonvulsants) are drugs used to manage epilepsy, the most prevalent neurological disorder. Antiseizure agents of choice depends on the type of epilepsy, age of the patient, patient tolerance, and specific patient characteristics. Table of Common Drugs and Generic Names Here is a table of commonly encountered antiseizure agents So let's take a look at a few nursing considerations. Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to Find information on Gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant) in Davis’s Drug Guide including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half life, administration, and more. Davis Drug Guide PDF. nursing considerations As needed, open gabapentin capsules and mx contents with water, fruit juice, apple sauce or pudding before administration. Give drug at least 2 hours after an antacid. Gabapentin (Neurontin) Nursing Considerations Created Date: 3/23/2022 10:18:38 PM Antiseizure agents (also known as antiepileptic drugs or anticonvulsants) are drugs used to manage epilepsy, the most prevalent neurological disorder. Antiseizure agents of choice depend on the type of epilepsy, age of the patient, patient tolerance, and specific patient characteristics. It is thought that Gabapentin may play a role in neural membranes. We use Gabapentin for the prevention of seizures for peripheral neuropathy, for neuropathic pain and for the prevention of migraines. Nursing Considerations for Gabapentin. When administering or caring for patients taking gabapentin, nurses should consider several important factors. Nursing Assessment. 1. Assess the patient’s medical history, including any known allergies, previous adverse reactions to gabapentin or similar medications, and relevant medical conditions. Monitor closely for notable changes in behavior that could indicate the emergence or worsening of suicidal thoughts or behavior or depression. Assess location, duration, and characteristics of seizure activity. Assess location, characteristics, and intensity of pain periodically during therapy. Monitor frequency and intensity of pain on pain scale. So let's take a look at a few nursing considerations. Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to ANTIEPILEPTICS, PART 2: DRUG NAME: vigabatrin (Sabril) gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise) CLASS: GABA inhibitors: GABA analogues: MECHANISM OF ACTION: Prevent GABA reuptake into presynaptic neurons; ↑ GABA concentration in synapse; ↓ seizure activity Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used in the prevention of partial seizures. It is frequently used for neuropathic pain including diabetic neuropathy, radiculopathy, shingles, and trigeminal neuralgia. Apply nursing process considerations for gabapentin to specific patient situations. Correctly calculate dosage for gabapentin. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an amino acid that serves as a neurotransmitter in the normal central nervous system. It acts as a calming neurotransmitter to inhibit transmission of nerve impulses. Nursing Considerations Therapeutic Effects Side/Adverse Effects; Anticonvulsant: gabapentin: Administer first dose at bedtime to decrease dizziness and drowsiness Monitor for worsening depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior Taper dose; do not stop abruptly: Decreased neuropathic pain or seizures However, gabapentin is often used off-label for a variety of conditions. In fact, one study revealed that 83% of gabapentin prescriptions were for off-label use. Some of the common reasons gabapentin is prescribed are: Neuropathic pain and diabetic neuropathy (this is very common) Bipolar disorder and anxiety; Migraine prevention Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. Generic name: Gabapentin. Brand names: Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant, Gabarone. Pharmacologic class: Anticonvulsant, Antiepileptic. Therapeutic class: Anticonvulsant, Analgesic for neuropathic pain. In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Read this chapter of Davis's Drug Guide for Rehabilitation Professionals online now, exclusively on F.A. Davis PT Collection. F.A. Davis PT Collection is a subscription-based resource from McGraw Hill that features trusted content from the best minds in PT. Gabapentin is structurally related to the neurotransmitter GABA but is neither a GABA agonist nor antagonist. Gabapentin-binding sites have been identified throughout the brain tissues e.g. neocortex and hippocampus. However, the exact mechanism of action is still unknown.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |