Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
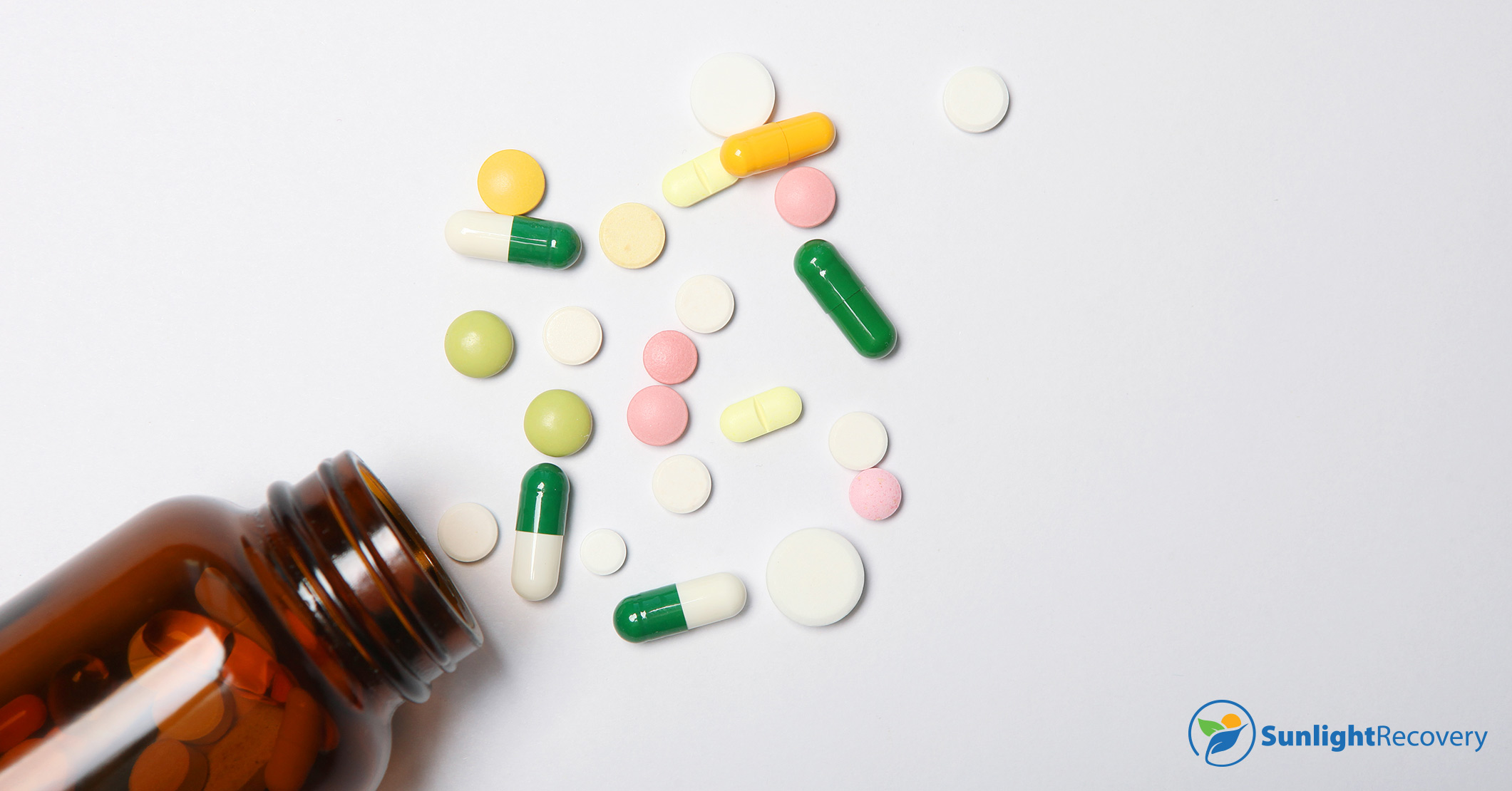
Gabapentin is widely used in the United States for a number of off-label indications, often as an alternative to opioid therapy. Increasing evidence has emerged suggesting that gabapentin may not be as benign as once thought and may be associated with substance abuse in concert with opioids. “Gabapentin is widely used in the United States for a number of off-label indications, often as an alternative to opioid therapy. Increasing evidence has emerged suggesting that gabapentin may not be as benign as once thought and may be associated with substance abuse in concert with opioids Off-label prescribing does not necessarily signify that the medication is being used improperly, and in some cases, reliable research might validate its use. Nonetheless, prescribing gabapentin for off-label use might also result in negative consequences, including adverse drug effects, liability concerns, and a lack of reimbursement due to the OBJECTIVES: (1) Describe the relevance of off-label use of gabapentin to man-aged care pharmacy; (2) summarize recent FDA warnings and media reports related to off-label gabapentin use; (3) review medical information pertaining to the off-label use of gabapentin; (4) outline alternatives to off-label use of The drug Neurontin is used as an example of why it is permissible for physicians to engage in off-label prescribing, but off-label marketing by pharmaceutical companies is prohibited by the FDA. Off-label gabapentin (Neurontin) got a bad rep when it missed the mark in bipolar disorder, but there may be something worth salvaging in this drug. Here, we weigh its pros and cons for anxiety, substance use disorders, sleep, pain, and hot flashes, and compare it to its underutilized cousin, pregabalin (Lyrica). For gabapentin, the only pain-related indication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is postherpetic neuralgia. For pregabalin, FDA-approved indications related to pain are limited to postherpetic neuralgia, neuropathic pain associated with diabetic neuropathy or spinal cord injury, and fibromyalgia. The authors concluded that gabapentin is associated with reduction in acute pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (the later indication is not approved by the FDA), and that there is limited evidence to support the use of gabapentin for other types of neuropathic pain and pain disorders. 1 This Editorial Gabapentin is widely used in the United States for a number of off-label indications, often as an alternative to opioid therapy. Increasing evidence has emerged suggesting that gabapentin may not be as benign as once thought and may be associated with substance abuse in concert with opioids. Observations: This report summarizes the limited published evidence to support off-label gabapentinoid uses, describes clinical cases in which off-label use is problematic, and notes how review articles and guidelines tend to overstate gabapentinoid effectiveness. This study examined off-label use of gabapentin for psychiatric indications and its concomitant use with CNS-D prescription drugs in a nationally representative sample of ambulatory care office visits. Less than 1% of outpatient gabapentin use was for FDA-approved indications. Methods: National Ambulatory Care Medical Survey data (2011-2016) were used to identify encounters involving gabapentin (gabapentin visits) for adults (ages ≥18) (N=5,732). FDA-approved uses and off-label psychiatric use indications were identified with ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes. CNS-D drugs examined were opioids, benzodiazepines Gabapentin is sold generically and under brand names like Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant, SmartRx Gaba-V Kit, and Neuraptine. Not all forms of gabapentin are pharmacologically the same and therefore these brands cannot be used interchangeably. We examined clinical trials of gabapentin (Neurontin, Pfizer) for off-label use for migraine prophylaxis, bipolar disorders, neuropathic pain, or nociceptive pain. In addition to being used to treat pain, gabapentin is used off label to treat anxiety, alcohol use disorder (AUD), alcohol withdrawal, depression, substance use disorders (SUDs), sleep problems, and more. Vedula SS, Bero L, Scherer RW, et al. Outcome reporting in industry-sponsored trials of gabapentin for off-label use. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(20):1963-1971. Goodman CW, Brett AS. A clinical While Gabapentin is FDA-approved for partial seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, its off-label uses are more extensive, especially in psychiatry. In today’s video, we explore the off-label uses of Gabapentin, also known as Neurontin. Like gabapentin, it is sometimes used with opiates, with toxic or even lethal results. Similarly, when in combination with alcohol or nervous system depressants, there is the possibility of greater toxicity. Choosing gabapentin and pregabalin: These drugs are widely used off-label as an alternative to benzodiazepines for anxiety disorders. Radley et al. indicated that gabapentin was among the medications with the highest proportion of off-label use, with 83% of its use being off label.9 Gabapentin was initially approved in Canada in April 1994 as adjunctive therapy for the management of epilepsy among patients over 18 years of age who are not controlled by conventional therapy.11 Off-label: It is estimated that approximately 9/10 prescriptions for Gabapentin are “off-label” or for conditions that the drug isn’t approved to treat. Off-label prescriptions have a reduce chance of actually working for the treatment of anxiety.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |